Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Electrolysis of Molten Compounds
Electrolysis of Molten Compounds | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Electrolysis of Molten Compounds
- A binary ionic compound is one consisting of just two elements joined together by ionic bonding
- When these compounds undergo electrolysis they always produce their corresponding elements
- To predict the products made at each electrode, first identify the ions
- The positive ion will migrate towards the cathode and the negative ion will migrate towards the anode
- Therefore, the cathode product will always be the metal, and the product formed at the anode will always be the non-metal
Electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide
Method
- Add lead(II) bromide into a beaker and heat it so it will turn molten, allowing ions to be free to move and conduct an electric charge
- Add two graphite rods as the electrodes and connect this to a power pack or battery
- Turn on the power pack or battery and allow electrolysis to take place
- Negative bromide ions move to the positive electrode (anode) and each loses one electron to form bromine molecules. There is bubbling at the anode as brown bromine gas is given off
- Positive lead ions move to the negative electrode (cathode) and gain electrons to form a grey lead metal which deposits on the surface of the electrode
Diagram showing the electrolysis of lead(II) bromide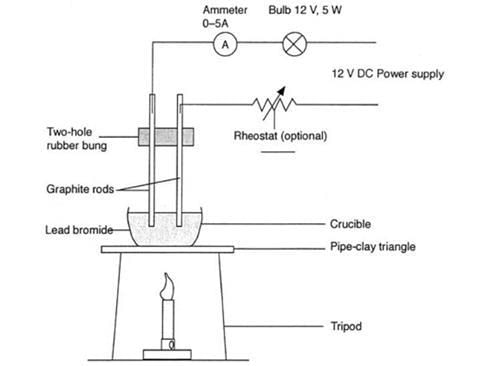
Question for Electrolysis of Molten CompoundsTry yourself: What is the product formed at the cathode during the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide?View Solution
The document Electrolysis of Molten Compounds | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Electrolysis of Molten Compounds - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the purpose of electrolysis of molten compounds? |  |
Ans. Electrolysis of molten compounds is used to extract metals from their ores or to produce chemical compounds that are difficult to obtain by other means.
| 2. How does electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide work? |  |
Ans. In the process of electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide, when an electric current is passed through the molten compound, lead is deposited at the cathode, while bromine gas is evolved at the anode.
| 3. What are the products of electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide? |  |
Ans. The products of electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide are lead metal deposited at the cathode and bromine gas evolved at the anode.
| 4. Why is lead(II) bromide chosen as a compound for electrolysis in this process? |  |
Ans. Lead(II) bromide is chosen for electrolysis due to its high melting point, which allows it to be in a molten state at a suitable temperature for the process to occur.
| 5. What are some applications of electrolysis of molten compounds in industry? |  |
Ans. Electrolysis of molten compounds is used in industry for the extraction of metals like aluminum and magnesium, as well as for the production of chemicals such as chlorine and sodium hydroxide.
Related Searches















