Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Ionic Half Equations
Ionic Half Equations | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Ionic Half Equations
- In electrochemistry, the focus is primarily on electron transfer, so the definitions of oxidation and reduction are based on the gain or loss of electrons rather than the presence or absence of oxygen.
- Oxidation occurs when a substance loses electrons, while reduction occurs when a substance gains electrons.
- When ions make contact with the electrode, they either lose or gain electrons, resulting in the formation of neutral substances.
- These neutral substances are then discharged as products at the electrodes.
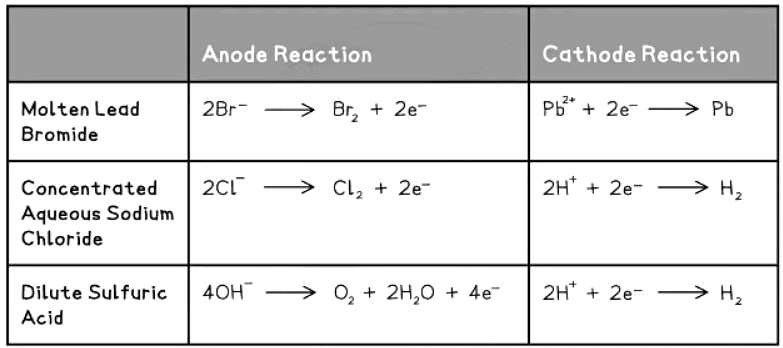
- At the anode, negatively charged ions lose electrons and undergo oxidation.
- At the cathode, positively charged ions gain electrons and undergo reduction.
- Ionic half-equations illustrate the oxidation and reduction processes of the ions involved, and it's crucial to ensure that the charges are balanced.
Table of Reduction and Oxidation Reactions at the Electrodes
Question for Ionic Half EquationsTry yourself: What is oxidation in electrochemistry?View Solution
The document Ionic Half Equations | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Ionic Half Equations - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are ionic half equations? |  |
Ans. Ionic half equations are representations of the oxidation and reduction reactions that occur in an electrochemical cell. They show the transfer of electrons between reactants, indicating the reduction or oxidation of each species.
| 2. How are ionic half equations balanced? |  |
Ans. To balance ionic half equations, the number of atoms of each element and the total charge must be equal on both sides of the equation. This is done by adding or adjusting coefficients in front of the species involved in the reaction.
| 3. Why are ionic half equations important in electrochemistry? |  |
Ans. Ionic half equations are crucial in electrochemistry as they provide a clear understanding of the redox reactions occurring in an electrochemical cell. They help in determining the flow of electrons and the overall cell potential.
| 4. Can you give an example of an ionic half equation? |  |
Ans. An example of an ionic half equation is the oxidation of zinc metal to zinc ions: Zn(s) -> Zn^2+(aq) + 2e^-. This represents the loss of electrons by zinc during the oxidation process.
| 5. How do ionic half equations relate to the overall redox reaction in a cell? |  |
Ans. Ionic half equations contribute to the overall redox reaction in a cell by showing the individual oxidation and reduction processes taking place. When combined, these half equations give the complete picture of electron transfer and chemical changes occurring in the cell.
Related Searches















