Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell
Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
- A fuel is a substance that releases energy when burned.
- Hydrogen serves as a fuel in rocket engines and fuel cells for powering certain vehicles.
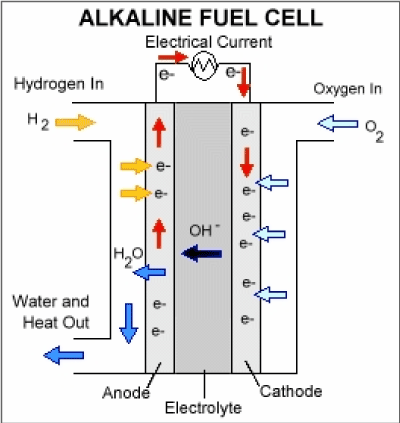
- A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell where a fuel provides electrons at one electrode and oxygen receives electrons at the other electrode.
- Hydrogen: H2 → 2H+ + 2e–
- Oxygen: O2 + 4e– → 2O2–
- The hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell generates electricity by combining both elements, producing energy and water.
- The comprehensive equation for the reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell is:
hydrogen + oxygen → water - The hydrogen fuel cell configuration involves the intake of hydrogen and oxygen.
- Oxygen is provided by the incoming air while hydrogen serves as the fuel.
- The sole byproduct generated in this process is water.
Question for Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel CellTry yourself: What is the purpose of a hydrogen fuel cell?View Solution
Advantages & Disadvantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Increasing Usage in Automotive Industry
- Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells are progressively being employed in vehicles to supplant traditional petrol or diesel engines.
Advantages
- They generate no pollution, with water being the sole byproduct, unlike petrol engines that emit carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
- They yield higher energy output per kilogram compared to both petrol and diesel.
- They incur no power loss during transmission since they lack moving components, unlike internal combustion engines.
- They operate quietly, resulting in reduced noise pollution when compared to petrol engines.
Disadvantages
- The materials required for manufacturing fuel cells are costly.
- Storing hydrogen is more challenging and expensive than storing petrol due to its high flammability, which can lead to explosions under pressure.
- Fuel cells experience reduced efficiency in low temperatures.
- There is a limited availability of hydrogen filling stations nationwide.
- Hydrogen is often obtained through processes involving the combustion of fossil fuels, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
Question for Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel CellTry yourself: What is one advantage of hydrogen fuel cells over petrol engines?View Solution
The document Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How do hydrogen fuel cells work? |  |
Ans. Hydrogen fuel cells work by converting the chemical energy of hydrogen and oxygen into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction. Hydrogen is fed into the anode of the fuel cell, while oxygen is fed into the cathode. The hydrogen molecules are split into protons and electrons at the anode, with the protons moving through an electrolyte membrane to the cathode and the electrons creating an electrical current.
| 2. What are the advantages of using hydrogen fuel cells? |  |
Ans. Some advantages of hydrogen fuel cells include zero emissions of harmful pollutants, high energy efficiency, quiet operation, and the ability to produce electricity continuously as long as hydrogen fuel is supplied. They also offer fast refueling times compared to electric vehicles.
| 3. What are the disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells? |  |
Ans. Some disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells include the high cost of production and infrastructure development, the need for hydrogen storage and transportation solutions, the current limited availability of hydrogen fueling stations, and the energy-intensive production of hydrogen.
| 4. Can hydrogen fuel cells be used to power vehicles? |  |
Ans. Yes, hydrogen fuel cells can be used to power vehicles such as cars, buses, and trucks. Fuel cell vehicles produce electricity on board using hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air, with water vapor being the only byproduct emitted. These vehicles offer a longer driving range and faster refueling times compared to battery electric vehicles.
| 5. Are hydrogen fuel cells a sustainable energy solution? |  |
Ans. Hydrogen fuel cells have the potential to be a sustainable energy solution when produced using renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power. By utilizing green hydrogen, which is produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, hydrogen fuel cells can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a cleaner energy future.
Related Searches















