Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Heat Exchange in Reactions |

|
| Exothermic Reactions |

|
| Endothermic Reactions |

|
| Reaction Pathway Diagrams |

|
Heat Exchange in Reactions
- Chemical reactions occur to help elements reach a more stable energy state by acquiring a full outer shell of electrons.
- This is achieved through chemical bonding, where old bonds are broken, and new bonds are formed.
- The process involves the exchange of thermal energy into and out of the reaction mixtures.
- It is essential to understand the terms 'system', which refers to what occurs in the chemical reaction, and 'surroundings', encompassing everything other than the reacting chemicals.
- Energy within the system originates from the chemical bonds themselves, acting as small reservoirs of chemical energy.
Exothermic Reactions
- In exothermic reactions, thermal energy is transferred to the surroundings, leading to an increase in the surrounding temperature.
- Energy is moved from the chemical energy store of the chemical system to the surroundings, resulting in a decrease in the system's energy. This denotes a negative energy change.
- The overall energy transfer occurs from the system to the surroundings.
- Common examples of exothermic reactions include combustion, oxidation, and neutralization reactions.
- Practical applications of exothermic reactions include hand warmers that release heat during wintertime and self-heating cans of food and beverages.
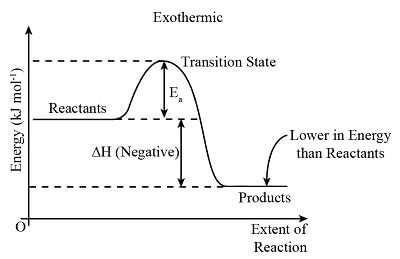
- Diagram showing the transfer of heat energy outwards from an exothermic reaction:
Question for Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsTry yourself: Which of the following best describes an exothermic reaction?View Solution
Endothermic Reactions
- Endothermic reactions absorb heat energy from the surroundings, causing a decrease in the temperature of the surroundings. This energy is transferred from the surroundings to the chemical system, leading to a positive energy change.
- Endothermic reactions are less common compared to exothermic reactions. Processes like photosynthesis, thermal decomposition reactions, and electrolysis are examples of endothermic reactions.
- Cold packs used in sports injury treatments are based on endothermic reactions. They absorb heat from the injured area, helping to reduce swelling and provide relief.
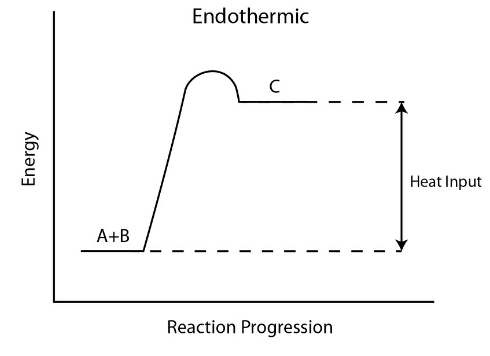
- Diagram showing the transfer of heat energy from the surroundings into an endothermic reaction:
Reaction Pathway Diagrams
- Reaction pathway diagrams, also known as energy level diagrams, visually represent the relative energies of the reactants and products in chemical reactions.
- The energy of the reactants and products is typically shown on the y-axis, while the progression of the reaction is illustrated on the x-axis, akin to a timeline.
- The disparity in height between the energy levels of reactants and products signifies the overall energy alteration during a reaction. While usually depicted as a sketch, it can be drawn to scale with the availability of relevant data.
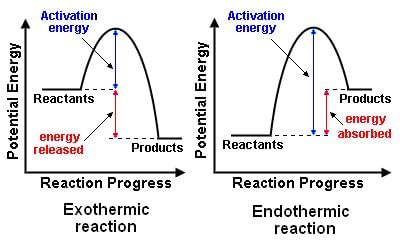
- Arrows incorporated in these diagrams indicate whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic. In an exothermic reaction, the overall arrow points downwards, indicating a release of energy from the system. Conversely, an endothermic reaction shows an upward-pointing arrow, depicting an absorption of energy by the system.
- The initial spike in energy levels on the diagram symbolizes the activation energy (Ea), which denotes the minimum energy required for colliding particles to engage in a reaction.
- The magnitude of the initial energy rise correlates with the energy necessary to initiate the reaction—higher rises imply a greater input of energy, such as heat.
- Identification of reaction pathway diagrams for different types of reactions is feasible based on the energy comparison between products and reactants. For an exothermic reaction, the product energy is lower than that of the reactants due to energy transfer to the surroundings. Conversely, an endothermic reaction exhibits higher product energy, indicating absorption of thermal energy from the surroundings.
- Reaction Pathway Diagram of an Exothermic Reaction and an Endothermic Reaction:
Question for Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsTry yourself: Which of the following is an example of an endothermic reaction?View Solution
The document Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions? |  |
Ans. In exothermic reactions, heat is released to the surroundings, resulting in an increase in temperature. On the other hand, endothermic reactions absorb heat from the surroundings, causing a decrease in temperature.
| 2. Can you provide an example of an exothermic reaction? |  |
Ans. An example of an exothermic reaction is the combustion of fuel, such as burning wood or gasoline, where heat and light are released.
| 3. How does heat exchange play a role in reaction pathway diagrams? |  |
Ans. Heat exchange is represented in reaction pathway diagrams by showing the energy changes throughout the reaction. Exothermic reactions have a negative energy change, while endothermic reactions have a positive energy change.
| 4. How can you determine if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic by looking at its reaction pathway diagram? |  |
Ans. In a reaction pathway diagram, if the products have a lower energy level than the reactants, the reaction is exothermic. Conversely, if the products have a higher energy level than the reactants, the reaction is endothermic.
| 5. Why is it important to understand exothermic and endothermic reactions in chemistry? |  |
Ans. Understanding exothermic and endothermic reactions is crucial in chemistry as it helps predict the energy changes that occur during a reaction and allows for the optimization of reaction conditions for desired outcomes.
Related Searches




















