Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Rate of a Reaction
Rate of a Reaction | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Rates of Reaction Factors
- There are various factors that can influence how quickly a reaction occurs.
- These include:
- Concentration of the reactants: The amount of reactants in a solution or the pressure of gases involved.
- Temperature: The level of heat at which the reaction takes place. Higher temperatures usually lead to faster reactions.
- Surface area of solid reactants: The exposed area of solid substances that can react.
- Use of a catalyst: A substance that can speed up a reaction without being used up itself.
- Changes in these variables directly impact the speed of a reaction.
- It is important in terms of cost-effectiveness to have a faster reaction rate, as it implies increased production efficiency and sustainability.
The effect of increased concentration or pressure
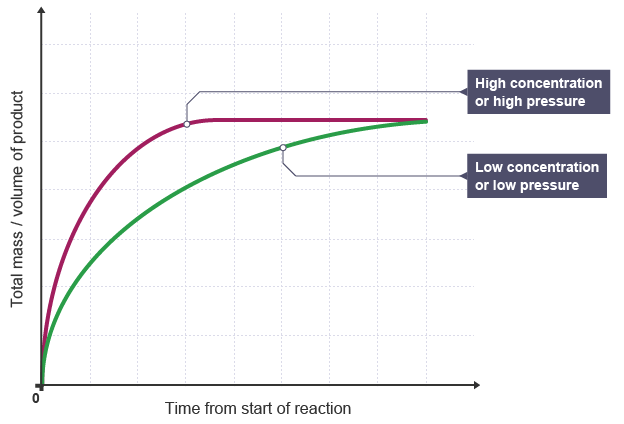
Explanation:
- When a solution or gas has a higher concentration/pressure, the rate of reaction increases.
- This is evident from the steeper gradient and quicker horizontal level in reaction graphs.
Question for Rate of a ReactionTry yourself: What factor can influence the rate of a reaction by increasing the concentration or pressure of the reactants?View Solution
The effect of surface area
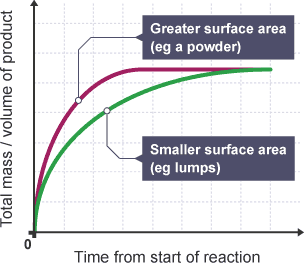
Explanation:
- Increasing the surface area of a solid in a reaction boosts the reaction rate.
- This is depicted by faster reaction completion shown in graphs with powdered reactants.
The Effect of Temperature
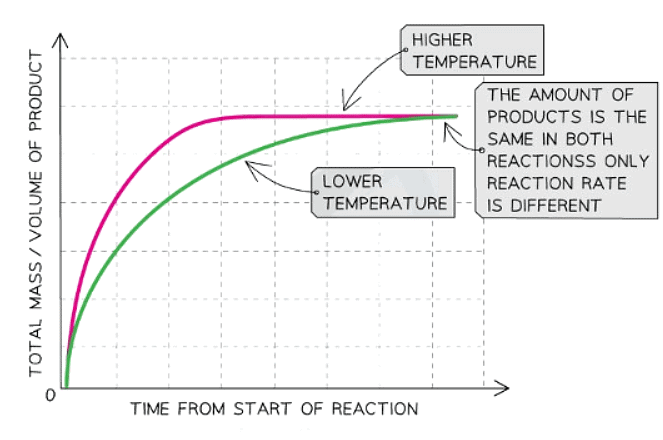
Explanation:
- When comparing a reaction at low temperature to the same reaction at a higher temperature, the graph line demonstrates a steeper initial gradient and reaches a horizontal plateau sooner.
- This illustrates that as temperature rises, the reaction rate accelerates.
The Effect of Catalysts on Rate of Reaction
- Catalysts are agents that enhance reaction rates without undergoing alteration or consumption themselves.
- The catalyst's mass remains unchanged from the beginning to the end of the reaction, and it does not factor into the reaction equation.
Graph showing the effect of using a catalyst on the rate of reaction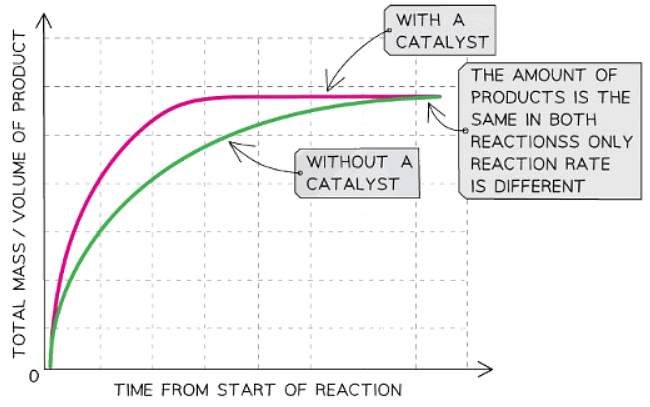
Explanation:
- Compared to a reaction without a catalyst, the graph line for the same reaction but with a catalyst has a steeper gradient at the start and becomes horizontal sooner.
- This shows that with a catalyst, the rate of reaction will increase.
Question for Rate of a ReactionTry yourself: How does increasing the surface area of a solid in a reaction affect the reaction rate?View Solution
The document Rate of a Reaction | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Rate of a Reaction - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the factors that can affect the rate of a reaction? |  |
Ans. Factors that can affect the rate of a reaction include the concentration of reactants, temperature, surface area, presence of a catalyst, and pressure (for gas-phase reactions).
| 2. How does the concentration of reactants influence the rate of a reaction? |  |
Ans. An increase in the concentration of reactants typically leads to a higher rate of reaction, as there are more reactant molecules available to collide and form products.
| 3. Why does temperature play a significant role in determining the rate of a reaction? |  |
Ans. Increasing the temperature of a reaction usually results in a faster rate of reaction because the higher temperature provides reactant molecules with more energy, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions.
| 4. Can the surface area of solid reactants impact the rate of a reaction? |  |
Ans. Yes, a larger surface area of solid reactants can lead to a higher rate of reaction as there is more surface area available for collisions to occur, increasing the likelihood of successful collisions.
| 5. How does the presence of a catalyst affect the rate of a reaction? |  |
Ans. A catalyst can increase the rate of a reaction by providing an alternative pathway with lower activation energy, allowing the reaction to proceed faster without being consumed in the process.
Related Searches





















