Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Properties of Metals
Properties of Metals | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Physical Properties of Metals & Non-Metals
Metals and non-metals
- The Periodic Table contains over 100 different elements
- They can be divided into two broad types: metals and non-metals
- Most of the elements are metals and a small number of elements display properties of both types. These elements are called metalloids or semimetals.
- The metallic character diminishes moving left to right across the Periodic Table:
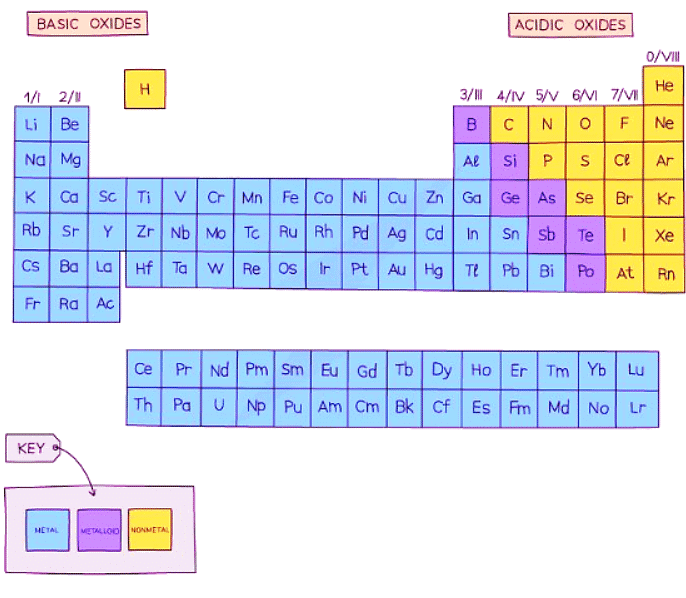
Properties of Metals
- Metals can conduct heat and electricity.
- They are malleable, meaning they can be hammered into different shapes, and ductile, meaning they can be drawn into wires.
- Metals tend to be lustrous, giving them a shiny appearance.
- They have high density and usually high melting points.
- Metals form positive ions through the loss of electrons and produce basic oxides.
Properties of Non-Metal Elements
- Non-metals do not conduct heat and electricity.
- They are brittle when solid and easily break up.
- Non-metals tend to be dull and nonreflective.
- They have low density and low melting points, with many being gases at room temperature.
- Non-metals form negative ions through electron gain (except for hydrogen) and create acidic oxides.
Question for Properties of MetalsTry yourself: Which property is characteristic of metals?View Solution
Chemical Properties of Metals
- Metals possess specific chemical characteristics
- Understanding metal chemistry involves examining reactions with water, dilute acid, and oxygen
- These reactions help establish a reactivity series of metals
Reactivity with Water
- Some metals react with water, producing a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas
- For instance, calcium reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas:
- Ca (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
- Other metals, like zinc, react with steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen gas:
- Zn (s) + H2O (g) → ZnO (s) + H2 (g)
Reactivity of Metals with Acids
- Most metals, like iron, react with dilute acids, for example, hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- During the reaction between acids and metals, the metal atom replaces the hydrogen atom in the acid, resulting in the formation of a salt and hydrogen gas.
- Example: Iron:
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
Fe (s) + 2HCl (aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Reactivity of Metals with Oxygen
- Unreactive metals such as gold and platinum do not react with oxygen.
- Some reactive metals, like the alkali metals, readily react with oxygen.
- Metals like copper and iron can also react with oxygen, but at a slower rate.
- When metals react with oxygen, they form metal oxides.
- Example: Copper:
metal + oxygen → metal oxide
2Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2CuO (s)
Question for Properties of MetalsTry yourself: Which of the following reactions between a metal and a substance produces a metal oxide?View Solution
The document Properties of Metals | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Properties of Metals - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are some examples of physical properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
Ans. Physical properties of metals include high density, malleability, ductility, and conductivity of heat and electricity. Non-metals, on the other hand, typically have lower density, lack malleability and ductility, and are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
| 2. How do the chemical properties of metals differ from non-metals? |  |
Ans. Metals tend to form positive ions in chemical reactions, while non-metals tend to form negative ions or share electrons with other atoms. Metals generally react with acids to form salts and hydrogen gas, while non-metals may react with metals to form compounds.
| 3. Can you provide examples of how the physical properties of metals and non-metals are used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Physical properties of metals like conductivity are used in electrical wiring and cooking utensils, while the lack of conductivity in non-metals is useful in insulating materials. Malleability of metals is utilized in making coins and jewelry, while the brittleness of non-metals is seen in ceramics.
| 4. How do the physical properties of metals and non-metals affect their roles in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. Metals are found on the left side of the periodic table and tend to lose electrons to form positive ions, while non-metals are located on the right side and may gain electrons to form negative ions. This arrangement is based on their physical properties and reactivity.
| 5. How do the physical and chemical properties of metals and non-metals impact their use in various industries? |  |
Ans. The physical properties of metals like strength and conductivity make them ideal for construction and electronics industries. Non-metals, with properties like low density and non-reactivity, are used in industries such as pharmaceuticals and plastics.
Related Searches




















