Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Alloys and their Properties
Alloys and their Properties | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Properties & Uses of Alloys
- Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals or a metal with a non-metal like carbon.
- Alloys often exhibit unique properties distinct from the metals they are composed of, such as increased strength, hardness, and resistance to corrosion or extreme temperatures.
- These enhanced characteristics can render alloys more practical than pure metals.
Common Alloys and Their Uses
- Alloys are mixtures of metals that exhibit enhanced properties compared to their individual components. They are not chemically combined like compounds.
- Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, known for its superior strength compared to the individual metals.
- Utilized in crafting musical instruments, ornamental pieces, and door knobs due to its durability.
- Stainless steel comprises iron along with elements like chromium, nickel, and carbon. It is valued for its toughness and resistance to rust.
- Commonly employed in the production of cutlery owing to its hardness and anti-corrosive properties.
- Alloys of iron, when combined with elements like tungsten, chromium, or nickel, exhibit specialized properties.
- Iron alloys with tungsten are renowned for their extreme hardness and ability to withstand high temperatures.
- Alloys incorporating chromium or nickel are known for their corrosion resistance.
- Aluminium alloys are created by blending aluminium with metals like copper, manganese, and silicon to enhance strength while maintaining low density.
Explaining the Properties of Alloys
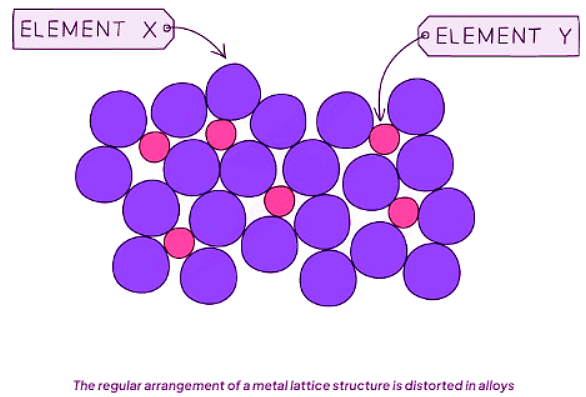
- Alloys are composed of atoms of varying sizes, leading to a distortion of the typically regular atomic arrangements found in pure metals. This distortion significantly impacts the properties of alloys.
- This distortion effect plays a crucial role in increasing the hardness of alloys compared to pure metals. It hinders the smooth sliding of atomic layers over each other, making the material stronger and more resistant to deformation.
Question for Alloys and their PropertiesTry yourself: What is the main reason why alloys exhibit enhanced properties compared to pure metals?View Solution
The document Alloys and their Properties | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Alloys and their Properties - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are some common alloys and their uses? |  |
Ans. Some common alloys and their uses include steel (iron and carbon) for construction, stainless steel (iron, chromium, and nickel) for kitchenware, brass (copper and zinc) for musical instruments, bronze (copper and tin) for statues and coins, and solder (tin and lead) for electronics.
| 2. What are the properties of alloys? |  |
Ans. Alloys have properties that are often superior to their individual component metals, such as increased strength, hardness, durability, and resistance to corrosion. They can also have specific properties tailored to their intended use, such as electrical conductivity or heat resistance.
| 3. How are alloys made? |  |
Ans. Alloys are typically made by melting the base metals together and then allowing them to solidify. Sometimes additional elements are added to the mix to create specific properties, and the ratio of the components can be adjusted to fine-tune the alloy's characteristics.
| 4. What are the advantages of using alloys over pure metals? |  |
Ans. Using alloys can provide a combination of properties that pure metals may not possess, such as increased strength, improved corrosion resistance, and better heat resistance. Alloys can also be more cost-effective and easier to work with in manufacturing processes.
| 5. How do the properties of alloys make them suitable for various applications? |  |
Ans. The properties of alloys can be customized to meet the specific requirements of different applications. For example, adding certain elements to an alloy can make it more resistant to high temperatures, while adjusting the composition can improve its durability or electrical conductivity. This versatility makes alloys suitable for a wide range of uses across industries.
Related Searches















