Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Corrosion of Metals
Corrosion of Metals | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Rusting of Iron
- Rusting is a chemical process involving iron, water, and oxygen, resulting in the formation of hydrated iron(III) oxide, commonly known as rust.
- The presence of both oxygen and water is essential for rust formation.
- In the rusting process, iron undergoes oxidation.
iron water oxygen → hydrated iron(III) oxide
Investigating rusting
- Prepare three test tubes according to the diagram provided.
- In the second test tube, the presence of oil prevents air from entering, and the water has been boiled to remove any remaining air.
- The third test tube contains calcium chloride, which serves to eliminate moisture from the air.
- After several days, only the iron nail in the first test tube will exhibit signs of rusting.
- Diagram showing the requirements of oxygen and water for rust to occur: only the nail on the left rusts:

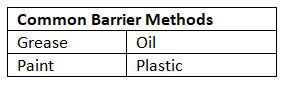
Rust Prevention Methods
Barrier methods
- Rust formation on iron can be hindered by applying protective coatings that create barriers, thus preventing direct contact with water and oxygen.
- However, if these coatings are removed or damaged, allowing water and oxygen to reach the iron surface, rusting can occur once more.
Question for Corrosion of MetalsTry yourself: What are the essential requirements for rust formation?View Solution
The document Corrosion of Metals | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Corrosion of Metals - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is rust and how does it form? |  |
Ans. Rust is the result of the oxidation of iron in the presence of oxygen and water. When iron comes into contact with oxygen and moisture, it forms iron oxide, commonly known as rust.
| 2. Why is rusting a problem for iron materials? |  |
Ans. Rusting is a problem for iron materials because it weakens the structure of the metal, making it more susceptible to damage and corrosion. This can lead to the deterioration and eventual failure of the iron object.
| 3. What are some common methods used to prevent rusting of iron? |  |
Ans. Some common methods used to prevent rusting of iron include painting, galvanizing, applying protective coatings, using sacrificial anodes, and keeping the iron dry.
| 4. How does galvanizing help prevent rusting of iron? |  |
Ans. Galvanizing involves coating iron with a layer of zinc, which acts as a protective barrier against moisture and oxygen. The zinc sacrificially corrodes before the iron, preventing rust from forming on the iron surface.
| 5. What are some signs that iron is beginning to rust? |  |
Ans. Some signs that iron is beginning to rust include the appearance of reddish-brown spots or patches on the surface of the metal, a rough or pitted texture, and the presence of flakes or powdery residue.
Related Searches















