Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Extraction of Iron from Hematite
Extraction of Iron from Hematite | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Extraction of Iron from Hematite
- Iron extraction occurs in a specialized structure known as a blast furnace, typically from hematite ore.
- Contemporary blast furnaces have a notable output, yielding around 10,000 tons of iron daily.
- The process of iron extraction involves specific steps, which are outlined and elucidated below:
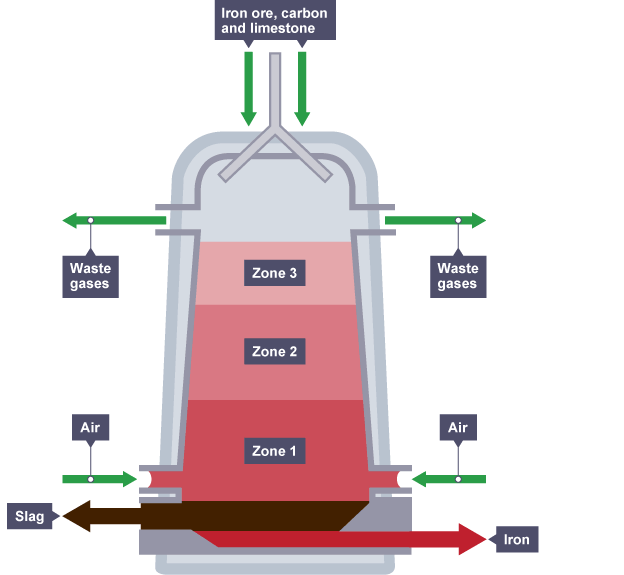 Diagram showing the carbon extraction of iron
Diagram showing the carbon extraction of iron
- In the blast furnace, hematite ore, coke, and limestone are introduced from the top.
- Hot air is blown into the bottom of the furnace.
- Coke, an impure carbon variant, undergoes combustion in Zone 1 with the hot air, producing carbon dioxide and releasing heat.
- The generated heat aids in heating the furnace due to the exothermic nature of the reaction.
- In Zone 2, coke reacts further with carbon dioxide at elevated temperatures, yielding carbon monoxide.
- This step involves the reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide.
- In Zone 3, carbon monoxide acts as a reducing agent for iron(III) oxide in the hematite ore, resulting in the formation of molten iron.
- The molten iron accumulates at the furnace's base and is extracted periodically.
- Limestone is incorporated into the furnace to eliminate ore impurities.
- The thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate from limestone produces calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
- Calcium oxide then reacts with silicon dioxide, an impurity in the ore, to produce calcium silicate.
- The resulting calcium silicate forms a molten slag that floats atop the molten iron, allowing for separate removal.
Question for Extraction of Iron from HematiteTry yourself: What is the purpose of introducing limestone into the blast furnace during the extraction of iron from hematite?View Solution
Equations for Extraction of Iron from Hematite
- Introduction: In the extraction of iron from hematite, several stages are involved, each with specific reactions.
- Zone 1 - Burning of Carbon: This stage involves the burning of carbon (coke) to provide heat and produce carbon dioxide.
C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) - Zone 2 - Reduction of Carbon Dioxide: Carbon dioxide is reduced to carbon monoxide in this stage.
CO2 (g) + C (s) → 2CO (g) - Zone 3 - Reduction of Iron(III) Oxide: Iron(III) oxide is reduced by carbon monoxide in this crucial stage.
Fe2O3 (s) + 3CO (g) → 2Fe (l) + 3CO2 (g) - When calcium carbonate (limestone) is heated, it undergoes thermal decomposition to produce calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2 (g) - The Formation of Slag:
CaO (s) + SiO2 (s) → CaSiO3 (l)
The document Extraction of Iron from Hematite | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Extraction of Iron from Hematite - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How is iron extracted from hematite? |  |
Ans. Iron is extracted from hematite through a process called reduction. In this process, the iron ore is heated with carbon in the form of coke (a type of coal) in a blast furnace. The carbon monoxide produced from the coke reduces the iron oxide in the hematite to iron metal.
| 2. What are the equations involved in the extraction of iron from hematite? |  |
Ans. The main equation involved in the extraction of iron from hematite is:
Fe2O3 (s) + 3CO (g) → 2Fe (s) + 3CO2 (g)
This equation represents the reduction of iron oxide in hematite by carbon monoxide to produce iron metal and carbon dioxide.
| 3. Why is hematite a common source of iron for extraction? |  |
Ans. Hematite is a common source of iron for extraction because it contains a high percentage of iron in the form of iron oxide (Fe2O3). This makes it easier to extract iron from hematite compared to other iron ores with lower iron content.
| 4. What is the role of coke in the extraction of iron from hematite? |  |
Ans. Coke is used in the extraction of iron from hematite as a source of carbon. When heated in the blast furnace, coke reacts with oxygen to produce carbon monoxide, which is the reducing agent that reacts with the iron oxide in hematite to extract iron metal.
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of extracting iron from hematite? |  |
Ans. The extraction of iron from hematite can result in environmental impacts such as air pollution from the release of carbon dioxide and other gases during the reduction process. Additionally, the mining of hematite can lead to habitat destruction and soil erosion if not managed properly.
Related Searches















