Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Alkanes
Alkanes | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Alkanes: Properties & Bonding
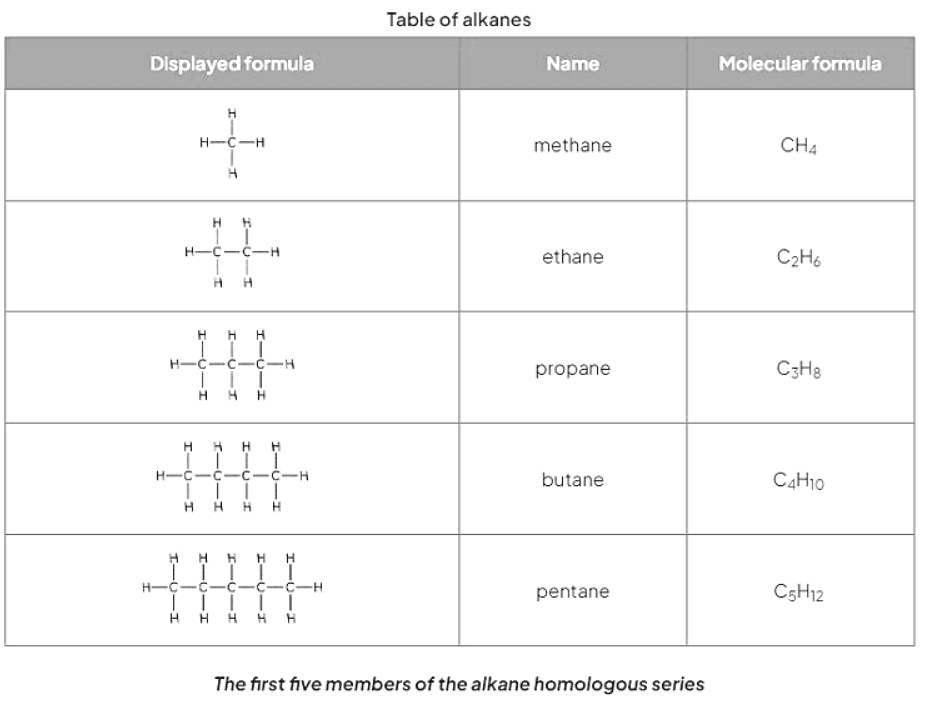
- Alkanes belong to a category of hydrocarbons characterized by having only single carbon-carbon bonds, making them saturated compounds devoid of double bonds.
- Their general formula is CnH2n+2, with physical properties gradually changing as the carbon atom count in the chain increases.
- Despite being generally unreactive, alkanes can undergo combustion reactions, be subjected to cracking processes yielding smaller molecules, and participate in substitution reactions with halogens under light exposure.
- Methane, a prime example of an alkane, constitutes a significant portion of natural gas and, upon complete combustion, produces carbon dioxide and water according to the equation: CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l).
Question for AlkanesTry yourself: What is the general formula for alkanes?View Solution
Substitution Reaction of Alkanes with Halogens
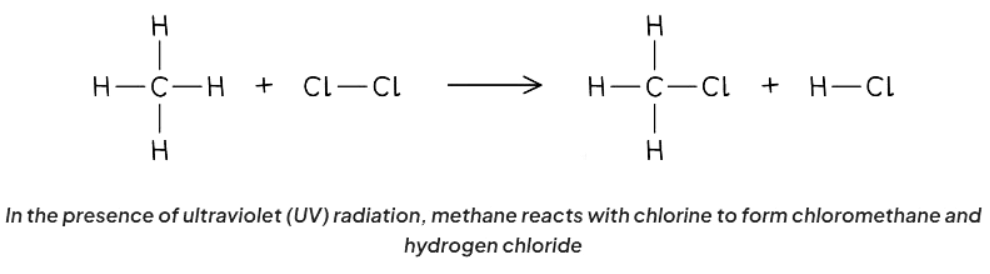
- Substitution reactions involve the exchange of one atom or group of atoms with another in a compound.
- Alkanes participate in substitution reactions with halogens when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, a process known as photochemical reaction.
- Ultraviolet light serves as the activation energy (Ea) required for the reaction to proceed.
- In this reaction, a hydrogen atom in the alkane is replaced by a halogen atom.
- The extent of substitution can vary depending on the intensity of ultraviolet radiation present.
Question for AlkanesTry yourself: Which of the following is true about substitution reactions of alkanes with halogens?View Solution
The document Alkanes | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Alkanes - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the general formula for alkanes? |  |
Ans. The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2, where n represents the number of carbon atoms in the alkane molecule.
| 2. How do halogens react with alkanes in substitution reactions? |  |
Ans. In substitution reactions, halogens can replace hydrogen atoms in alkanes to form alkyl halides, with the halogen atom taking the place of the hydrogen atom in the alkane molecule.
| 3. What are some physical properties of alkanes? |  |
Ans. Alkanes are typically nonpolar, have low boiling points, and are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents. They also exhibit a decrease in boiling point with increasing carbon chain length.
| 4. How do the carbon atoms bond in alkanes? |  |
Ans. In alkanes, carbon atoms form single covalent bonds with each other, resulting in a tetrahedral geometry around each carbon atom. This bonding arrangement contributes to the stability and inertness of alkanes.
| 5. What role do alkanes play in organic chemistry? |  |
Ans. Alkanes serve as the foundation for many organic compounds and are used as starting materials for the synthesis of various organic molecules. They are also important in fuel production and industrial applications.
Related Searches





















