Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Nylon and PET
Nylon and PET | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Plastics & their Disposal
- Synthetic polymers, including nylon, terylene, and lycra, are produced in factories.
- Nylon, categorized as a polyamide, is utilized in the manufacturing of clothing, fabrics, nets, and ropes.
- PET, also known as Terylene, is a polyester formed by linking monomers through ester links.
- PET is extensively used in the textile industry and is often blended with cotton to create clothing.
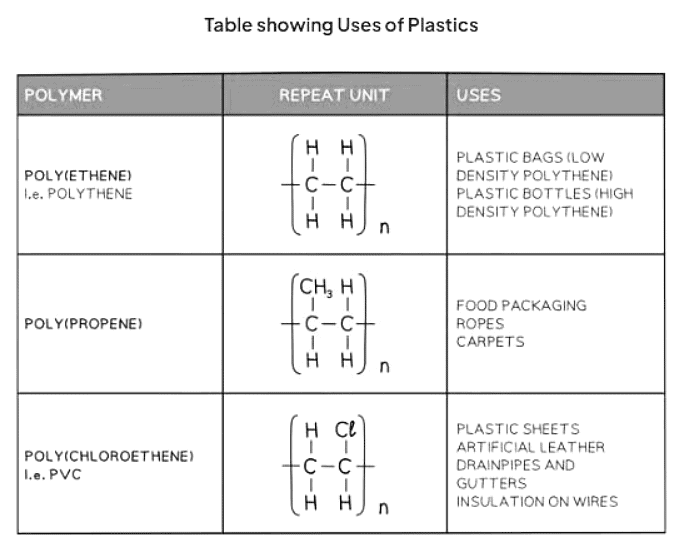
Non-biodegradable plastics
- These plastics are non-biodegradable or degrade very slowly, leading to significant environmental pollution.
- Plastic waste, particularly, is entering oceans and seas, causing extensive harm to marine ecosystems.
- In landfills, these polymers occupy valuable space without decomposing, accelerating the filling of landfill sites.
- When polymers are incinerated, they release considerable heat energy and emit carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas contributing to global warming.
- Incomplete combustion of polymers can generate carbon monoxide, a toxic gas that interferes with oxygen transport in the blood.
- While polymers can be recycled, separating different types of polymers for recycling is a challenging and costly process.
Question for Nylon and PETTry yourself: Which synthetic polymer is extensively used in the textile industry and often blended with cotton to create clothing?View Solution
PET Re-polymerisation
- PET, which stands for polyethylene terephthalate, is a commonly used polymer for producing items like plastic bottles.
- This polymer is a type of polyester known as a condensation polymer, comprised of recurring ester units, similar to terylene.
- A significant challenge in recycling polymers is the harsh conditions required to break them down, such as high temperatures and pressures, which can damage the monomers, rendering them unsuitable for re-polymerisation.
- PET is notably straightforward to convert back into its original monomers.
- Depolymerisation of PET can be accomplished through enzymatic processes or chemical methods.
- Microbial enzymes play a role in breaking down PET into its initial monomers, a process that can also be replicated using solvents, a catalyst, and gentle heating.
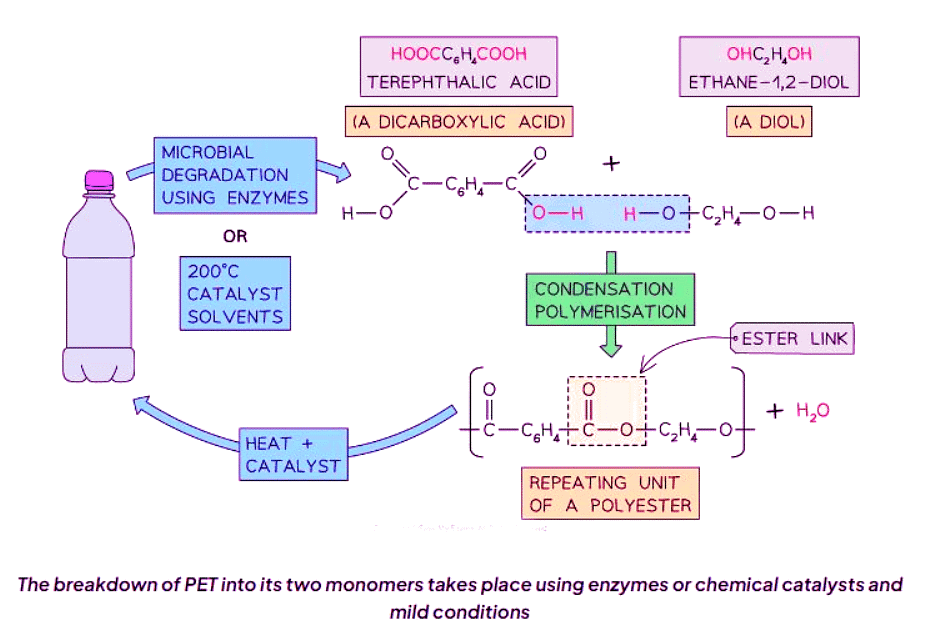
- The monomers are reclaimed and can be reprocessed into fresh PET through polymerization.
- This conservation method helps conserve resources and energy, thereby diminishing the carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing procedure.
Question for Nylon and PETTry yourself: How can PET be converted back into its original monomers?View Solution
The document Nylon and PET | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Nylon and PET - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is PET re-polymerisation and how does it help in the disposal of plastics? |  |
Ans. PET re-polymerisation is a process where used PET plastics are broken down and converted into new PET material. This helps in recycling plastic waste and reducing the environmental impact of plastic disposal.
| 2. How is nylon different from PET in terms of disposal methods? |  |
Ans. Nylon is a synthetic polymer that can be recycled through various methods, while PET is commonly recycled through re-polymerisation. Nylon can also be incinerated for energy recovery, whereas PET is not typically incinerated.
| 3. Why is it important to properly dispose of plastics like nylon and PET? |  |
Ans. Proper disposal of plastics like nylon and PET is important to prevent environmental pollution and reduce the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills or oceans. Recycling these plastics also helps conserve resources and reduce energy consumption.
| 4. What are some common challenges faced in the disposal of nylon and PET plastics? |  |
Ans. Some common challenges in the disposal of nylon and PET plastics include contamination of recyclable materials, lack of infrastructure for recycling, and limited awareness among consumers about proper disposal methods.
| 5. How can individuals contribute to the proper disposal of plastics like nylon and PET? |  |
Ans. Individuals can contribute to proper disposal by recycling their plastic waste, avoiding single-use plastics, supporting businesses that use sustainable packaging, and educating others about the importance of responsible plastic disposal.
Related Searches















