Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Acid Base Titration
Acid Base Titration | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Acid-Base Titrations
- Titrations are a method of analyzing solution concentrations
- They help determine the exact amount of alkali needed to neutralize a given quantity of acid, and vice versa
- These experiments may involve calculating the moles in a specified quantity, as well as the concentration or volume required to neutralize an acid or base
- Titrations are also useful for the preparation of salts
Materials Required for Titration
- 25 cm3 volumetric pipette
- Pipette filler
- 50 cm3 burette
- 250 cm3 conical flask
- Small funnel
- 0.1 mol/dm3 sodium hydroxide solution
- Sulfuric acid – concentration unknown
- A suitable indicator
- Clamp stand, clamp & white tile
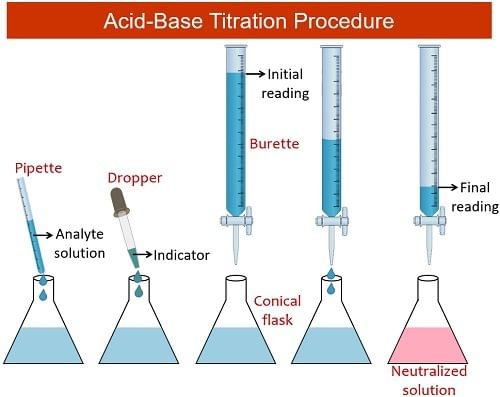
Steps in Performing a Titration
Describing the method:
- Use the pipette and pipette filler to transfer exactly 25 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution into the conical flask.
- Position the conical flask on a white tile with the burette tip inside.
- Add a few drops of a suitable indicator to the solution in the conical flask.
- Conduct a rough titration by incrementally adding the solution from the burette in 1 – 3 cm3 portions while swirling the flask vigorously.
- Close the tap swiftly when the sharp color change signals the end-point and record the volume, aligning your eye with the meniscus.
- Repeat the titration process with a fresh batch of sodium hydroxide.
- Approach the rough end-point volume carefully, adding solution drop by drop until the indicator changes color precisely.
- Record the volume accurately to the nearest 0.05 cm3.
- Repeat the titration until two concordant results are achieved (results within 0.1 cm3 of each other) to enhance precision.
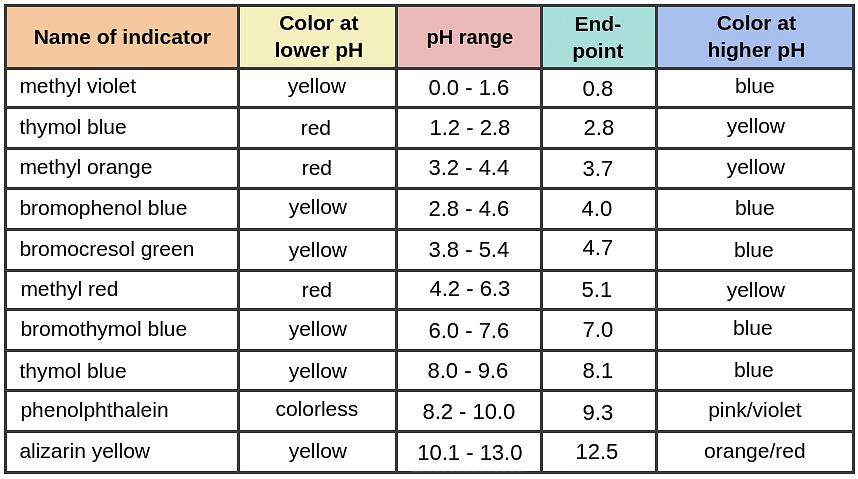
Indicators
- Indicators play a crucial role in titration by indicating the endpoint.
- Wide range indicators like litmus are unsuitable due to their lack of a sharp color change at the endpoint.
- On the other hand, indicators like methyl orange and phenolphthalein are highly suitable for this purpose.
- Here are some common indicators along with their respective colors:
Question for Acid Base TitrationTry yourself: Which indicator is highly suitable for acid-base titrations?View Solution
The document Acid Base Titration | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Acid Base Titration - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is an acid-base titration? |  |
Ans. An acid-base titration is a technique used in chemistry to determine the concentration of an acid or base in a solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration.
| 2. How do indicators work in acid-base titrations? |  |
Ans. Indicators are substances that change color in response to changes in pH. In acid-base titrations, indicators are used to signal the endpoint of the titration by changing color when the solution reaches a certain pH.
| 3. What is the purpose of performing an acid-base titration? |  |
Ans. The purpose of performing an acid-base titration is to accurately determine the concentration of an acid or base in a solution. This information is important for various applications in chemistry, such as in analytical chemistry and in determining the purity of a substance.
| 4. How do you calculate the concentration of an unknown acid or base in an acid-base titration? |  |
Ans. The concentration of the unknown acid or base can be calculated using the volume and concentration of the known solution used in the titration, along with the stoichiometry of the reaction between the acid and base.
| 5. What are some common indicators used in acid-base titrations? |  |
Ans. Some common indicators used in acid-base titrations include phenolphthalein, methyl orange, and bromothymol blue. These indicators change color at different pH ranges, making them suitable for different types of acid-base titrations.
Related Searches





















