Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Paper Chromatography Using Locating Agents
Paper Chromatography Using Locating Agents | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Locating Agents
- For chromatography to be useful, it's essential for the chemist to observe the components moving up the paper. This visibility challenge arises with colorless substances like amino acids or sugars.
- Locating agents play a crucial role in chromatography. These substances interact with the sample, generating a colored product that becomes visible.
- After the chromatography process is complete, the chromatogram is treated with the locating agent. This treatment makes the sample runs visible to the naked eye.
Retention Factor (Rf) Values
- Retention factor (Rf) values are crucial for identifying components within mixtures.
- The Rf value for a specific compound remains consistent.
- Chemists use Rf values to pinpoint unknown substances by comparing them with known substances' Rf values in identical conditions.
Calculation
- The formula for calculating the retention factor is a fundamental step in chromatography analysis.
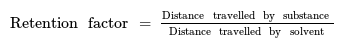
- Rf values are ratios and are unitless, simplifying comparisons across different substances.
Using Rf values to identify components of a mixture: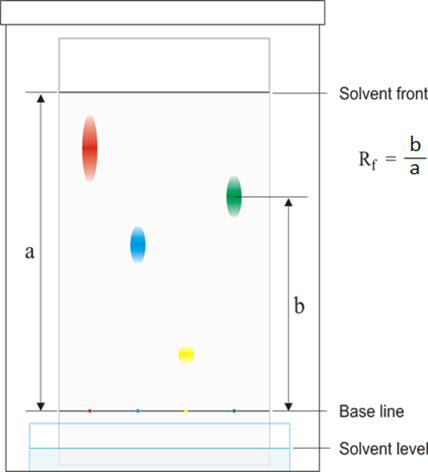
Question for Paper Chromatography Using Locating AgentsTry yourself: What is the purpose of locating agents in chromatography?View Solution
The document Paper Chromatography Using Locating Agents | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Paper Chromatography Using Locating Agents - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How are locating agents used in paper chromatography? |  |
Ans. Locating agents are substances that help visualize the separated components in paper chromatography. They react with the compounds being separated to produce a visible color or fluorescence.
| 2. What is the significance of retention factor (Rf) values in paper chromatography? |  |
Ans. Rf values indicate how far a compound has traveled in relation to the solvent front in paper chromatography. It helps in identifying and comparing different compounds based on their relative mobility.
| 3. How can Rf values be calculated in paper chromatography? |  |
Ans. Rf values are calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the compound by the distance traveled by the solvent. It is a ratio that helps in quantifying the relative mobility of different compounds.
| 4. Why is it important to use a standardized system for calculating Rf values in paper chromatography? |  |
Ans. Standardizing the calculation of Rf values ensures consistency and accuracy in comparing results obtained from different experiments or labs. It helps in making reliable conclusions about the components being analyzed.
| 5. Can Rf values be used to determine the identity of unknown compounds in paper chromatography? |  |
Ans. Yes, Rf values can be compared with known values of compounds to help identify unknown substances in paper chromatography. However, other analytical techniques may also be needed for confirmation.
Related Searches















