Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Separation and Purification
Separation and Purification | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Filtration & Crystallisation
- The selection of the separation method hinges on the characteristics of the substances involved.
- Each method relies on a distinction, typically in a physical attribute like boiling point, among the substances undergoing separation.
Separating a mixture of solids
- Differences in solubility provide a method for separating solids.
- Selecting an appropriate solvent is essential to ensure that only the desired substance dissolves, leaving impurities behind.
- For instance, water is suitable for dissolving salt in a mixture of sand and salt, while leaving the sand unaffected.
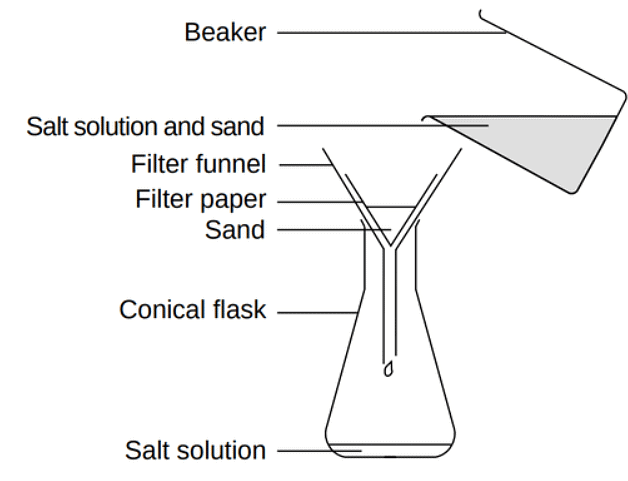
Filtration
- Separation technique used to isolate an undissolved solid from a mixture with a liquid/solution (e.g., separating sand from a sand-water mixture).
- Centrifugation is an alternative method for such separations.
- Process involves placing filter paper in a filter funnel above a receiving beaker.
- Mixture of insoluble solid and liquid is then poured onto the filter paper.
- Filter paper permits only small liquid particles to pass through as filtrate.
- Large solid particles remain trapped on the filter paper as residue.
- Filtration of a sand and water mixture:
Crystallisation
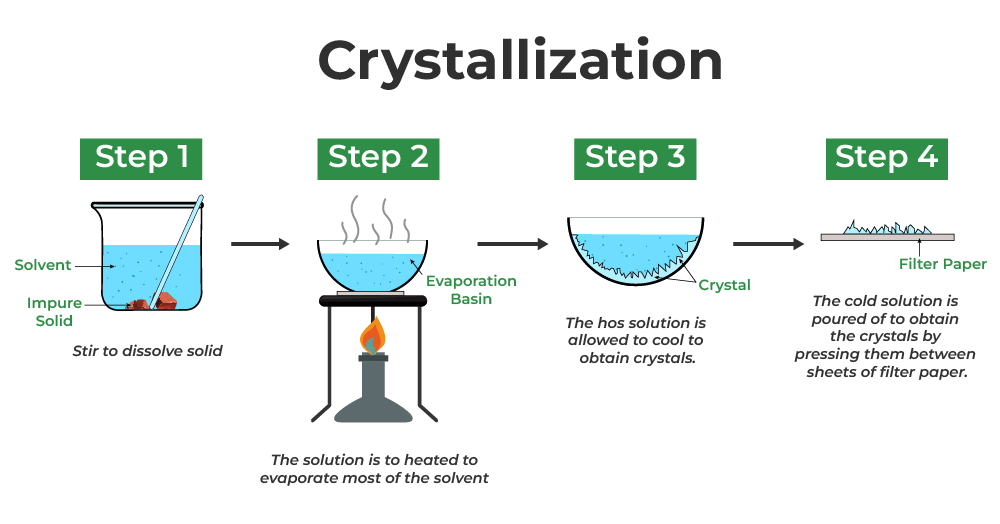
- Crystallisation is a technique used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution.
- It is employed when the solid is more soluble in a hot solvent than in a cold one.
- The process involves heating the solution, allowing the solvent to evaporate, and leaving a saturated solution behind.
- To check for saturation, a clean, dry, cold glass rod is dipped into the solution. If crystals form on the rod upon cooling, the solution is saturated.
- The saturated solution is then cooled slowly, causing solids to precipitate out as the solubility decreases, leading to crystal formation.
- Crystals are collected by filtering the solution to separate them from the remaining liquid.
- Subsequently, the crystals are washed with distilled water to eliminate impurities and then dried.
Question for Separation and PurificationTry yourself: Which method is used to separate an undissolved solid from a mixture with a liquid/solution?View Solution
Distillation: Simple & Fractional
Simple Distillation
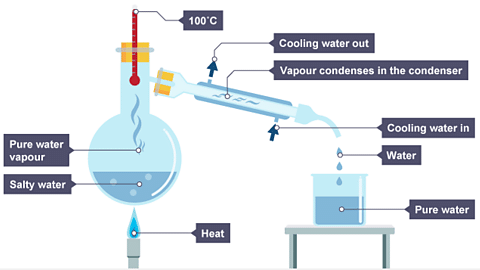
- Used for separating a liquid and soluble solid from a solution (e.g., separating water from saltwater solution) or a pure liquid from a mixture of liquids.
- The process involves heating the solution. The pure water evaporates, forming vapor that travels through the neck of the round-bottomed flask.
- The vapor then moves through the condenser, where it cools and condenses back into pure water, collected in a beaker.
- Once all the water has evaporated, only the solid solute remains behind.
- Diagram showing the distillation of a mixture of salt and water:
- Simple distillation is an option for separating fermentation products like alcohol and water.
- Yet, for enhanced separation, fractional distillation is preferred, especially when dealing with liquids that have similar boiling points and when higher purity levels are necessary.
Fractional Distillation
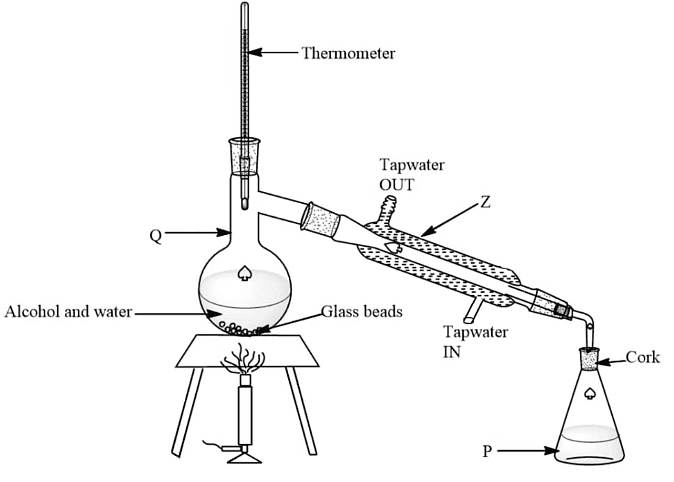
- Distillation is employed for separating multiple miscible liquids, like ethanol and water from a blend of the two.
- The mixture is heated to the boiling point of the liquid with the lowest boiling point.
- This particular substance evaporates first, rises, and then passes through a condenser.
- In the condenser, the vapors cool down and condense, turning into a liquid collected in a beaker.
- Once all of the targeted substance is evaporated and collected, the remaining components of the mixture are left behind.
- For instance, in the case of water and ethanol, the mixture is heated until it reaches 78 ºC, at which point the ethanol boils and distills out, condensing into the beaker.
- Heating should be ceased when the temperature starts increasing to 100 ºC, at which point water and ethanol are separated.
- Fractional distillation of a mixture of ethanol and water:
- Using an electric heater is recommended for safety in the presence of flammable liquids.
- In industries, the separation of components in petroleum is achieved through fractional distillation.
- Fractional distillation of crude oil, due to its toxic components, isn't typically conducted in school labs. Instead, a synthetic crude oil can be used for simulation.
Assessing Purity
- Pure substances exhibit specific and distinct melting and boiling points. For instance, water boils at 100°C and melts at 0°C, showcasing sharp temperature transitions.
- Mixtures, on the other hand, encompass a range of melting and boiling points due to the presence of different components with varying temperature properties.
- By analyzing melting and boiling point data, one can differentiate between pure substances and mixtures effectively.
- Identification of an unknown pure substance involves experimental determination of its melting and boiling points, followed by comparison with established literature values or data tables. Boiling points are typically ascertained through distillation.
- Melting point test using an oil bath:
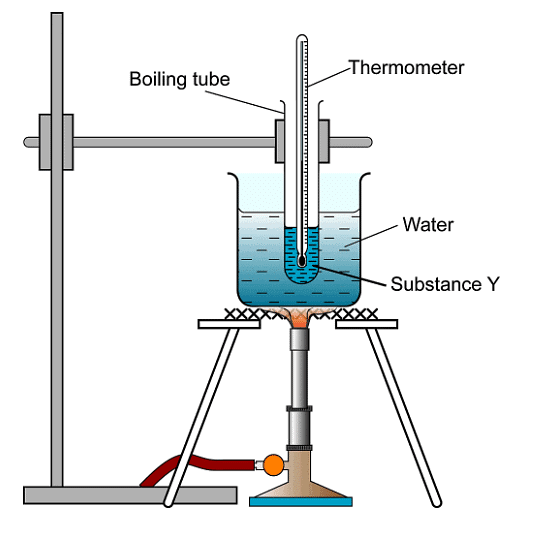
- Comparing experimental values with data tables helps determine sample purity.
- The proximity of measured values to the actual boiling or melting points indicates sample purity.
- Impurities in a sample can cause deviations:
- Impurities may elevate the boiling point beyond the actual value.
- Impurities may depress the melting point below the actual value.
Question for Separation and PurificationTry yourself: What is the purpose of simple distillation?View Solution
The document Separation and Purification | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Separation and Purification - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between simple distillation and fractional distillation? |  |
Ans. In simple distillation, a liquid mixture is heated, and the vapor is collected and condensed into a separate container. This method is used when the boiling points of the components in the mixture are significantly different. Fractional distillation, on the other hand, is used when the boiling points of the components are close. It involves multiple distillations using a fractionating column to achieve better separation.
| 2. How does filtration work in the separation and purification process? |  |
Ans. Filtration is a method used to separate solid particles from a liquid or gas by passing the mixture through a filter medium that retains the solid particles while allowing the liquid or gas to pass through. This process is effective in removing impurities and achieving purification.
| 3. What is crystallization and how is it used in purification processes? |  |
Ans. Crystallization is a method of purifying a solid by dissolving it in a hot solvent and then allowing the solution to cool, causing the solid to crystallize out. The impurities remain dissolved in the solvent or are excluded from the crystal lattice, resulting in a purified solid product.
| 4. How can the purity of a substance be assessed in the separation and purification process? |  |
Ans. The purity of a substance can be assessed through various techniques such as melting point determination, boiling point determination, chromatography, spectroscopy, and elemental analysis. These methods help in determining the composition and purity of the substance.
| 5. What are some common applications of distillation, filtration, and crystallization in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Distillation is commonly used in the production of alcoholic beverages, purification of water, and extraction of essential oils. Filtration is used in coffee making, wastewater treatment, and air purification. Crystallization is used in sugar production, pharmaceuticals, and chemical synthesis.
Related Searches




















