Deforestation of Tropical Rainforest | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Deforestation of Tropical Rainforest in Malaysia |

|
| Environmental impacts of deforestation |

|
| Example Case Study: Malaysia |

|
| Example Case Study: Hot Desert, Namib Desert |

|
Deforestation of Tropical Rainforest in Malaysia
- Deforestation is the process of cutting down and clearing trees.
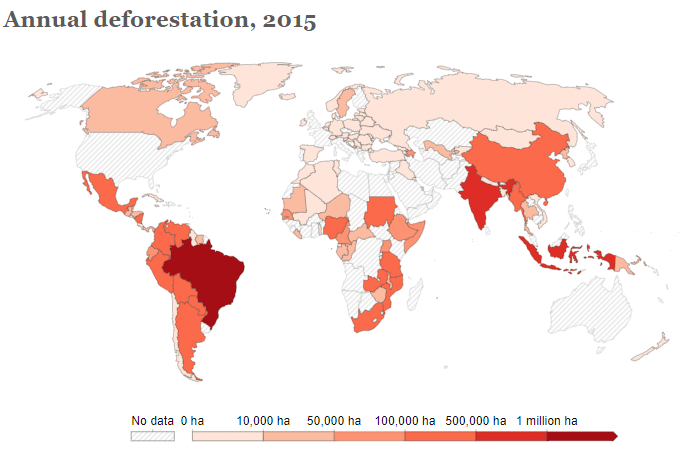
- Malaysia, Brazil, India, and Indonesia are currently experiencing the highest rates of deforestation globally.
- The Malaysian government has historically not provided the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) with accurate data on forest loss.
- Six primary human factors contribute to deforestation.
- Wildfires represent a natural factor in deforestation:
- The frequency and intensity of wildfires have risen, correlating with human-induced climate change.
Human Causes of Deforestation: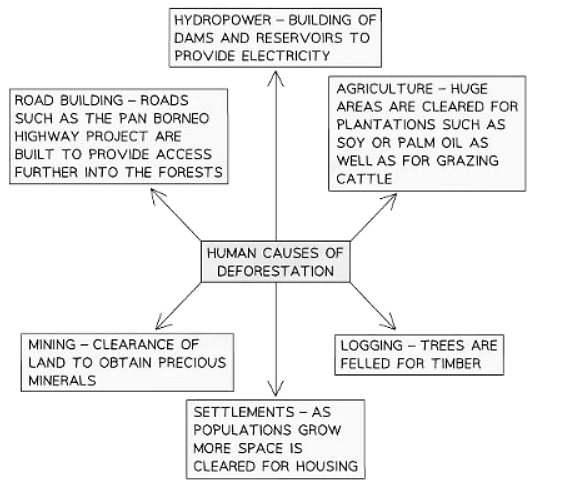
Environmental impacts of deforestation
Environmental impacts of deforestation include:
- Conversion of deforested areas to monoculture plantations, reducing biodiversity.
- Decrease in interception and infiltration, leading to reduced evapotranspiration and subsequent decrease in precipitation.
- Increase in overland flow causing soil erosion and river sedimentation.
- Accumulation of sediment in riverbeds, elevating flood risks.
- Reduced nutrient retention due to decreased interception.
- Increased atmospheric CO2 levels due to fewer trees, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
Impact on the nutrient cycle
- Most of the nutrients in the tropical rainforest are stored in the biomass.
- When trees and vegetation are cleared through deforestation, the primary reservoir of nutrients is depleted.
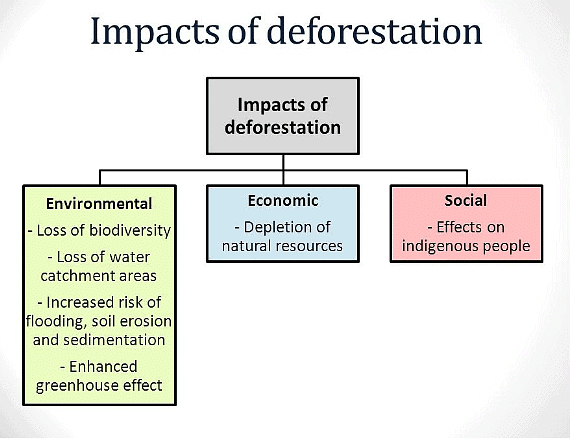
Social impacts of deforestation
Indigenous communities experience reduced land for sustaining their traditional lifestyle, resulting in several consequences:
- Limited land recovery opportunities.
- Decreased food availability.
- Some individuals benefit from improved income and employment prospects.
- Indigenous cultures and traditions may be forsaken, leading to cultural loss.
- Elevated risk of landslides, causing property damage and road blockages.
- Diminished access to potential medicinal resources.
- Heightened vulnerability to flooding in settlements.
Economic Impact of Deforestation
- Expansion of job markets in mining, forestry, agriculture, and hydroelectric power
- Rise in income through the export of forest resources like minerals, timber, and crops
- Approximately a quarter of Brazil's GDP is derived from deforested Amazon regions
Example Case Study: Malaysia
- Malaysia is situated in Southeast Asia.
- Location of Malaysia:
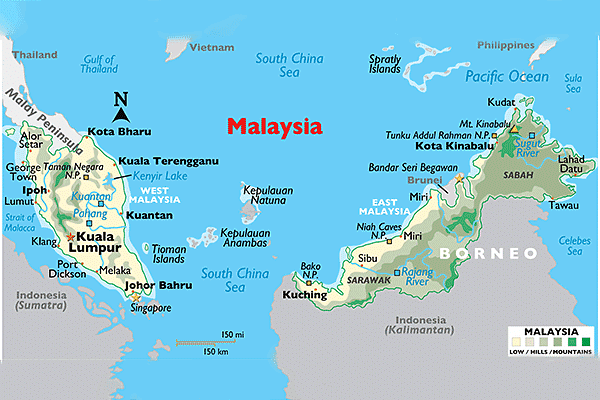
- Approximately 70% of the land in Malaysia is covered by tropical rainforest.
Climate
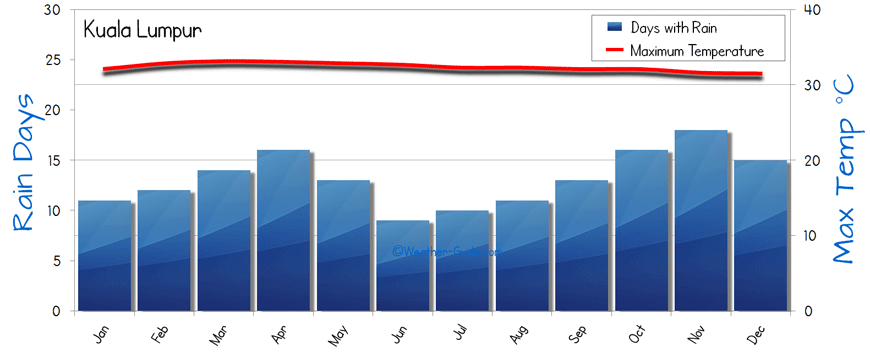
- The climate in Malaysia is characterized by high rainfall and temperatures throughout the year, typical of tropical rainforest climates.
- Climate Graph of Kuala Lumbar, Malaysia:
- The Malaysian rainforest boasts high biodiversity, including:
- 15,000 plant species, which consist of 5,500 flowering plants and 2,600 tree species.
- 750 bird species.
- 250 mammal species.
- 350 reptile species.
- 190 amphibian species.
- 350 fish species.
- 1000 butterfly species.
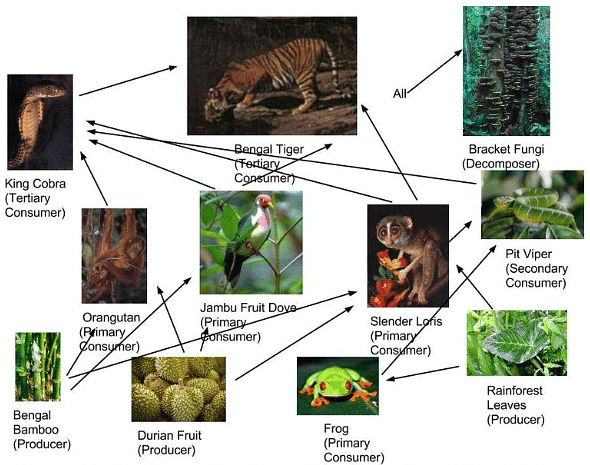
- Malaysian Rainforest Food Web:
Adaptations
The rainforest climate has spurred various adaptations among its flora and fauna, such as: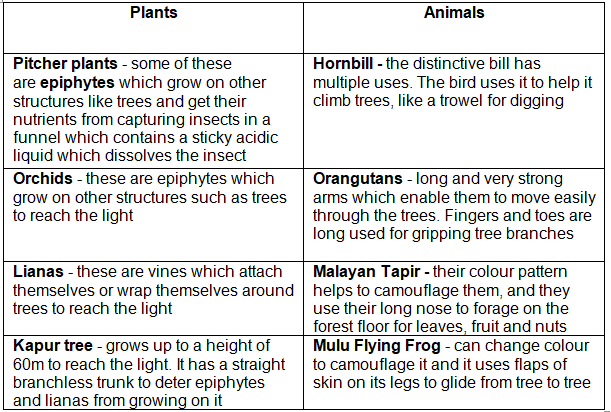
Deforestation in Malaysia:
- Malaysia has been experiencing alarming rates of deforestation, with over 140,000 hectares of forest being cleared annually since 2000.
Causes
Logging
- Malaysia holds the position of the largest provider of tropical hardwoods worldwide.
- Although Malaysia boasts environmental safeguarding policies, unauthorized logging activities are still observable in Borneo.
- The practice of selective logging prevails, demanding the establishment of roads and settlements, consequently leading to deforestation.
Energy
- Building dams to produce hydroelectric energy leads to the flooding of significant forested areas.
- The Bakun Dam initiative is poised to inundate 700km² of land in Sarawak, Malaysia.
Mining
- Tin mining operations are extensive and require deforestation for both the mining sites and road infrastructures.
- An iron ore mine proposed for the Som Forest Reserve is projected to lead to the deforestation of more than 60 hectares.
- Furthermore, drilling activities for oil and gas resources are also ongoing.
Commercial Plantations
- Malaysia plays a significant role in the global palm oil industry, exporting over 30% of the world's palm oil and ranking as the second-largest producer.
- To mitigate deforestation, many palm oil producers are now adopting zero-deforestation policies to avoid sourcing from deforested regions.
- However, there are instances where clear-felling permits are utilized in Malaysia to clear land, followed by palm oil plantation establishment at a later stage.
Settlements
- Historically, there was a push for urban residents to relocate to rural areas before 1980 to alleviate urban pressures, leading to the deforestation of around 15,000 hectares of rainforest.
Subsistence farming
- This may include the method of slash-and-burn, where fires are used to clear areas, sometimes resulting in uncontrolled spread and extensive destruction of rainforest.
Effects of deforestation
Soil Erosion
- Without the presence of tree roots to hold the soil in place, it becomes prone to erosion through the effects of wind and rain. This leads to the soil being washed away more easily.
- Exposed soil is at a higher risk of losing essential nutrients through leaching, making the land less fertile over time.
Loss of Biodiversity
- Deforestation results in the destruction of habitats, directly impacting ecosystems and reducing the variety of plant and animal species. For instance, the establishment of oil palm plantations has led to a significant 35% decline in various species like orangutans, pygmy elephants, Sumatran rhinos, and Malayan tigers.
Local Climate Change
- The removal of trees disrupts the natural processes of transpiration and evaporation, leading to a decrease in precipitation levels and an increase in temperatures. This alteration in climatic conditions can cause shifts in rainfall patterns, making them less predictable and more extreme.
Global Climate Change
- Deforestation contributes to the rise in carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere since trees play a crucial role in absorbing this greenhouse gas. Additionally, the use of fire for clearing land further intensifies carbon dioxide emissions, exacerbating human-induced climate change.
Impact on Indigenous Communities
- Indigenous communities such as the Orang Asli and Temiar are often displaced from their lands due to deforestation activities. The decline in pollinating insects and animals, like bats, reduces the natural pollination of fruits, leading to a decrease in available food sources for these communities.
- An unfortunate incident in Kuala Koh village in 2019 saw the tragic deaths of at least 15 indigenous Batek individuals following a disease outbreak, possibly linked to the presence of loggers in close proximity to the village.
Example Case Study: Hot Desert, Namib Desert
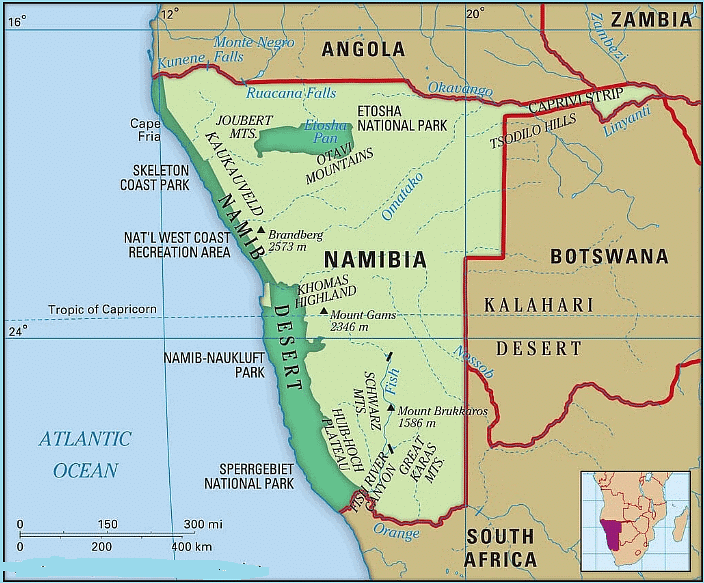
- The Namib Desert is primarily situated in Namibia along the western coast of Southern Africa.
- It stretches over 2,000km from Angola in the north to South Africa in the south, covering a width of 160km.
- Location of the Namib Desert:
Climate of Namibia
The climate in Namibia exhibits extreme temperature variations:
- Daytime temperatures can soar above 45°C.
- Nighttime temperatures can plummet to 0°C.
- Proximity to the coast brings cooler conditions due to the Benguela current.
- The Benguela current's influence can trigger fog formation, significantly impacting coastal regions for over half the year.
- Annual precipitation ranges widely from 2mm to 200mm.
Climate Graph of Swakopmund: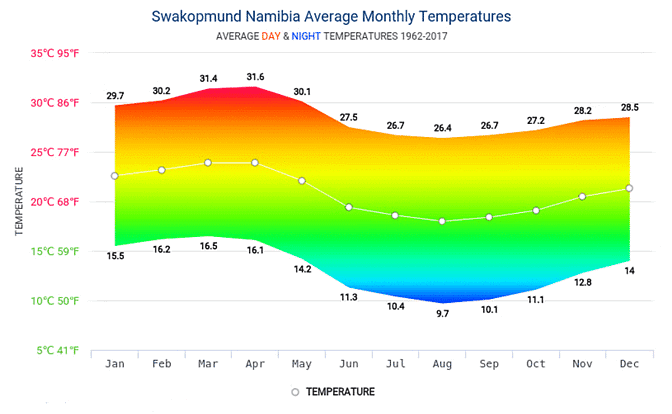
The Namib Desert boasts unique biodiversity compared to other hot deserts:
- It is home to numerous endemic species, showcasing higher biodiversity levels.
- Approximately 3,500 plant species thrive, with over 50% being exclusive to the region.
- The desert hosts 200 mammal species, 268 reptile species, and over 6,000 insect species.
Adaptations
Various methods exist by which plants and animals have adjusted to the distinctive climate of the Namib Desert.
Threats and impacts on the desert ecosystem
Tourism:
- Increasing tourism in the Namib Desert has resulted in a rise in activities like off-roading and sandboarding.
- Desert soil may take over 2000 years to recover from vehicular damage.
- Vehicles often damage small but essential lichens and plants, which are fundamental to the desert's food chain.
Mining:
- Mining operations for diamonds, uranium, copper, and zinc, including the Rössing uranium mine near Swakopmund, remove large sand areas, leading to habitat destruction.
- These operations intensify pressure on scarce water resources due to extensive water usage in processing, resulting in increased pollution of air, soil, and water.
- Toxic waste from mining activities can leach into the ground, affecting water sources.
Agriculture:
- Agricultural practices such as irrigation raise soil salt levels and diminish plant life, further straining limited water resources.
- Overgrazing in confined areas reduces plant diversity and affects species like the Golden Mole.
- Farmers may perceive the desert lion as a threat to livestock and resort to shooting them, endangering the lion population.
Poaching:
- Illegal poaching of animals like pangolins disrupts the desert's food web.
- Black rhino populations have declined significantly due to poaching activities.
|
55 videos|68 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Deforestation of Tropical Rainforest - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the main reasons for deforestation of tropical rainforests in Malaysia? |  |
| 2. How does deforestation in Malaysia impact the environment? |  |
| 3. What are the consequences of deforestation for local communities in Malaysia? |  |
| 4. What measures are being taken to address deforestation in Malaysia? |  |
| 5. How can individuals help combat deforestation in Malaysia? |  |














