Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Analysis & Conclusions
Analysis & Conclusions | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Analysis
- Once data has been collected and presented, it needs to be analyzed.
- Analysis is the process of making sense of the collected data by identifying patterns, trends, significance, connections, and meanings within it.
- It involves identifying patterns, trends, significance, connections, and meanings within the data.
- Analysis includes several stages:
- Describing the data presented in graphs, photographs, or maps.
- Identifying the highest and lowest results.
- Recognizing any patterns and trends present.
- Identifying relationships between different sets of data.
- The methods of analysis employed depend on the type of data collected.
- Quantitative data is typically analyzed using numerical and statistical methods.
Numerical and statistical skills
- Statistical techniques aid in examining and elucidating the findings acquired during data collection.
Mean, median and mode
- Mean, median, and mode are considered measures of central tendency.
- The mean, or average, is computed by summing all values in the dataset and dividing by the total count.
- The median denotes the middle value in a dataset, selected after arranging the numbers in rank order.
- The mode represents the value that appears most frequently in the dataset.
Range
- Dispersion refers to the spread of data around the average
- Range represents the span between the highest and lowest data points
- Interquartile range covers the central 50% of the dataset
Anomalies
- These are results which do not fit the pattern or trend
- They need to be described and explained
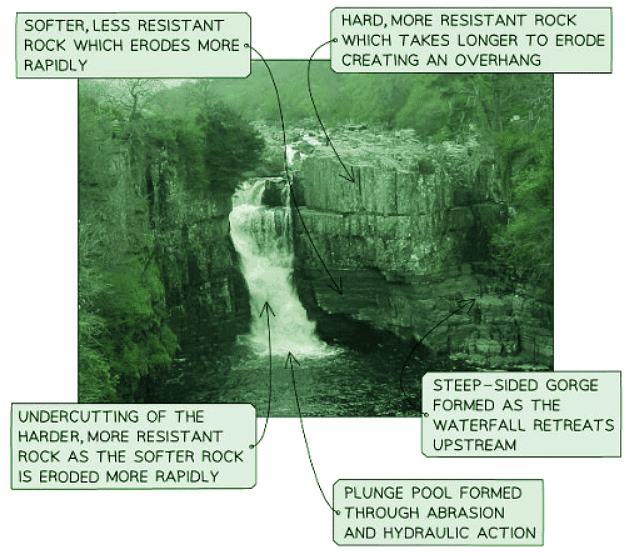
Analysing photographs and field sketches
- Annotation of photographs and field sketches is part of analysis
- The use of photographs and field sketches is a qualitative analysis
- Analysis in annotation gives meaning to the features shown in the photograph/field sketch
Question for Analysis & ConclusionsTry yourself: What is the purpose of analysis in data collection?View Solution
Concluding
The fieldwork conclusion should:
- Return to the hypothesis and aim
- Identify evidence supporting the hypothesis
- Outline evidence contradicting the hypothesis
- Describe and explain links to geographical theories
- Acknowledge any unusual results
- Determine whether the hypothesis is supported
Key Steps in Hypothesis Testing
- Return to the hypothesis and aim
- Identify any evidence that supports the hypothesis
- Outline any evidence that contradicts the hypothesis
- Describe and explain any links to geographical theories
- Acknowledge any unusual results
- State whether the hypothesis is supported or not
Evaluation of Data Collection in Fieldwork Questions
- A key focus in the fieldwork questions in the exam is the evaluation of data collection
- Enquiry evaluation should:
- Identify any problems with, and limitations of, data collection methods
- Suggest other data which would have been useful in the study or improvements which could be made
- Evaluate how reliable the conclusions were
- Suggesting how the scope of the study could be extended
Identifying Problems and Limitations of Data Collection Methods
- Accessibility of Sample Sites: This refers to the ease of access to the locations from which data is being collected. For instance, were all the sample sites easily reachable, or were there any obstacles that hindered access?
- Size of Sample: The sample size plays a crucial role in the reliability of the data collected. Was the sample size sufficient to draw meaningful conclusions, or was it too small to represent the population accurately?
- Duration of Data Collection: The duration of data collection impacts the comprehensiveness of the study. Was the time allocated for data collection adequate to gather all necessary information, or was it insufficient?
- Methods Used: The methods employed for data collection must align with the study's objectives. Were the questionnaire questions appropriate for the research goals and hypothesis testing, or were they inadequate?
- Equipment Issues: Equipment malfunctions can compromise the quality of data collected. Were there any issues with the tools used for data collection that may have affected the accuracy of the results?
- Human Errors: Mistakes in recording data or operating equipment can introduce inaccuracies. Were there any instances of human error during the data collection process that could have influenced the findings?
- Timing of Data Collection: The timing of data collection can impact the results obtained. Did external factors such as weather conditions or time of day affect the data collected?
- Unforeseen Circumstances: Unexpected events can disrupt the data collection process. Were there any unforeseen issues, such as road construction or natural phenomena, that interfered with the data collection?
Other data and improvements
Enhancements to data collection methods are always possible and may involve:
- Expanding the sample size.
- Conducting additional measurements.
- Exploring a broader array of secondary sources.
- Considering alternative equipment; for instance, a flow meter could offer greater accuracy in measuring river velocity compared to a float.
Evaluating the conclusions
To assess the conclusion, students should consider the following:
- Determine if the conclusions align with the initial aims and hypotheses established at the beginning of the inquiry.
- Evaluate the suitability of the aim and hypothesis. Could the hypothesis be readily evaluated?
- Assess if the chosen location was appropriate for the study.
- Reflect on whether the accuracy of the results could be enhanced through repetition of the data collection process.
Question for Analysis & ConclusionsTry yourself: Which factor can impact the reliability of the data collected in fieldwork?View Solution
The document Analysis & Conclusions | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
55 videos|68 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Analysis & Conclusions - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the key themes in William Shakespeare's play "Macbeth"? |  |
Ans. The key themes in "Macbeth" include ambition, power, fate, guilt, and the supernatural.
| 2. Who are the main characters in "Macbeth" and what roles do they play in the story? |  |
Ans. The main characters in "Macbeth" are Macbeth, Lady Macbeth, Banquo, and King Duncan. Macbeth is the protagonist who becomes consumed by ambition, while Lady Macbeth manipulates him to achieve their goals. Banquo is Macbeth's loyal friend, and King Duncan is the ruler of Scotland.
| 3. What is the significance of the three witches in "Macbeth"? |  |
Ans. The three witches, also known as the Weird Sisters, play a crucial role in the play by predicting Macbeth's rise to power and ultimately his downfall. They represent the supernatural forces at work in the story and symbolize the themes of fate and destiny.
| 4. How does the character of Macbeth evolve throughout the play? |  |
Ans. At the beginning of the play, Macbeth is a brave and loyal soldier, but as he becomes consumed by ambition and greed for power, he descends into madness and tyranny. His character evolves from a noble hero to a ruthless and paranoid ruler.
| 5. What is the importance of the motif of blood in "Macbeth"? |  |
Ans. The motif of blood symbolizes guilt, violence, and the consequences of ambition in "Macbeth." It is a recurring image throughout the play that reflects the characters' moral decay and the bloody deeds they commit in their pursuit of power.
Related Searches




















