Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Compound Measures - Speed, Density, Pressure
Compound Measures - Speed, Density, Pressure | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Compound Measures
What is a compound measure?
- Compound measures involve calculations that incorporate multiple measurements.
- They are commonly employed to quantify rates or ratios.
- This concept measures how much one quantity changes when another is increased by 1.
- Examples of such measurements include:
- Speed: Speed refers to how much the distance changes for each unit of time.
- Density: Density signifies how heavy an object is for each unit of its area or volume.
- Pressure: Pressure indicates the amount of force applied to an object for each unit of its area.
- Flow Rate: Flow rate represents how much the volume changes for each unit of time.
- Population Density: Population density reveals how many people there are for each unit of area.
How do I find the units for a compound measure?
- Employ the formula for a compound measure to deduce its units.
- Utilize the units associated with the quantities in the formula to determine the units of the compound measure.
- Represent a division as a/b or ab-1 and pronounce it as "a per b."
- Examples include:
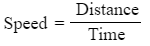
If the distance is measured in km and the time is measured in mins then the speed is measured in km/min.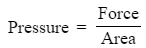
If the force is measured in N and the area is measured in cm2 then the pressure is measured in N/cm2.
How do I find the formula for a compound measure?
- The units associated with a compound measure can aid in recalling its formula.
- Simply remember the purpose of each unit of measurement.
- For a unit expressed as a/b, the corresponding formula will involve the quantity measured by a divided by the quantity measured by b.
- Examples include:
- kg is a measure of mass and cm3 is a measure of volume
- Therefore
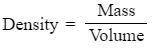
- Density can be measured in kg/cm3
Can I use a formula triangle?
- Formula triangles can be used based on personal preference.
- Follow these steps if you choose to use them:
- Steps:
- Identify the units provided in the question or information to formulate an initial equation.
- Construct a formula triangle, like for Speed, Distance, and Time, as needed.
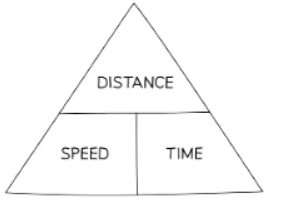
- Break down the question into known and unknown components.
- Rearrange the formula using the triangle if necessary.
- Substitute the known values and compute the solution.
Speed, Density & Pressure
What are speed, density and pressure?
- Speed, density, and pressure are combined measurements that are derived from other fundamental measures.
- Speed is connected to distance and time.
- Density is linked to mass and volume.
- Pressure is associated with force and area.
- The relationship between each of these sets of measures follows the same pattern
- Sometimes referred to as “formula triangles”
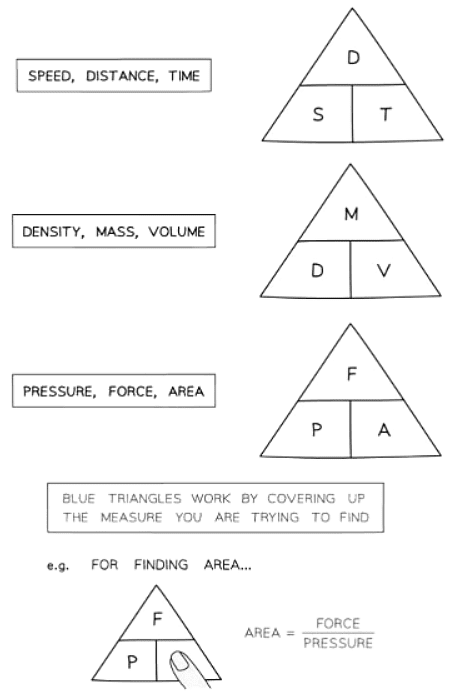
- It's important to recall the formula triangle for speed, distance, and time.
- In exams, formulas for other rates will typically be provided, allowing you to construct the corresponding formula triangle.
- If you don't remember the formula triangles, don't fret. You can often deduce them from the information provided in the question or from the units involved.
Problems involving speed, distance & time
- Speed is typically quantified in units such as meters per second (m/s) or miles per hour (mph), with alternatives like kilometers per hour (km/h) also prevalent.
- These units signify that speed denotes the distance covered per unit of time, as expressed by the formula speed = distance ÷ time.
- In this context, "speed" generally refers to average speed, especially in more challenging problems featuring multiple journeys or segments within a longer journey.
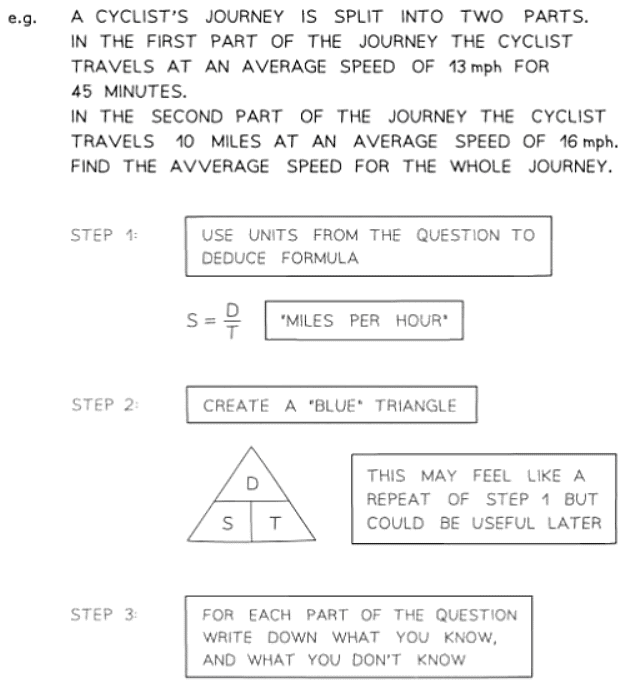
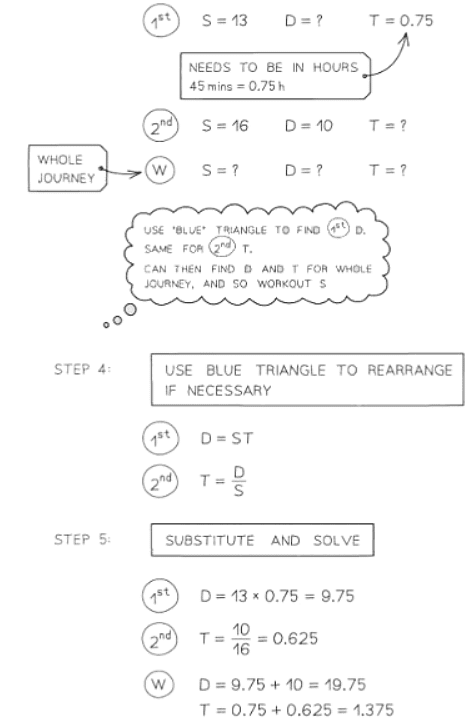
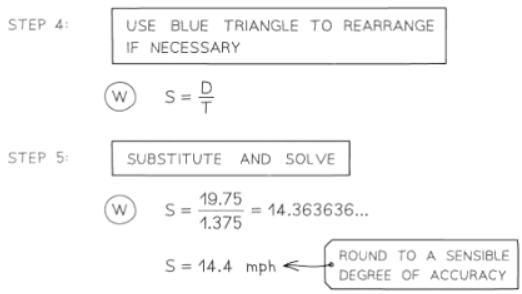
Problems involving density, mass & volume
- Density is commonly expressed in units such as grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³).
- These units signify that density represents the mass contained within a given volume, as denoted by the formula density = mass ÷ volume.
- In more challenging problems involving alloys, liquids, or gases, it's not uncommon to encounter scenarios where two or more substances have been combined. In such cases, it may be necessary to employ a volume formula to ascertain the volume of an object beforehand.
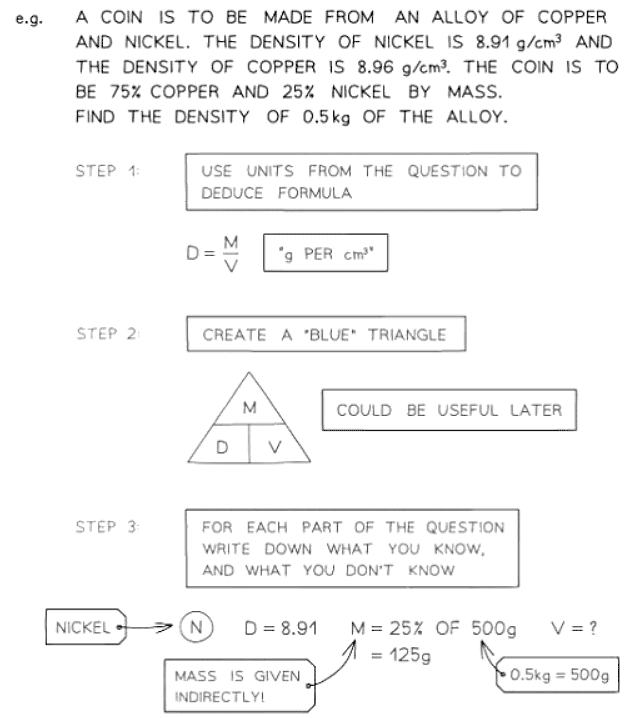
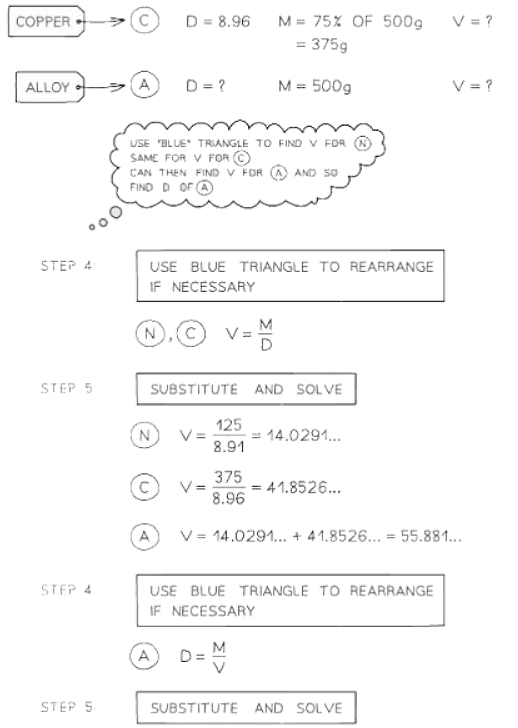
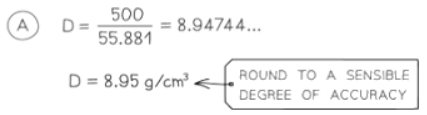
Problems involving pressure, force & area
- Pressure is commonly quantified in units such as Newtons per square meter (N/m²).
- These units of pressure are frequently referred to as Pascals (Pa) rather than N/m².
- The units of pressure signify that pressure denotes the force exerted over a given area, expressed by the formula pressure = force ÷ area.
- It's important to recognize that weight represents a force; it should not be confused with mass.
The document Compound Measures - Speed, Density, Pressure | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|674 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Compound Measures - Speed, Density, Pressure - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the relationship between speed, density, and pressure in compound measures? |  |
Ans. Speed, density, and pressure are interconnected in compound measures. Speed is the rate at which an object moves, density is the mass per unit volume of a substance, and pressure is the force applied over a certain area. Changes in one of these factors can affect the others in various ways.
| 2. How does an increase in speed affect pressure in compound measures? |  |
Ans. An increase in speed can lead to an increase in pressure in compound measures. This is because as an object moves faster, it can collide with other objects or surfaces with more force, resulting in higher pressure being exerted.
| 3. Can density affect the speed of an object in compound measures? |  |
Ans. Yes, density can affect the speed of an object in compound measures. A higher density of a substance can create more resistance for an object moving through it, which can slow down the object's speed. On the other hand, a lower density can allow the object to move more freely and at a higher speed.
| 4. How is pressure related to both speed and density in compound measures? |  |
Ans. Pressure in compound measures is influenced by both speed and density. A higher speed of an object can result in increased pressure when it collides with other objects or surfaces. Similarly, a higher density of a substance can also contribute to increased pressure when force is applied over a smaller area.
| 5. What are some real-life examples where the interaction between speed, density, and pressure in compound measures is important? |  |
Ans. Real-life examples where the interaction between speed, density, and pressure in compound measures is important include aerodynamics in vehicles, fluid dynamics in pipelines, and atmospheric pressure changes affecting weather patterns. These interactions play a crucial role in various scientific and engineering applications.
Related Searches
















