Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Understanding Money
Understanding Money | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
The Meaning of Money
- Prior to the invention of money, individuals and firms had to either accept other goods or services as payment or be entirely self-sufficient by producing everything they needed.
- Often, due to a lack of self-sufficiency or a desire for a greater variety of goods and services, bartering became a common practice. However, bartering also presented its own set of challenges.
- As individuals and firms engage in trade to obtain goods or raw materials, they require a medium of exchange that is widely accepted and easy to use.
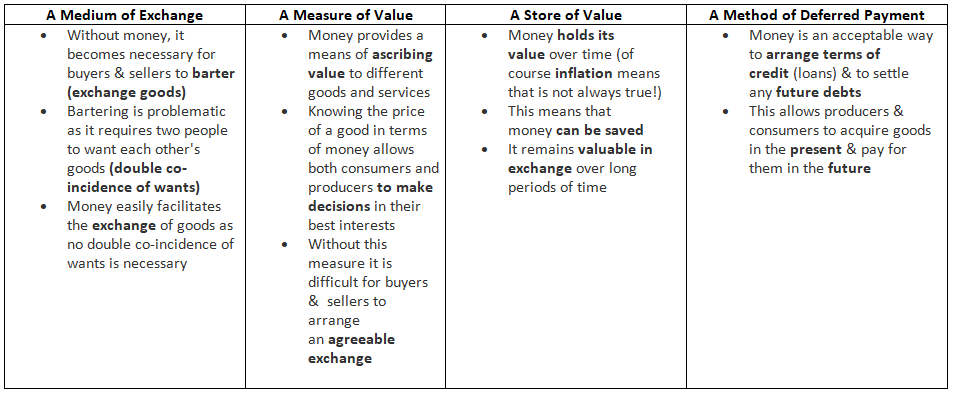
- Modern currency serves this purpose, functioning as a medium of exchange, a unit of value, a store of value, and a method of deferred payment.
The Functions of Money
The Four Functions of Money
Question for Understanding MoneyTry yourself: What are the four functions of money?View Solution
The Characteristics of Money
- Throughout history, various items such as gold, silver, shells, beer, and tobacco have served as forms of money.
- However, each of these items had limitations that made them less than ideal for exchange in certain situations.
- Good money possesses several essential characteristics, all of which are met by modern currency.
The six characteristics of good money
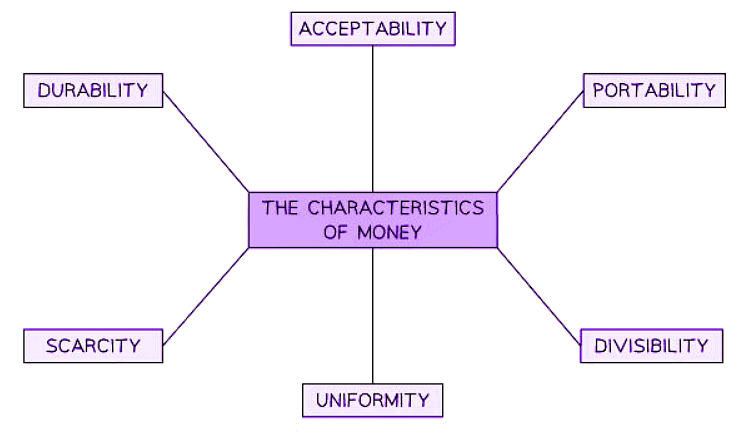
- Divisibility: Currency must be easily divisible to facilitate transactions of various sizes. For example, being able to exchange a €50 note for €10 notes or €1 coins.
- Acceptability: Society must widely recognize and accept the currency as a legitimate means of payment for goods and services.
- Durability: Money should be built to last, resistant to damage, and able to withstand the test of time.
- Scarcity: The currency's supply should be controlled to maintain its value in the market. An oversupply would decrease its worth.
- Uniformity: All denominations of the currency must be identical to maintain consistency and trust in its value. For instance, every $50 note should be exactly the same.
- Portability: Good money is convenient to carry and conceal, ensuring ease of use in daily transactions.
The document Understanding Money | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
56 videos|97 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding Money - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the meaning of money? |  |
Ans. Money is a medium of exchange that is widely accepted for transactions of goods, services, and payment of debts. It serves as a unit of account, store of value, and standard of deferred payment.
| 2. What are the functions of money? |  |
Ans. The functions of money include serving as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, a store of value, and a standard of deferred payment. Money facilitates trade, helps in measuring value, preserves purchasing power, and allows for future transactions.
| 3. What are the characteristics of money? |  |
Ans. The characteristics of money include durability, portability, divisibility, uniformity, limited supply, and acceptability. Money must be able to withstand wear and tear, be easily carried around, divided into smaller units, have a consistent value, not be easily counterfeited, and be widely accepted by individuals and businesses.
| 4. How does money impact the economy? |  |
Ans. Money plays a crucial role in the economy by facilitating economic transactions, influencing inflation and interest rates, and acting as a measure of wealth. The availability and circulation of money affect consumer spending, investment, and overall economic growth.
| 5. Why is understanding money important in economics? |  |
Ans. Understanding money is essential in economics as it is the basis of all economic transactions and activities. Money affects the behavior of individuals, businesses, and governments, and plays a significant role in shaping economic policies and outcomes.
Related Searches















