Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Monopoly Markets
Monopoly Markets | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Characteristics of Monopoly Markets
- A monopoly is a market structure where there is only one seller.
- Lack of substitute products in a monopoly market.
- Monopolies possess complete market power, enabling them to set prices and regulate output to maximize profits.
- Monopolies can maintain high levels of profit in the long run because potential competitors face significant barriers to entry.
- One key barrier to entry for monopolies is their ability to prevent competition by acquiring potential threats, such as purchasing rival companies.
- Many governments define a monopoly as a firm holding over 25% market share.
- Regulators intervene to stop market share from exceeding this threshold to maintain a competitive market environment.
Question for Monopoly MarketsTry yourself: What is a characteristic of monopoly markets?View Solution
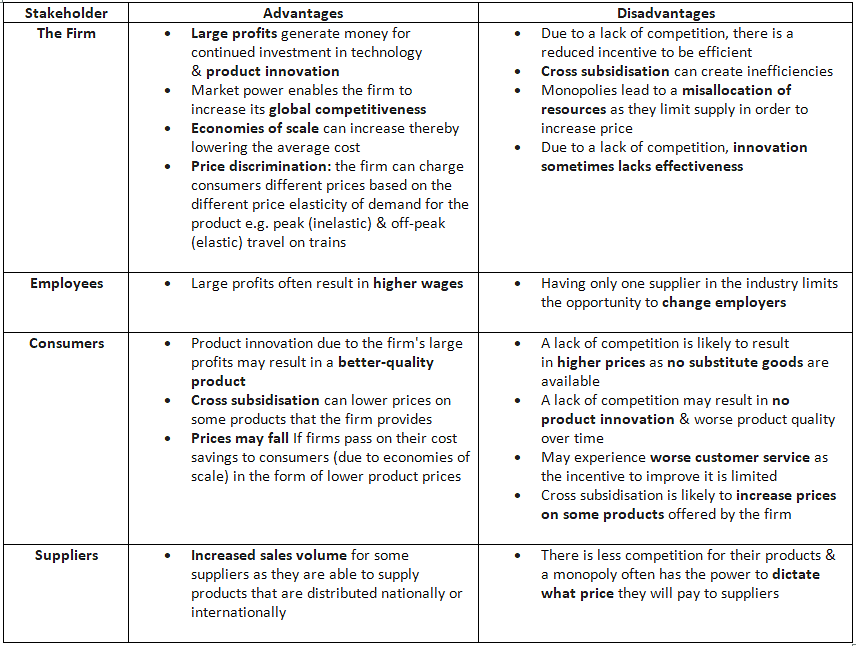
The Advantages & Disadvantages Of Monopoly Power
The document Monopoly Markets | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
57 videos|110 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Monopoly Markets - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the key characteristics of monopoly markets? |  |
Ans. Monopoly markets are characterized by a single seller or producer, barriers to entry for other competitors, control over prices, and unique products or services.
| 2. How do monopoly markets impact consumer choice and pricing? |  |
Ans. In monopoly markets, consumers have limited choice as there is only one seller. This lack of competition can lead to higher prices for consumers due to the seller's control over pricing.
| 3. What are some examples of industries that typically operate as monopolies? |  |
Ans. Examples of industries with monopoly markets include utilities like water and electricity, as well as some pharmaceutical companies with patents on specific drugs.
| 4. How do government regulations impact monopoly markets? |  |
Ans. Government regulations can intervene in monopoly markets to prevent abuse of power by the single seller. This can include setting price controls, breaking up monopolies, or imposing antitrust laws.
| 5. What strategies can a monopoly market use to maintain its dominance? |  |
Ans. Monopoly markets can maintain their dominance by investing in research and development to create unique products, engaging in exclusive contracts with suppliers, and lobbying for favorable government policies.
Related Searches




















