Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Protection
Protection | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
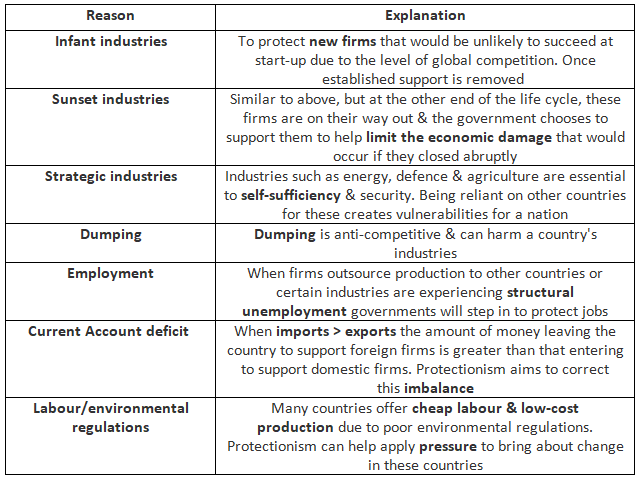
Reasons for Protection
- Free trade is geared towards increasing global production by emphasizing national expertise in specific areas.
- Nonetheless, nations may opt to restrict free trade for various reasons to shield themselves from unfavorable consequences.
- This strategy, termed protectionism, can materialize in the form of taxes on imports, subsidies on exports, limits on quantities, or complete trade restrictions.
- It's imperative to bear in mind that other nations could respond in kind to protective measures, highlighting the necessity of weighing the pros and cons before enacting such policies.
Methods of Protection
- The most common methods of trade protectionism encompass tariffs, subsidies, quotas, embargoes, and administrative barriers.
Tariffs
- Tariffs are taxes levied on imported goods and services, making them more expensive.
- This scenario benefits domestic firms by enhancing their competitiveness and market share as consumers shift towards locally produced goods and services.
- However, this shift can lead to less efficient domestic firms displacing more efficient international counterparts.
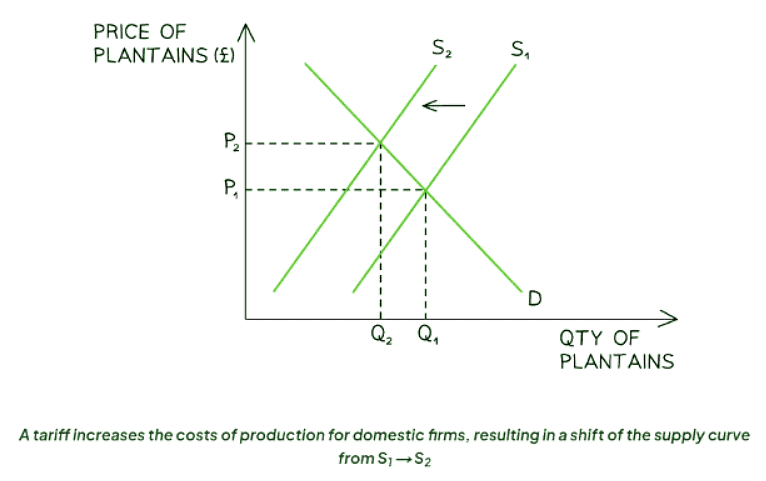
Diagram Analysis:
- The initial equilibrium in the plantains market before the tariff is set at price P1 and quantity Q1.
- After the tariff imposition, the costs of production for local firms rise due to paying the tariff upon plantains' entry, causing a shift in the supply curve from S1 to S2.
- This leads to a new market equilibrium at price P2 and quantity Q2.
- According to the law of demand, the quantity demanded decreases from Q1 to Q2, resulting in a price increase from P1 to P2.
- Tariffs are commonly used for protectionism, impacting stakeholders in various ways. An Evaluation of the Use of Tariffs to Protect Domestic Firms
An Evaluation Of The Use Of Tariffs To Protect Domestic Firms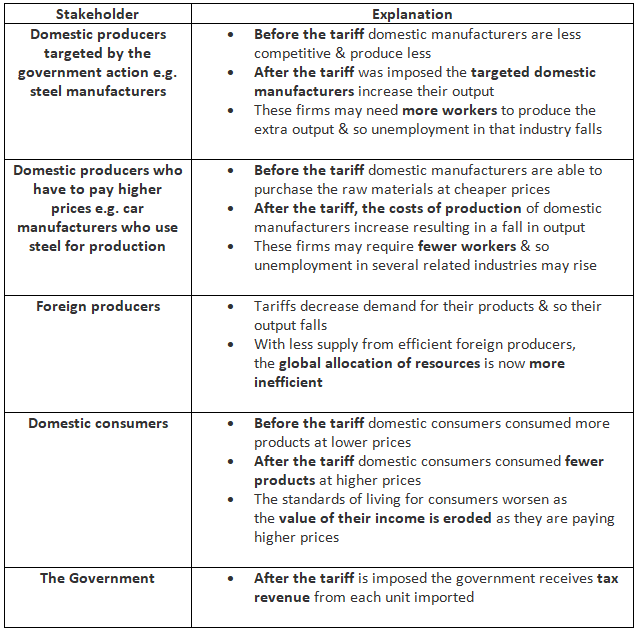
Question for ProtectionTry yourself: What is the purpose of protectionism in trade?View Solution
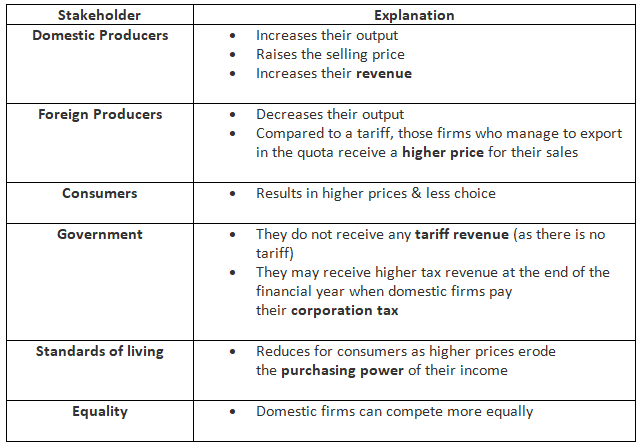
Quotas
- A quota denotes a physical constraint on imports. For instance, in June 2022, the UK elongated its restriction on steel imports for an additional two-year span to safeguard employment within its domestic steel sector. Such limits typically fall below the free market import volume.
- By curbing cheaper imports, quotas elevate market prices. However, they might also lead to scarcity. Consequently, certain domestic firms stand to gain as they can amplify their supply due to the reduced influx of imports, potentially boosting employment rates.
An Evaluation Of The Use of Quotas To Protect Domestic Firms
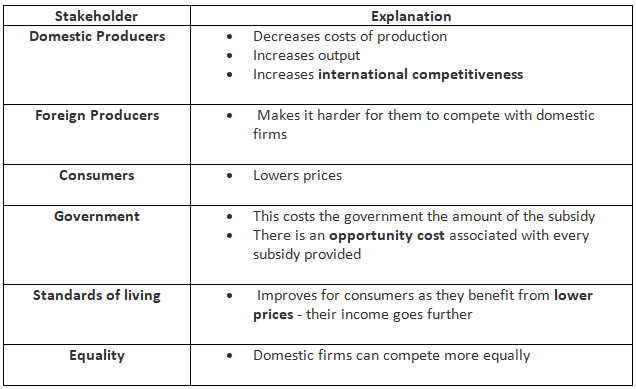
Subsidies to Domestic Producers
A subsidy reduces production costs for domestic firms, enabling them to boost output and potentially lower prices.
- Lower prices enhance the competitiveness of their goods or services in the international market.
- This competitiveness often leads to an increase in exports.
- The expanded output may also generate higher levels of domestic employment.
An Evaluation Of The Use of Subsidies To Protect Domestic Firms
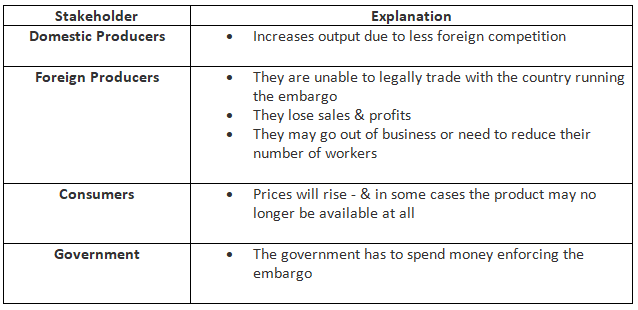
Embargoes
- An embargo constitutes a total trade ban with a specific country, often due to political conflicts. For instance, the USA imposed a prolonged embargo on Cuban products.
An Evaluation Of The Use of Embargoes To Protect Domestic Firms
Administrative Barriers
There exist numerous tactics for implementing trade barriers that are subtler than tariffs, quotas, and subsidies.
- Health and Safety Regulations: In 2017, the European Union implemented a new health regulation that controlled the allowable level of aflatoxins in nuts. Since aflatoxin levels are naturally higher in countries in the southern hemisphere, this regulation effectively halted the import of nuts from these regions.
- Product Specifications: For instance, Canada mandated that all imported jam must be packaged in a specific jar size. This posed a challenge because many countries do not typically produce jars in the required size, creating a barrier to entry for foreign jam manufacturers.
- Environmental Regulations: In November 2021, both the EU and the USA introduced new regulations to restrict the influx of 'dirty steel' imports. This type of steel is primarily produced using coal-fired power plants, a practice common in China. These regulations effectively hindered the entry of such steel into their markets.
- Product Labelling: Companies may encounter obstacles due to the cost of applying product labels, which could reduce their inclination to sell in specific markets. This acts as a deterrent for firms looking to enter markets with stringent labelling requirements.
Question for ProtectionTry yourself: How does a quota on imports affect market prices?View Solution
The document Protection | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
57 videos|110 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Protection - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How can individuals protect themselves from cyber threats? |  |
Ans. Individuals can protect themselves from cyber threats by using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, keeping software and devices updated, being cautious of phishing emails, and using reputable security software.
| 2. What are some common methods hackers use to gain unauthorized access to personal information? |  |
Ans. Some common methods hackers use to gain unauthorized access to personal information include phishing scams, malware attacks, social engineering tactics, and exploiting vulnerabilities in software or devices.
| 3. Why is it important to protect personal information online? |  |
Ans. It is important to protect personal information online to prevent identity theft, financial fraud, and privacy breaches. Unauthorized access to personal information can lead to various negative consequences for individuals.
| 4. How can businesses protect their sensitive data from cyber threats? |  |
Ans. Businesses can protect their sensitive data from cyber threats by implementing strong security measures such as encryption, access controls, regular security assessments, employee training, and incident response plans.
| 5. What should individuals do if they believe their personal information has been compromised in a cyber attack? |  |
Ans. If individuals believe their personal information has been compromised in a cyber attack, they should immediately change their passwords, notify relevant financial institutions, report the incident to the appropriate authorities, and monitor their accounts for any suspicious activity.
Related Searches















