Best Study Material for Year 11 Exam
Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Introduction to Exchange Rates
Introduction to Exchange Rates | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Foreign Exchange Rates (Forex)
- An exchange rate denotes the value of one currency relative to another, such as £1 being equivalent to €1.18.
- Foreign currencies are essentially commodities traded on the foreign exchange market (forex).
- The control over the exchange rate system, which determines a nation's currency value, lies with the Central Bank of a country.
- Two primary exchange rate systems are:
- Floating exchange rates
- Fixed exchange rates
A Floating Exchange Rate System
- Various currencies are tradable commodities, subject to buying and selling like any other product.
- The interaction of demand and supply dictates the exchange rate between different currencies.
- Similar to any market, when there is a surplus demand for a currency in the forex market, its value increases (appreciates).
- Conversely, if there is an oversupply of a currency in the forex market, its value decreases (depreciates).
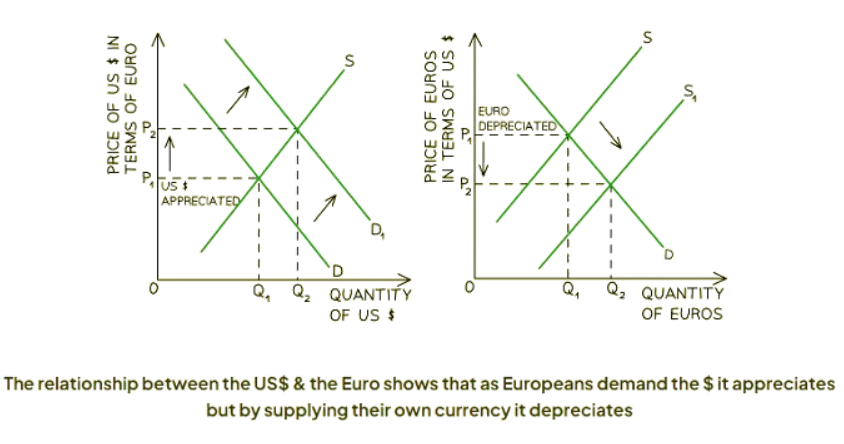
Diagram Analysis:
- The Euro/US$ market is depicted with two separate market diagrams: one representing the USD market on the left and another for the Euro market on the right.
- Initially, the exchange rate equilibrium is established at P1Q1 in both markets.
- When Europeans travel to the USA, they demand US dollars and supply Euros.
- This surge in demand for US dollars shifts the demand curve to the right, causing the value of the dollar to appreciate from P1 to P2 in the USD market, and a new equilibrium emerges at P2Q2.
- Simultaneously, the increased supply of Euros shifts the supply curve to the right, resulting in the depreciation of the Euro from P1 to P2, and a new equilibrium is established at P2Q2.
Question for Introduction to Exchange Rates
Try yourself:
What determines the exchange rate between different currencies in the forex market?View Solution
A Fixed Exchange Rate System
- In a fixed exchange rate system, the country's Central Bank intervenes in the currency market to establish a specific value (peg) for its currency in relation to another currency, such as the US dollar.
- When the Central Bank aims to strengthen its currency, it purchases its own currency in the forex market using its foreign reserves, thereby increasing its demand.
- Conversely, when the Central Bank seeks to weaken its currency, it sells its currency in the forex market, thereby increasing its supply.
- Pegs may sometimes be set at parity, such as 1 Brunei Dollar equaling 1 Singapore Dollar.
- However, pegs are often not at parity, as seen with Hong Kong pegging its currency to the US dollar at a rate of HK$ 7.75 to US$ 1.
- A revaluation occurs when the Central Bank decides to adjust the peg to increase the strength of its currency.
- Conversely, a devaluation occurs when the Central Bank decides to adjust the peg to decrease the strength of its currency.
Evaluating Exchange Rate Systems
- Every exchange rate system comes with its own set of benefits and drawbacks.
 |
Download the notes
Introduction to Exchange Rates
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
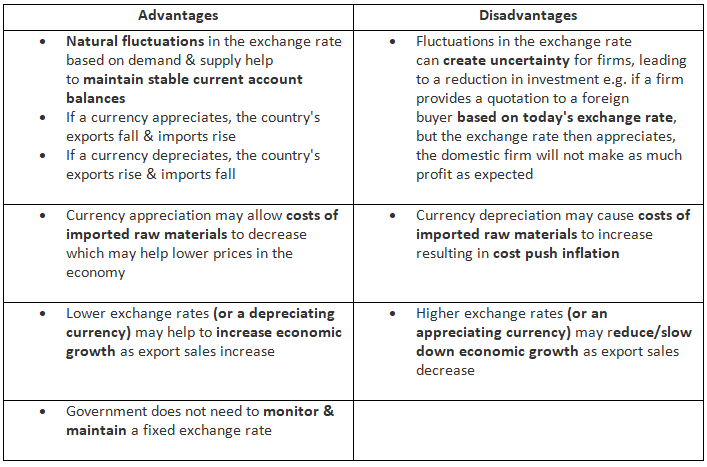
An Evaluation of A Floating Exchange Rate Mechanism
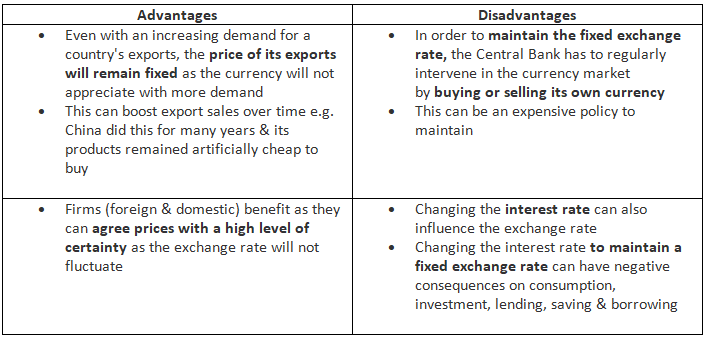
An Evaluation of A Fixed Exchange Rate Mechanism
The document Introduction to Exchange Rates | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
71 videos|82 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Exchange Rates - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the significance of foreign exchange rates in the global economy? |  |
| 2. How does the exchange rate between the US Dollar and Euro affect trade between the United States and European countries? |  |
Ans. The exchange rate between the US Dollar and Euro influences the cost of imports and exports between the two regions, affecting the competitiveness of goods and services traded between them.
| 3. What factors can lead to currency appreciation or depreciation in the foreign exchange market? |  |
Ans. Currency appreciation or depreciation can be influenced by factors such as interest rates, inflation, political stability, economic performance, and market speculation in the foreign exchange market.
| 4. How does a strong US Dollar impact US exporters and importers? |  |
Ans. A strong US Dollar can make US exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially reducing demand for American goods abroad. Conversely, it can make imports cheaper for US consumers, leading to increased imports.
| 5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of different exchange rate systems, such as fixed, floating, and managed exchange rates? |  |
Ans. Fixed exchange rates provide stability but may lead to currency misalignment, while floating exchange rates allow for market-determined values but can be volatile. Managed exchange rates combine elements of both systems to balance stability and flexibility in the currency market.
Related Searches



















