Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Computer for GCSE/IGCSE > Secondary Storage
Secondary Storage | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Understanding Secondary Storage
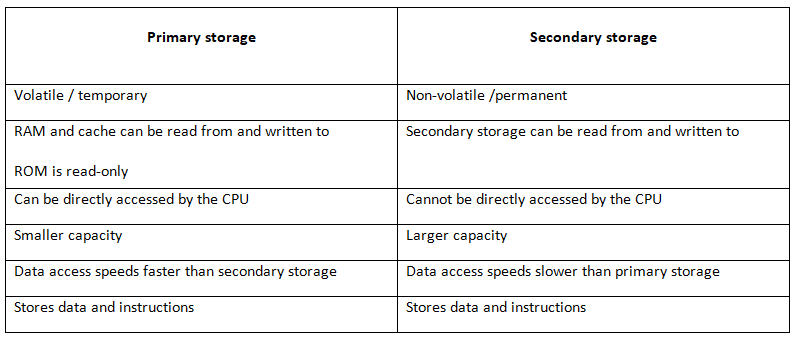
- Secondary storage is essential for storing data permanently, as opposed to volatile primary storage like RAM.
- Unlike primary storage, secondary storage is non-volatile, ensuring data retention even when the device loses power.
- Secondary storage, including HDDs, SSDs, and USB drives, allows both reading from and writing to, unlike ROM which is read-only.
- Examples of secondary storage media are varied, ranging from hard drives to optical discs, facilitating data transfer between systems.
- Data access speeds for secondary storage devices are typically slower compared to primary storage like RAM.
- Secondary storage devices are known for their large storage capacities, enabling the storage of significant amounts of data.
- Operating system software is permanently stored on secondary storage, transferring to RAM when in use.
- Secondary storage devices can be either internal or external to the computer system.
Comparison of primary and secondary storage
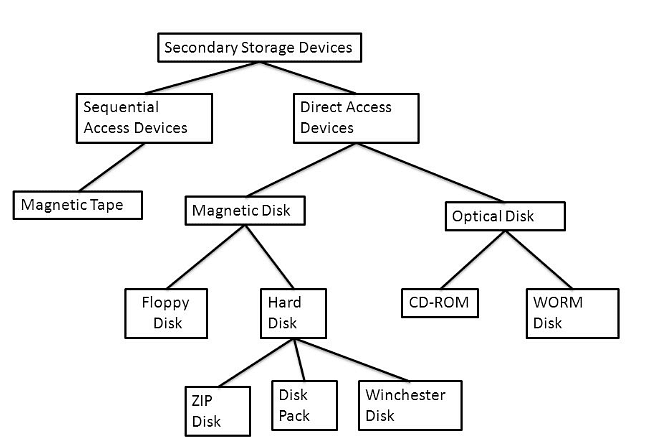
Types of Secondary Storage
- There are three main types of secondary storage: magnetic, solid state, and optical.
Magnetic
- Magnetic hard disk drives have historically been the primary form of internal secondary storage in personal computers. However, solid-state drives are gaining popularity due to their durability, low power consumption, and high read/write speeds.
- A magnetic hard disk comprises multiple metal discs coated with a magnetic material known as platters. Each platter's iron particles are magnetized to represent binary data (0s and 1s).
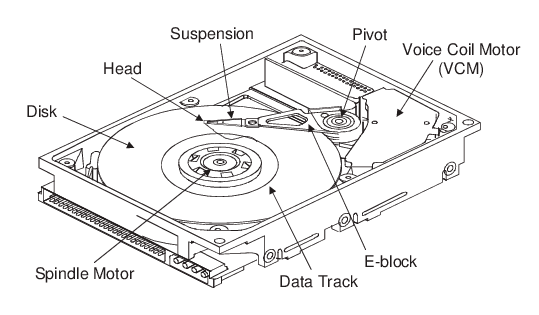 Structure of a magnetic hard disk
Structure of a magnetic hard disk
- Every disk is segmented by circular bands, forming numerous paths and pie-shaped sections. Their meeting points are called track sectors.
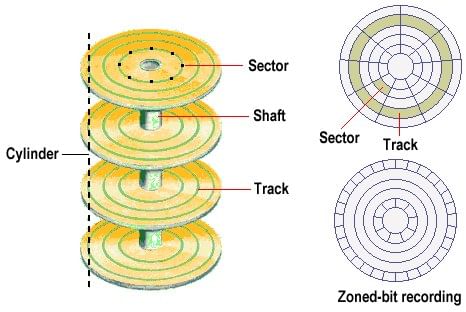 A diagram showing how each platter is divided by tracks and sectors
A diagram showing how each platter is divided by tracks and sectors
- The hard drive rotates the metallic disk(s) swiftly, usually at speeds ranging from 5400 to 7200 RPM, propelled by a motor.
- Guided by an actuator, a read/write arm shifts across the disk's surface to access the desired data location.
- Electromagnets are employed to read from or write data onto the disk.
Solid State
- Made of transistors arranged in a grid layout for storing data.
- Utilizes NAND and NOR gates in electrical circuits to control electron flow persistently.
- Represents binary values with 1 for current flow and 0 for no current.
- NAND gate: Requires both inputs to not be 1 to produce an output (1/electrical current).
The truth table for a NAND gate illustrates its functioning.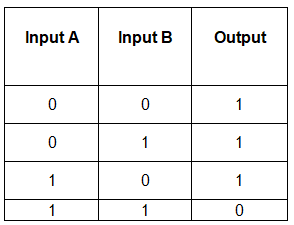
- A NAND gate produces an output of 0 only when both inputs are 1.
Truth Table for a NAND Gate:
Optical Devices
- Optical media types encompass CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays, with Blu-rays offering the highest storage capacity, while CDs have the lowest. CD-Rs are exclusively for reading, while CD-RWs allow both writing and reading. Similarly, DVD-RWs permit writing and reading.
- Optical devices function by directing a laser onto the disc's surface and analyzing the reflected light.
- A mechanism moves the laser across the disc's surface.
- In CD-Rs, data is permanently burned onto the disc by a laser, creating pits and lands.
- The laser also serves to read data from these pits and lands.
- When the laser encounters the transition between a pit and a land (or vice versa), the change in reflection is detected by a sensor, indicating a binary value alteration.
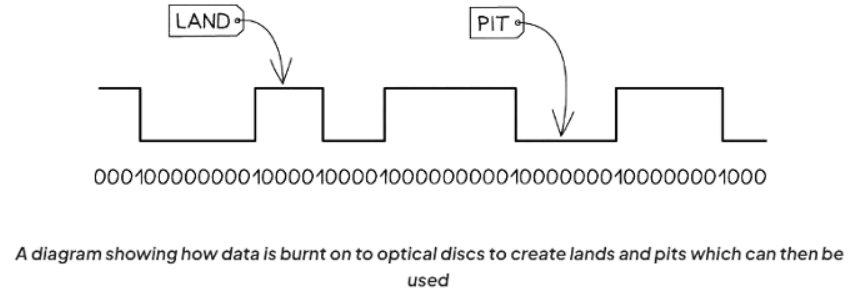
- In CD-RWs, the composition of the disk is altered to denote 0s and 1s, and this alteration is reversible, allowing for overwriting.
Question for Secondary StorageTry yourself: Which type of secondary storage uses transistors to store data?View Solution
The document Secondary Storage | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Computer for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
109 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Secondary Storage - Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the common types of secondary storage used in computers? |  |
Ans. Common types of secondary storage used in computers include hard disk drives, solid-state drives, optical drives (such as CDs and DVDs), USB flash drives, and memory cards.
| 2. How does secondary storage differ from primary storage in a computer system? |  |
Ans. Secondary storage is used for long-term storage of data and programs, while primary storage (such as RAM) is used for temporary storage during the computer's operation. Secondary storage has larger capacities but slower access times compared to primary storage.
| 3. What are the advantages of using secondary storage in a computer system? |  |
Ans. Secondary storage allows for the permanent storage of data and programs even when the computer is turned off. It also provides larger storage capacities than primary storage and allows for easy transfer of data between different computers.
| 4. How can secondary storage devices be connected to a computer system? |  |
Ans. Secondary storage devices can be connected to a computer system through various interfaces such as SATA, USB, Thunderbolt, or FireWire. These interfaces allow for data transfer between the storage device and the computer.
| 5. What factors should be considered when choosing a secondary storage device for a computer system? |  |
Ans. Factors to consider when choosing a secondary storage device include storage capacity, speed (read/write capabilities), durability, compatibility with the computer system, and cost. It is important to assess the specific needs and usage requirements before selecting a secondary storage device.
Related Searches















