Cyber Security Threats | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cyber Security Threats |

|
| Brute-Force Attack |

|
| Data Interception |

|
| Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack |

|
| Hacking |

|
| Malware |

|
| Phishing |

|
| Pharming |

|
| Social Engineering |

|
| Accidental Damage |

|
Cyber Security Threats
Cybersecurity threats present significant challenges for both individuals and organizations that depend on digital technology to safeguard and transmit sensitive data.
Brute-Force Attack
- A brute-force attack is a method of attempting to crack passwords or encryption keys through exhaustive trial and error until the correct combination is discovered.
- The primary objective of a brute-force attack is to illicitly access a system or network without proper authorization.
Data Interception
- Data interception refers to the act of eavesdropping on communication channels in order to illicitly intercept and acquire sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or personal data.
- The primary objective of data interception is to pilfer sensitive information for personal benefit or to utilize it in subsequent cyber attacks.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack
- A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack occurs when multiple computers, acting as bots, inundate a server with a high volume of requests simultaneously. This flood of traffic overwhelms the server, leading it to crash or become inaccessible to legitimate users.
- These attacks aim to disrupt the regular operation of a system or network by preventing users from accessing the services they require.
Hacking
- Hacking is the unauthorized access to a system or network with the intent to steal data, disrupt services, or cause harm.
- Motivations for hacking can range from personal gain to activism or cyber espionage.
Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, refers to programs designed to harm computer systems or networks and gain unauthorized access. There are various types of malware:
- Virus: A virus is a harmful code that attaches itself to legitimate files or programs, replicating and spreading across the system. It can lead to severe damage such as data loss or hardware issues.
- Worm: Unlike a virus, a worm acts independently as a program capable of self-replication over networks, consuming storage space or bandwidth.
- Trojan Horse: This type of malware disguises itself as genuine software but can cause data deletion or hardware damage upon installation.
- Spyware: Spyware covertly records keystrokes and sends them to unauthorized third parties.
- Adware: Adware displays unwanted advertisements without user consent, potentially containing spyware or leading to virus-infected links.
- Ransomware: Ransomware encrypts user files, demanding a ransom for decryption. It can result in data loss, financial harm, and disrupt business operations.
The motives behind malware attacks vary, ranging from data theft to extortion or service disruption.
Phishing
- Phishing occurs when a user receives an email that appears genuine.
- Phishing involves the user receiving an email that appears genuine.
- This email contains a link to a counterfeit website, prompting the user to input their information.
- This email includes a link to a counterfeit website, urging the user to provide their information.
- The primary objective of phishing is to pilfer sensitive data for personal gain or to fuel subsequent cyber assaults.
- The primary goal of phishing is to obtain sensitive data for personal benefit or to facilitate future cyber intrusions.
Pharming
- Pharming involves the stealthy download of malicious software without the user's awareness.
- This deceptive tactic redirects users to counterfeit websites, coaxing them into divulging personal information.
- The primary objective behind pharming is the illicit acquisition of sensitive data for personal profit or to facilitate subsequent cyber assaults.
Social Engineering
Social engineering is the practice of manipulating individuals to acquire confidential information or to carry out actions that benefit the attacker.
- Impersonation: This involves pretending to be someone else to gain trust or access to sensitive information. For instance, an attacker might pose as a co-worker, IT support personnel, or a law enforcement officer to trick individuals into revealing sensitive data or performing actions they wouldn't normally do.
- Baiting: Baiting is a tactic in social engineering where a victim is lured with a tempting item or promise to extract sensitive information or gain access to a system. As an example, an attacker could leave a USB drive labeled with something attractive like "salary information" in a public place. Once someone plugs it into a computer, the attacker can access data or install malicious software.
- Pretexting: Involves fabricating a scenario to obtain sensitive information. For instance, an attacker might impersonate a bank representative and request personal details under the guise of "verifying your account."
- Social engineering exploits human psychology and vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized entry into a system or network. It manipulates people into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
Accidental Damage
Data could also be accidentally damaged accidentally damaged in numerous ways: 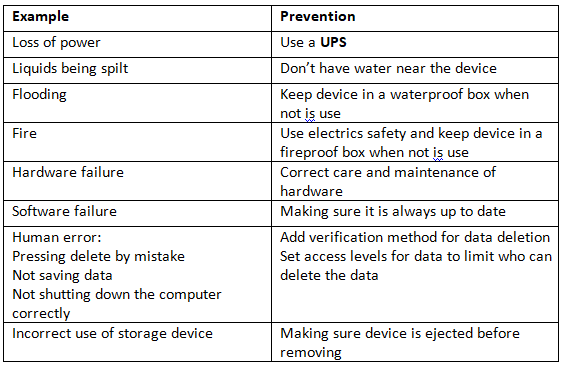
|
99 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Cyber Security Threats - Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is a Brute-Force Attack? |  |
| 2. How can data interception pose a threat to cyber security? |  |
| 3. What is a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack and how does it impact a system? |  |
| 4. How can individuals protect themselves from falling victim to phishing attacks? |  |
| 5. What is Social Engineering and how can it be used as a cyber security threat? |  |



















