Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Acceleration
Acceleration | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Acceleration
- Acceleration is the measure of how quickly an object's velocity changes. In simpler terms, it shows how much an object's speed changes every second.
- The following formula is employed to determine the average acceleration of an object:
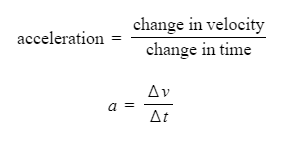
- Where:
- a = acceleration in metres per second squared (m/s²)
- Δv = change in velocity in metres per second (m/s)
- Δt = time taken in seconds (s)
- The change in velocity is determined by subtracting the initial velocity from the final velocity.
Change in Velocity Formula: It is calculated as the final velocity minus the initial velocity.
Δv = v - u - Where:
- v: Represents the final velocity in meters per second (m/s).
- u: Denotes the initial velocity in meters per second (m/s).
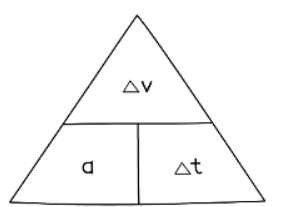
- The equation for acceleration can be rearranged using a formula triangle, as illustrated below:
Question for AccelerationTry yourself:What is the formula to calculate average acceleration?
View Solution
Understanding Acceleration
- Definition: Acceleration refers to the rate at which an object changes its velocity.
- Types of Acceleration:
- Positive Acceleration: Occurs when an object speeds up.
- Negative Acceleration (Deceleration): Happens when an object slows down.
- Interpreting Acceleration: Acceleration can be positive or negative, depending on whether the object is speeding up or slowing down.
- Examples:
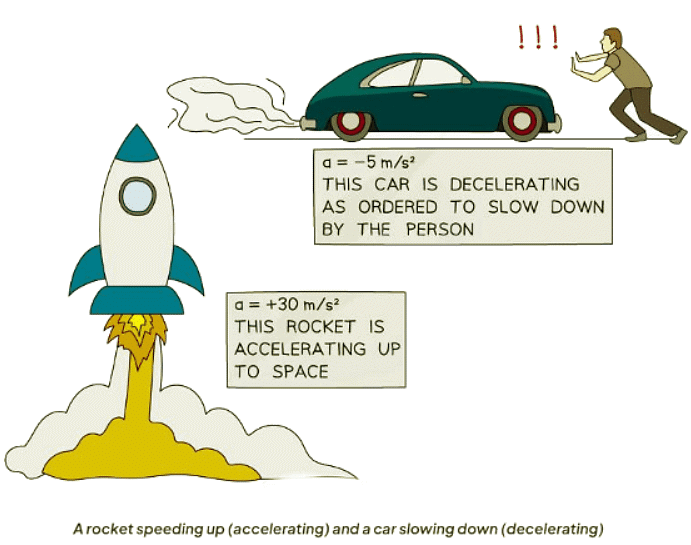
- Scenario 1: A rocket speeding up is an example of positive acceleration.
- Scenario 2: A car slowing down demonstrates negative acceleration or deceleration.
The document Acceleration | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Acceleration - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is acceleration in physics? |  |
Ans. Acceleration in physics is the rate of change of velocity of an object over time. It can be positive (speeding up), negative (slowing down), or zero (constant velocity).
| 2. How is acceleration calculated? |  |
Ans. Acceleration is calculated by dividing the change in velocity by the time taken for that change. The formula for acceleration is a = (v_f - v_i) / t, where a is acceleration, v_f is final velocity, v_i is initial velocity, and t is time.
| 3. What are the units of acceleration? |  |
Ans. The units of acceleration are typically meters per second squared (m/s^2) in the metric system and feet per second squared (ft/s^2) in the imperial system.
| 4. How does acceleration relate to force according to Newton's second law? |  |
Ans. According to Newton's second law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. The formula for this relationship is F = ma, where F is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration.
| 5. Can an object have acceleration without a change in its speed? |  |
Ans. Yes, an object can have acceleration without a change in its speed if it is changing direction. Acceleration is a vector quantity that includes changes in both speed and direction, so an object can accelerate even if its speed remains constant.
Related Searches