Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Density
Density | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Density
- Density is defined as: The mass per unit volume of a material
- Objects crafted from materials with low density usually exhibit low mass, whereas those fashioned from high-density materials tend to possess high mass.
- For instance, a bag filled with feathers is considerably lighter compared to a similar-sized bag filled with metal.
- Alternatively, a balloon, despite occupying a larger volume, is less dense than a small bar of lead.
- Density is determined by the relationship between mass and volume, expressed by the following equation:
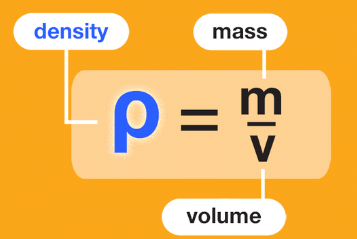
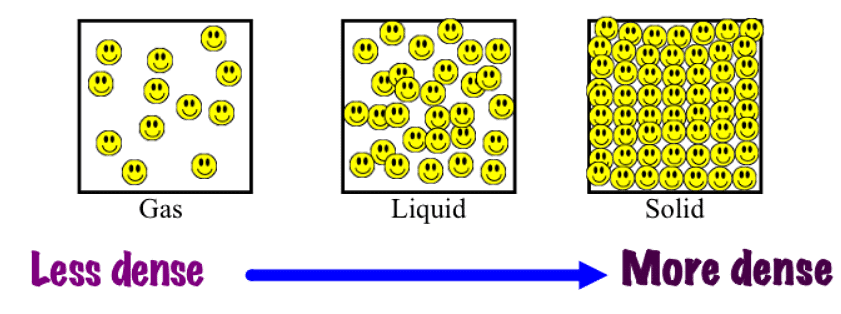
- Gases, for instance, have lower density compared to solids because their molecules are more dispersed, resulting in the same mass being spread over a larger volume.
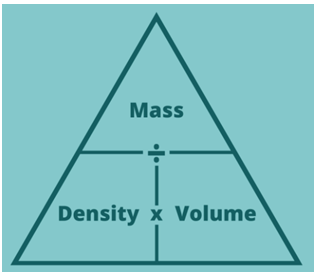
- This equation can be reorganized using a formula triangle:
- The units of density are determined by the units used for mass and volume. For example, if mass is in grams and volume in cubic centimeters, then density is expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3).
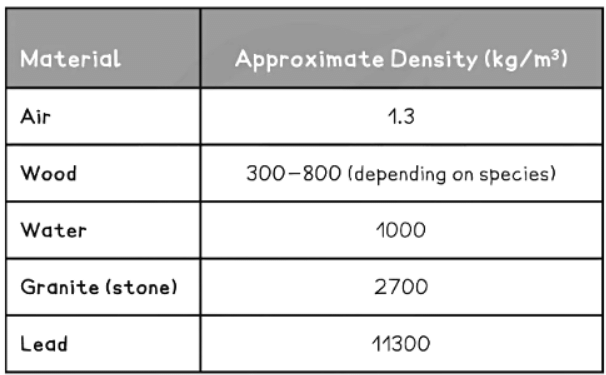
- Materials denser than water (1000 kg/m3) will sink when placed in water, as shown in the common materials density table:
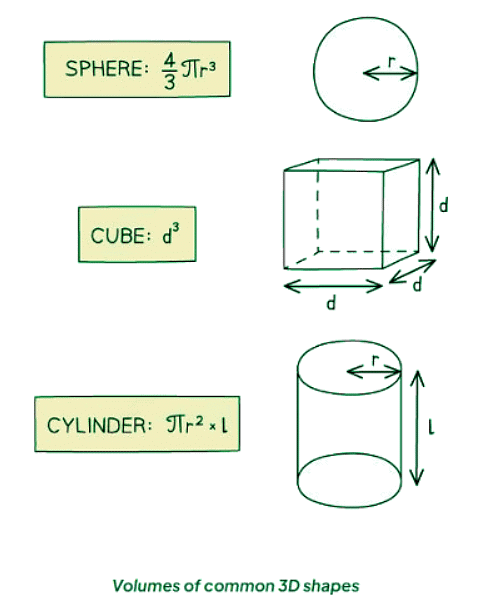
- The volume of an object may not always be given directly; it can be calculated using the appropriate equation based on the object's shape.
Question for DensityTry yourself: Which of the following materials is likely to have the highest density?View Solution
The document Density | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Density - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the formula for calculating density? |  |
Ans. Density is calculated by dividing the mass of an object by its volume. The formula for density is: Density = Mass / Volume.
| 2. How is density different from mass and volume? |  |
Ans. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, volume is the amount of space it occupies, and density is the mass of an object per unit volume. Density takes into account both mass and volume.
| 3. Why is density an important concept in physics? |  |
Ans. Density is important because it helps us understand the properties of different materials, their buoyancy, and their behavior under different conditions. It is also used in various calculations related to physics and engineering.
| 4. How can density be used to identify substances? |  |
Ans. Different substances have different densities, so by measuring the density of an unknown substance, we can compare it to known densities to identify the substance. This is commonly used in fields like chemistry and materials science.
| 5. What are some real-life applications of density in everyday situations? |  |
Ans. Density is used in various real-life applications, such as determining the purity of substances, designing ships and submarines to float or sink, and in the medical field for imaging techniques like CT scans and ultrasounds.
Related Searches















