Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Newton's First Law
Newton's First Law | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Newton's First Law of Motion
- Newton's first law of motion asserts that objects persist in their state of rest or uniform motion unless acted upon by a resultant force.
- If the resultant force on an object is zero:
- If the object was initially stationary, it will remain so.
- If the object was already in motion, it will continue moving at a constant velocity.
- When the resultant force is nonzero:
- The object's speed may alter.
- The object's direction may change.
Applying Newton's First Law
- Newton's first law elucidates why objects maintain a consistent velocity.
- When forces on an object are balanced, the resultant force is zero.
- Any alteration in velocity, encompassing speed and direction, only occurs when a resultant force acts upon the object.
- Below are some instances demonstrating uniform velocity:
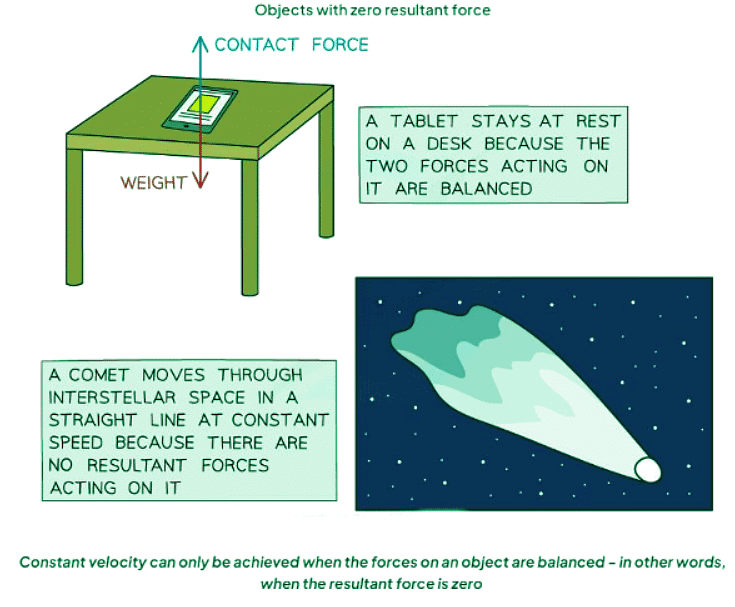
Question for Newton's First LawTry yourself: According to Newton's First Law of Motion, what happens to an object's velocity if the resultant force acting on it is zero?View Solution
The document Newton's First Law | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
126 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Newton's First Law - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is Newton's First Law of Motion? |  |
Ans. Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force.
| 2. How does Newton's First Law apply to everyday situations? |  |
Ans. Newton's First Law can be seen in everyday situations such as a book staying on a table until someone pushes it off, or a car continuing to move forward until the brakes are applied.
| 3. Can an object in motion come to a stop without any external force acting on it? |  |
Ans. According to Newton's First Law, an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line with constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. Therefore, an object in motion cannot come to a stop without an external force.
| 4. Is Newton's First Law of Motion applicable only on Earth? |  |
Ans. No, Newton's First Law of Motion is a fundamental principle of physics that applies universally to all objects in the universe, not just on Earth.
| 5. How does Newton's First Law relate to inertia? |  |
Ans. Newton's First Law is often referred to as the Law of Inertia because it describes how objects tend to resist changes in their state of motion. Inertia is the tendency of an object to maintain its current state of motion.
Related Searches




















