Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Hooke's Law
- Hooke’s law states:
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the applied force, as expressed by the equation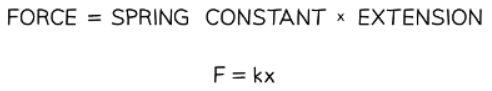
- In this equation:
F represents the applied force.
k denotes the spring constant.
x signifies the extension of the spring. - The spring constant k measures the force per unit extension, expressed in units of N/m.
- It serves as an indicator of the spring's stiffness.
- Hooke’s law is applicable to various materials, including metal wires.
- The law pertains primarily to the initial linear segment of a force-extension graph.
- Objects adhering to Hooke’s law will revert to their original length after being stretched.
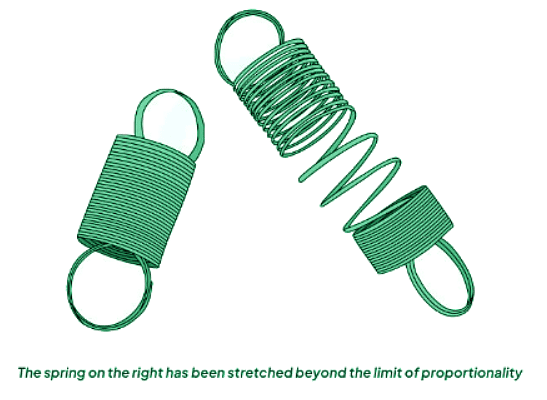
- Continued stretching of an object may exceed the limit of proportionality, also known as the elastic limit, beyond which the object no longer complies with Hooke’s law and fails to return to its original length.
Question for Hooke's LawTry yourself: What does Hooke's law state?View Solution
The document Hooke's Law | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Hooke's Law - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is Hooke's Law? |  |
Ans. Hooke's Law states that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by a certain distance is proportional to that distance.
| 2. How is Hooke's Law mathematically represented? |  |
Ans. Hooke's Law can be mathematically represented as F = -kx, where F is the force applied, k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position.
| 3. What is the significance of the spring constant in Hooke's Law? |  |
Ans. The spring constant, k, represents the stiffness of the spring. A higher spring constant indicates a stiffer spring, while a lower spring constant indicates a more flexible spring.
| 4. Can Hooke's Law be applied to materials other than springs? |  |
Ans. Yes, Hooke's Law can be applied to any elastic material, not just springs. It describes the linear relationship between force and deformation for elastic materials.
| 5. How is Hooke's Law used in real-life applications? |  |
Ans. Hooke's Law is used in various fields such as engineering and physics to design structures, determine material properties, and analyze the behavior of elastic materials under different conditions.
Related Searches















