Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Equilibrium
Equilibrium | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Equilibrium
- Equilibrium refers to a state where an object maintains its current state without any alteration.
- If the object is in motion, it will persist in moving, following a straight path.
- If the object is stationary, it will remain still.
- Furthermore, there will be no initiation or cessation of rotation.
- These conditions necessitate two factors:
- The forces acting upon the object must be in equilibrium, or balanced.
- There must be an absence of resultant force.
- Additionally, the total clockwise moments acting on the object must equal the total counterclockwise moments.
- This requirement ensures that there is no resultant moment present.
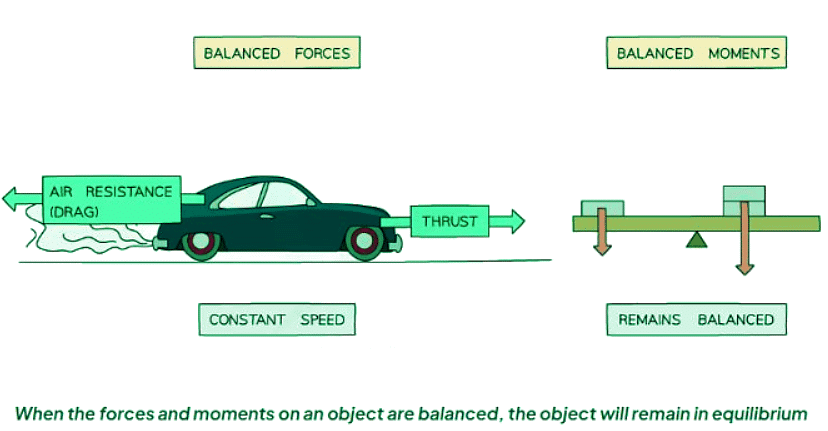
- Meeting the aforementioned two conditions ensures that the object achieves equilibrium.
Question for EquilibriumTry yourself: What are the two conditions that must be met for an object to achieve equilibrium?View Solution
Demonstrating Equilibrium
- When showcasing equilibrium in a simple experiment, we can replace the supports of an object like a beam with newton (force) meters.
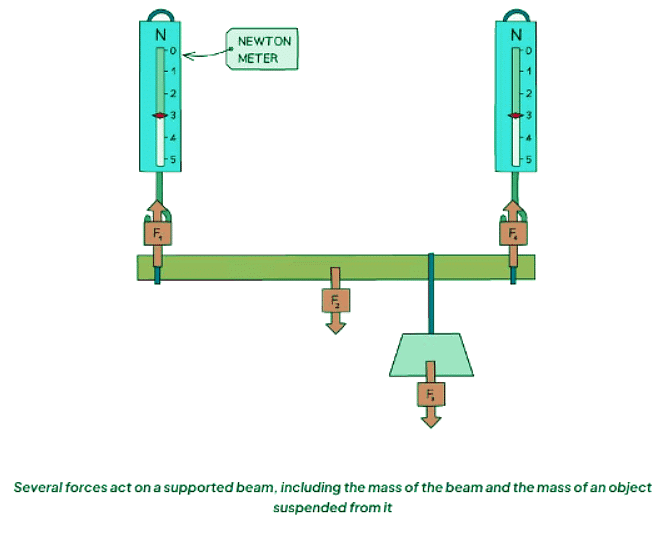
- The depicted beam is in a state of equilibrium.
- Determining the various forces acting on the beam can be accomplished by either recording readings from the Newton meters or by measuring the masses, subsequently calculating the weights of both the beam and the suspended mass.
- The distance of each force from the end of the ruler can then be gauged, enabling the calculation of the moment produced by each force around the end of the ruler.
- Consequently, it can be demonstrated that the total clockwise moments, resulting from forces F2 and F3, are equal to the total counterclockwise moments, arising from forces F1 and F4.
More detail on setting up this experiment
- Utilize a meter ruler for the beam
- Suspend the beam using two Newton meters, one on each side, hanging from a clamp stand
- F1 represents the reading from the Newton meter on the left side, and F4 represents the reading from the right side
- Create a loop of string, tie a secure knot, and slide the ruler through it
- F3 indicates the weight of a mass hook with 10 N weights suspended from this string
- F2 represents the weight of the beam
Question for EquilibriumTry yourself: Which of the following statements accurately describes the equilibrium of the beam in the experiment?View Solution
The document Equilibrium | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
126 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Equilibrium - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the key conditions for equilibrium in physics? |  |
Ans. The key conditions for equilibrium in physics are that the net force acting on an object must be zero and the net torque (or moment) acting on an object must also be zero.
| 2. Why is equilibrium significant in physics? |  |
Ans. Equilibrium is significant in physics as it represents a state where the object is at rest or moving with constant velocity. It is a crucial concept in understanding the stability of structures and the behavior of objects under different forces.
| 3. How can equilibrium be demonstrated in a physics experiment? |  |
Ans. Equilibrium can be demonstrated in a physics experiment by suspending an object from a string and adjusting the position and weights until the object remains stationary. This shows that the forces acting on the object are balanced.
| 4. Can you provide more detail on setting up an experiment to demonstrate equilibrium? |  |
Ans. To set up an experiment to demonstrate equilibrium, you can use a simple setup with a ruler, string, and weights. Hang the ruler horizontally from a support and attach weights to each end until it remains level. This demonstrates equilibrium where the torques are balanced.
| 5. Why is it important to understand equilibrium in physics? |  |
Ans. Understanding equilibrium in physics is important as it helps in analyzing and predicting the behavior of objects under different forces. It is essential in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and mechanics to ensure stability and safety in structures and systems.
Related Searches




















