Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Energy from the Sun
Energy from the Sun | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
The Sun
- The majority of Earth's energy resources originate from the Sun:
- Solar heating generates wind and generates waves in the atmosphere.
- Evaporation of water by the Sun results in rainfall, replenishing reservoirs.
- Sunlight facilitates plant growth, which forms the basis for various fuels, including biofuels and fossil fuels.
- Nevertheless, there are energy sources that do not stem from the Sun:
- Geothermal energy originates from the heat generated within the Earth's core.
- Nuclear energy is derived from elements found in a small fraction of the Earth's crust.
- Tidal energy primarily arises from the gravitational pull of the Moon.
Solar Cells
- Solar energy from the Sun reaching the Earth is transmitted primarily through radiation, predominantly in the form of visible light and infrared radiation.
- The quantity of solar energy transferred from the Sun to the Earth every hour is equivalent to the world's energy consumption over the course of a year.
- Consequently, scientists are diligently researching methods to harness this abundant energy source.
- Solar energy possesses a relatively low energy density, necessitating the use of large collecting devices.
- However, the process of collecting solar energy is costly due to the requisite equipment and is also inefficient.
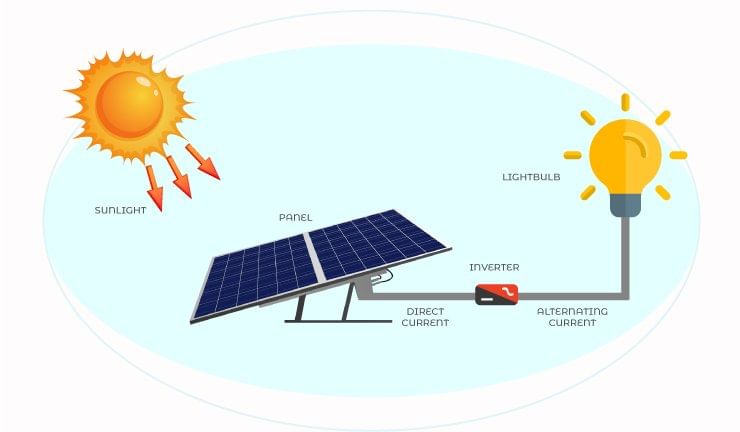
- Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, convert solar energy into electricity by generating an electric current through sunlight.
- Constructed from semiconducting materials, solar cells can be connected in series to supply electricity to homes, small businesses, communication devices, and satellites.
- Energy produced by solar cells can be stored in batteries for future utilization.
Advantages
- Solar energy is a renewable source of energy.
- Sunlight is a dependable energy resource in numerous locations on Earth, as it shines most of the time.
- Solar farms generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or causing pollution.
- Solar energy can be harnessed in remote areas lacking access to conventional electricity, such as powering solar street signs in rural regions.
Disadvantages
- Large-scale solar farms are necessary to generate significant amounts of electricity, which incurs high setup costs.
- The establishment of solar farms is costly.
- Many people find the appearance of large solar farms unappealing, referred to as visual pollution.
- In various regions, sunlight is not consistently available throughout the year, which may not justify the initial setup expenses.
Question for Energy from the SunTry yourself: What is the primary function of solar cells?View Solution
Solar Panels
- Solar panels harness energy from sunlight and convert it into heat energy, which is then used to warm water in the pipes. This process is commonly employed to heat water for domestic use.
- The utilization of solar panels for heating water can significantly decrease the expenses associated with producing hot water, as a portion of the water heating is powered by the solar panels.
- Solar furnaces are composed of large concave mirrors that concentrate the sun's rays onto a small area. These mirrors are capable of boiling water, leading to the generation of steam. The steam produced can subsequently be used to operate turbines, thereby generating electricity in a power station.
- In addition to heating water for domestic purposes, solar panels can also be used in solar furnaces to produce steam for electricity generation through the operation of turbines.
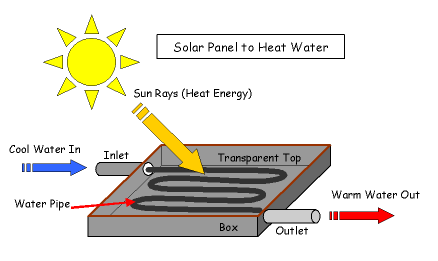
- Water is stored in a tank and circulated through small pipes within the solar panel.
- Infrared radiation from the sun heats the water as it flows through the pipes.
- The heated water returns to the tank at an increased temperature.
- Additional heating may be required to reach the desired temperature for various applications such as showers.
Advantages
- Renewable Resource: Solar energy is a sustainable source of power that can be relied upon in many regions where sunlight is abundant most of the time.
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar panels operate without emitting greenhouse gases or causing pollution once they are up and running.
- Cost-Efficient: By harnessing solar power, households can significantly reduce their energy expenses over time.
Disadvantages
- Scale Requirement: Solar furnaces need to be large to generate high temperatures effectively.
- Supplementary Energy Needs: Despite solar energy's benefits, additional energy is still necessary to heat water to higher temperatures in homes.
- Reliability Concerns: In areas where sunlight is not consistently available, setting up solar energy systems may not be cost-effective due to irregular sunshine.
Question for Energy from the SunTry yourself: What is the main advantage of using solar panels for heating water?View Solution
The document Energy from the Sun | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
Related Searches
















