Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Geothermal Energy
Geothermal Energy | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Geothermal Energy
- Radioactive substances located deep within the Earth emit energy as they undergo decay, leading to the heating of rocks, often to elevated temperatures.
- Water can be injected into underground shafts where it absorbs heat from the rocks, and then it's brought back up through another shaft as either steam or hot water.
- The steam produced can be utilized to power turbines, generating electricity, while the hot water can be employed for heating residences.
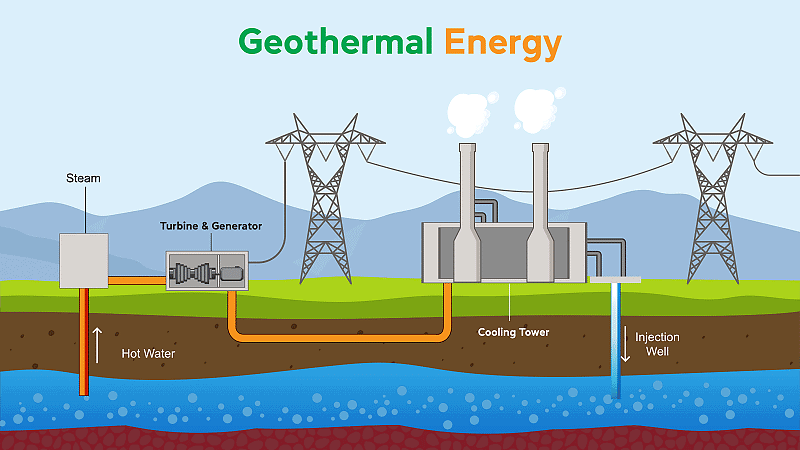
Advantages
- Renewable Resource: Geothermal energy is considered a renewable resource because it harnesses the heat from the Earth's core, which is a continuous source of energy.
- Reliable Source of Energy: Geothermal energy provides a consistent and reliable source of power, as it does not rely on external factors like weather conditions or fuel availability.
- Geothermal Power Station Size: Geothermal power stations are typically smaller in size compared to nuclear or fossil fuel power stations, making them suitable for various locations, including areas with limited space.
Disadvantages
- Few Suitable Locations for Large-Scale Production: Geothermal energy requires specific geological conditions for efficient electricity generation, limiting its widespread use to regions with suitable characteristics.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: In some cases, geothermal energy extraction can lead to the release of greenhouse gases trapped underground, contributing to environmental concerns.
- High Construction Costs: Building geothermal power plants involves significant initial investments due to the complex technology and infrastructure required for harnessing underground heat.
Question for Geothermal EnergyTry yourself: What is one advantage of geothermal energy?View Solution
The document Geothermal Energy | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Geothermal Energy - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is geothermal energy? |  |
Ans. Geothermal energy is heat energy that comes from the Earth's core. It can be harnessed and used for various purposes such as generating electricity or heating buildings.
| 2. How is geothermal energy produced? |  |
Ans. Geothermal energy is produced by tapping into natural underground reservoirs of hot water and steam. This hot water and steam can be used to turn turbines and generate electricity.
| 3. What are the advantages of using geothermal energy? |  |
Ans. Some advantages of using geothermal energy include its renewable nature, low environmental impact, and reliability as a constant source of energy.
| 4. Are there any disadvantages to using geothermal energy? |  |
Ans. Some disadvantages of geothermal energy include the high initial costs of setting up geothermal power plants, limited geographical availability, and potential environmental concerns such as the release of greenhouse gases.
| 5. How can geothermal energy be used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Geothermal energy can be used to heat homes and buildings, provide hot water, and generate electricity for residential and commercial use.
Related Searches




















