Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear Fusion | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Nuclear Fusion
- The Sun generates its energy through nuclear fusion occurring in its core.
- Nuclear fusion entails the merging (and bonding) of hydrogen nuclei to create helium nuclei, thereby releasing nuclear energy.
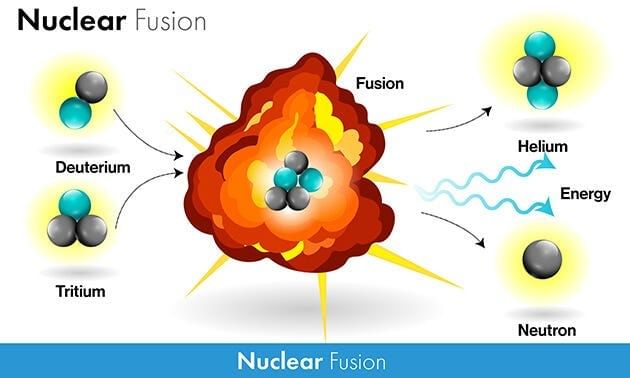
- Theoretically, the development of a fusion reactor capable of generating electricity is feasible.
- Such technology holds the potential to address the global energy shortage.
- Fusion necessitates exceedingly high temperatures, akin to those found at the core of a star.
- Scientists are presently investigating methods to maintain fusion reactions at reduced temperatures.
- International research initiatives, backed by major corporations, are advancing with encouraging outcomes.
- At present, fusion reactions demand nearly as much energy as they produce, but strides are being taken towards achieving net energy output.
- Success in this endeavor could unlock virtually boundless energy production, facilitating large-scale, carbon-free electricity generation.
Question for Nuclear FusionTry yourself: What is nuclear fusion?View Solution
The document Nuclear Fusion | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Nuclear Fusion - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is nuclear fusion? |  |
Ans. Nuclear fusion is a process in which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy in the process.
| 2. How is nuclear fusion different from nuclear fission? |  |
Ans. Nuclear fusion involves the combining of atomic nuclei to release energy, while nuclear fission involves the splitting of atomic nuclei to release energy.
| 3. What are the potential benefits of nuclear fusion? |  |
Ans. Some potential benefits of nuclear fusion include a virtually limitless supply of fuel, minimal radioactive waste, and the potential to provide a clean and sustainable source of energy.
| 4. What are some challenges facing nuclear fusion research? |  |
Ans. Some challenges facing nuclear fusion research include achieving and maintaining the high temperatures and pressures required for fusion to occur, as well as developing materials that can withstand the intense conditions inside a fusion reactor.
| 5. Are there any practical applications of nuclear fusion currently? |  |
Ans. While nuclear fusion has not yet been harnessed for practical energy production, research is ongoing to develop fusion reactors that could potentially provide a clean and sustainable source of energy in the future.
Related Searches















