Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Temperature & Pressure
Temperature & Pressure | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
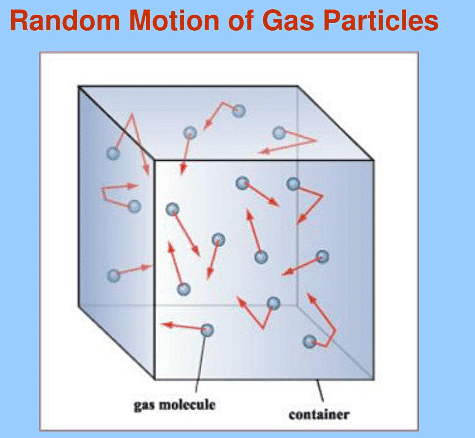
Motion of Particles in a Gas
- Molecules within a gas exhibit continual, erratic movement at elevated velocities.
- This random motion entails molecules traversing without a defined trajectory and experiencing abrupt alterations in their motion upon collision:
- With the walls of the container.
- With other molecules.
- The pressure exerted by a gas results from collisions with the surface (walls) of the container.
Pressure & Force of Particles in a Gas
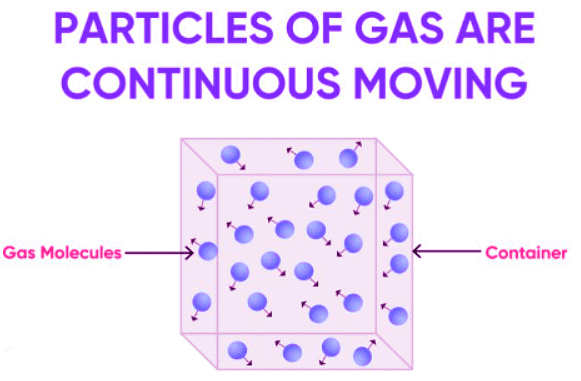
- Gases naturally fill their containers.
- Pressure is the force per unit area.
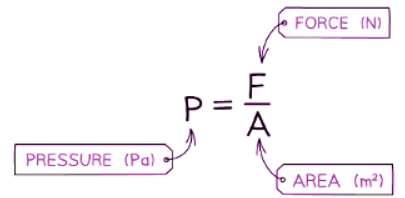
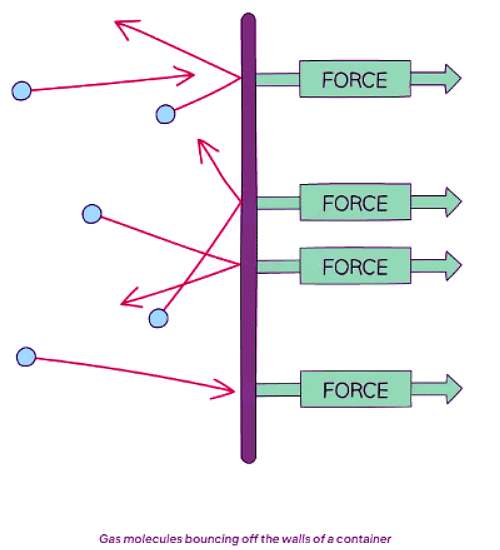
- As gas particles move randomly, they encounter the walls of their containers, resulting in collisions.
- These collisions generate a net force perpendicular to the container's wall (or any surface).
- Consequently, a gas under high pressure experiences more frequent collisions with the container walls and exerts a greater force.
- Thus, elevated pressure correlates with increased force exerted per unit area.
- You can feel this force by sealing your mouth and inflating your cheeks.
- The pressure on the cheeks results from the gas particles exerting force perpendicular to them.
Question for Temperature & PressureTry yourself: What causes the pressure exerted by a gas?View Solution
The document Temperature & Pressure | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Temperature & Pressure - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How do temperature and pressure affect the motion of particles in a gas? |  |
Ans. Temperature and pressure both affect the motion of particles in a gas. An increase in temperature causes the particles to move faster, while an increase in pressure causes the particles to be packed closer together and collide more frequently.
| 2. How does higher pressure impact the force of particles in a gas? |  |
Ans. Higher pressure in a gas means there are more particles in a given volume, leading to more frequent collisions between particles. This results in an increase in the force exerted by the particles.
| 3. What is the relationship between temperature and pressure in a gas? |  |
Ans. In a gas, the relationship between temperature and pressure is described by the ideal gas law. As temperature increases, the pressure of the gas also increases, assuming the volume and amount of gas remain constant.
| 4. How do changes in temperature and pressure affect the behavior of gases? |  |
Ans. Changes in temperature and pressure can alter the behavior of gases. For example, increasing the temperature can cause a gas to expand, while increasing the pressure can cause the gas to be compressed.
| 5. How do temperature and pressure impact the properties of gases on a molecular level? |  |
Ans. Temperature and pressure affect the kinetic energy and speed of gas particles. Higher temperatures result in faster-moving particles, while higher pressure leads to more frequent collisions between particles.
Related Searches




















