Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
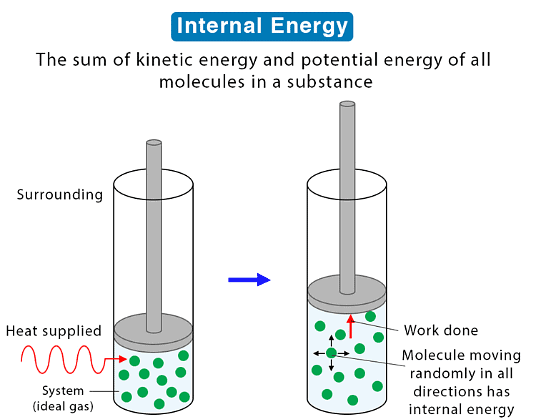
Internal Energy
- A rise in temperature increases the internal energy of an object. This rise can be attributed to the increase in the average speed of its particles, which in turn boosts their kinetic energy.
- Internal energy, essentially, signifies the total energy contained within a system, originating from the motion and positions of its constituent particles.
- Motion and Kinetic Energy: Motion of particles influences their kinetic energy. When particles move, they possess energy associated with their motion. For instance, a speeding car has high kinetic energy due to its motion.
- Positions and Potential Energy: The arrangement of particles relative to each other impacts their potential energy. Consider a stretched spring - it stores potential energy because of the positions of its particles. When released, this energy is converted into kinetic energy.
- Internal Energy Composition: Internal energy, comprising both kinetic and potential energies, characterizes the total energy within a system. It is the sum of the energies resulting from particle motion and positions relative to each other.
Average Kinetic Energy
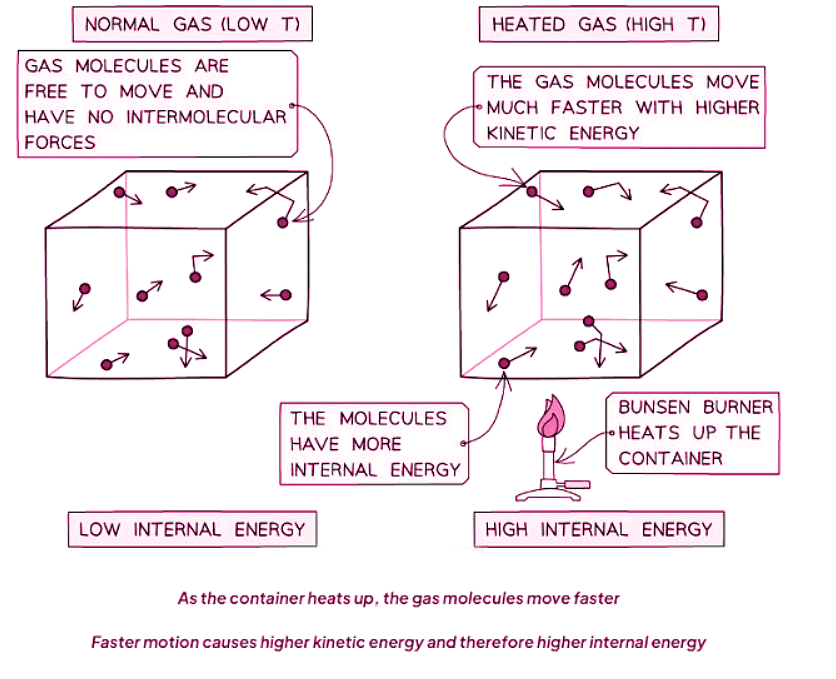
- When a system is heated, it alters the substance's internal energy by elevating the kinetic energy of its particles.
- Consequently, the material's temperature correlates with the average kinetic energy of its molecules.
- This augmentation in kinetic energy (and internal energy) can:
- Result in a rise in the system's temperature.
- Induce a change of state, such as solid to liquid or liquid to gas.
Question for Specific Heat CapacityTry yourself: What is the relationship between the rise in temperature and the internal energy of an object?View Solution
Specific Heat Capacity
- The extent to which the temperature of a system increases is influenced by:
- The mass of the substance undergoing heating.
- The type of material involved.
- The quantity of thermal energy transferred into the system.
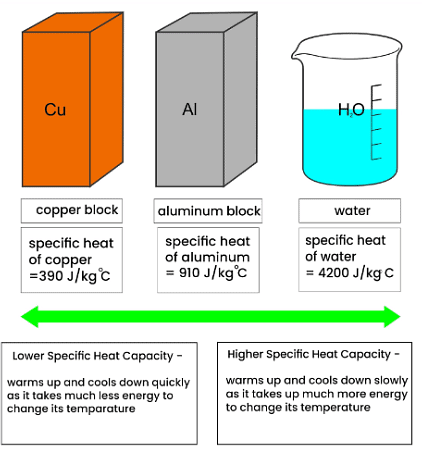
- The specific heat capacity, denoted as "c," of a substance is described as:
- The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 °C.
- Various substances possess distinct specific heat capacities.
- A substance with a low specific heat capacity heats up and cools down rapidly, meaning it requires less energy to alter its temperature.
- Conversely, a substance with a high specific heat capacity heats up and cools down slowly, necessitating more energy to change its temperature.
Calculating Specific Heat Capacity
- The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a given mass by a given amount can be calculated using the equation:
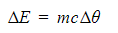
- Where:
- Δ E = change in thermal energy, in joules (J)
- m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
- c = specific heat capacity, in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg °C)
- Δ θ = change in temperature, in degrees Celsius (°C)
The document Specific Heat Capacity | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Specific Heat Capacity - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is specific heat capacity? |  |
Ans. Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of a substance by one degree Celsius.
| 2. How is specific heat capacity different from thermal conductivity? |  |
Ans. Specific heat capacity is a measure of how much heat energy a substance can store, while thermal conductivity is a measure of how well a substance can conduct heat.
| 3. Why is it important to know the specific heat capacity of a material? |  |
Ans. Knowing the specific heat capacity of a material is important for designing efficient heating and cooling systems, understanding how materials respond to changes in temperature, and predicting how much energy is needed to heat or cool a substance.
| 4. How does specific heat capacity affect the temperature change of a substance when heat is added or removed? |  |
Ans. The specific heat capacity of a substance determines how much its temperature will change when heat is added or removed. Substances with a high specific heat capacity require more heat energy to change their temperature compared to substances with a low specific heat capacity.
| 5. How can specific heat capacity be measured experimentally? |  |
Ans. Specific heat capacity can be measured experimentally by using a calorimeter to determine the amount of heat energy transferred to or from a substance and the resulting temperature change.
Related Searches




















