Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE > Product: Products & Brand Image
Product: Products & Brand Image | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to the Marketing Mix |

|
| New Product Development |

|
| The Importance of Brand Image |

|
| The Role of Packaging |

|
Introduction to the Marketing Mix
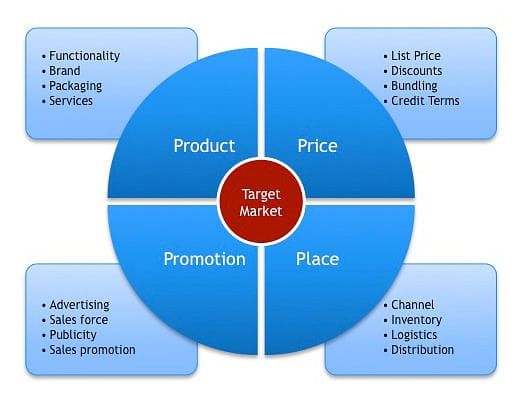
- The marketing mix offers a structured approach for companies to devise and execute effective marketing plans. It is often referred to as the 'Four P's', representing the essential elements of a marketing strategy: product, price, place, and promotion. These components collaborate to meet the demands and desires of a target market while fulfilling the company's goals. Through adept management of the marketing mix, organizations can distinguish themselves from rivals, amplify their marketing influence, and attain enduring prosperity.
- The marketing mix provides a framework for businesses to create and implement successful marketing strategies. It is commonly known as the 'Four P's', symbolizing the crucial components of a marketing strategy: product, price, place, and promotion. These elements synergize to cater to the needs and preferences of a specific market segment while accomplishing the company's objectives.
Four P's of the Marketing Mix
Product Design Mix
The product design mix encompasses the various elements that constitute a product's overall design, including functionality, aesthetics, and cost.
- Functionality, Aesthetics, and Cost
- The product design mix comprises the integration of function, aesthetics, and cost in a product's design. This blend is crucial for ensuring that the product is not only practical and visually appealing but also economically viable for both the manufacturer and the consumer.
- Balancing Elements
- Harmonizing the aspects of functionality, aesthetics, and cost is essential for creating a product that is both effective and visually pleasing while remaining cost-efficient. Many manufacturers strive to strike a balance among these three elements.
- For instance, Fentimans ginger beer offers a good balance by being reasonably priced, presented in attractive packaging, and maintaining high quality. On the other hand, Asda's generic ginger beer prioritizes low cost, making it available to consumers at a very affordable price.
- Businesses must be cautious in aligning customers' expectations regarding quality with these factors. Some target markets may prioritize price over quality, being unwilling to pay a premium even for superior goods.
Market Orientation in Product Development
- Companies predominantly adopt a market-oriented approach in creating new products.
- Significant financial resources are allocated to studying consumer buying behaviors, preferences, and trends.
- Products are crafted and packaged based on extensive research to align with consumer demands.
New Product Development
- One way to outperform competitors involves creating new products and enhancing existing ones.
- The new product development process encompasses several crucial stages.
Generating Ideas
- Brainstorming new product concepts is key, drawing from customer feedback, competitor insights, employee suggestions, and market/technical research.
Selecting the Best Idea
- Choosing the most promising idea involves evaluating factors like cost, anticipated demand, sales forecasts, and cost-benefit analyses.
Decision Making in Product Development
- Ideas are carefully considered, with some being discarded while others are earmarked for further exploration.
- Factors influencing these decisions include costs and projected demand for the product.
- Research involves evaluating forecasted sales, market size, and conducting cost-benefit analyses for each idea.
Prototype Development
- Creating a prototype is crucial in understanding the manufacturing process and identifying potential production challenges.
- Computer simulations are often employed to generate 3D prototypes for visualization.
Testing the Product
- Conducting a test launch involves selling the product on a small scale to gauge market response before a full-scale release.
- Adjustments might be necessary based on the performance during the test phase.
- Digital products like apps and software undergo beta testing to refine the product before official launch.
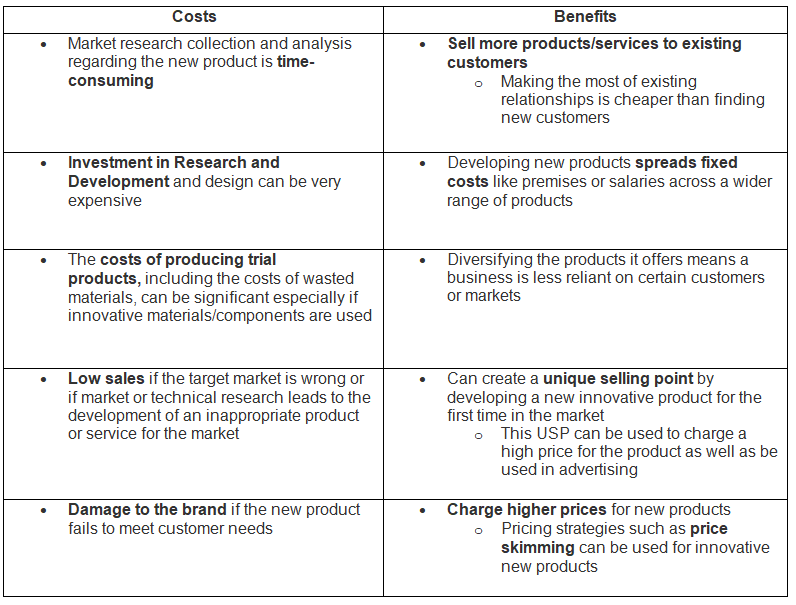
Costs and Benefits of New Product Development
Question for Product: Products & Brand ImageTry yourself: What are the essential components of the marketing mix?View Solution
The Importance of Brand Image
- Developing a strong brand is crucial for distinguishing a product or company from its competitors, involving the creation of a unique name, design, or symbol.
- A strong brand adds value, as customers are often willing to pay premium prices for brands they recognize and trust.
- Branding serves as a strategic tool to build awareness, foster strong customer relationships, cultivate loyalty, and establish a competitive edge.
Examples:
- Apple Inc. has built a strong brand identity with its distinctive logo and minimalist design, allowing it to charge premium prices for its products.
- Coca-Cola's brand image is associated with happiness and togetherness, leading consumers to choose it over generic soda brands.
Benefits of Strong Branding:
- Increased Perceived Value: Strong brands command higher prices due to the trust and recognition they evoke in consumers.
- Customer Loyalty: Brands that resonate with customers cultivate loyalty, leading to repeat purchases and advocacy.
- Competitive Differentiation: Effective branding sets businesses apart in crowded markets, helping them stand out from competitors.
3 main Types of Branding
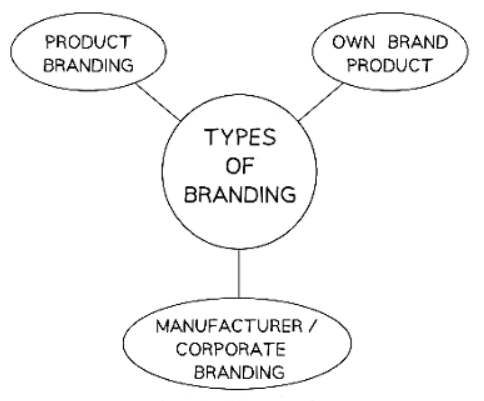
- Manufacturer/Corporate brandingPromote all the products or services offered by the company.
- This type of branding is used by companies like Nestlé, Nike, and Apple.
- Product brandingUnique name, design, or symbol.Specific product.
- Product branding refers to the use of a unique name, design, or symbol to promote a specific product. For example, KitKat, Coca-Cola, and McDonald's Big Mac are all products with distinct branding strategies.
- Branding Strategies
- Own brand or private label branding involves using a retailer's name to promote specific products or services. Supermarkets like ASDA, Tesco, and Sainsbury's use this strategy with products such as ASDA chocolate or Tesco's Finest range.
- Building Brands
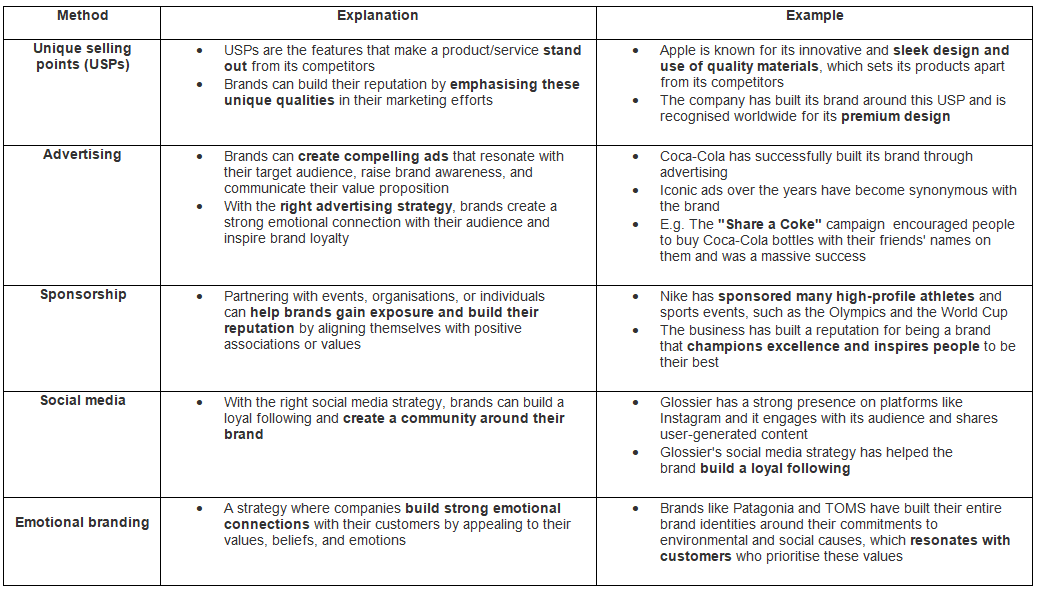
- Brands are constructed through various methods, including:
- Developing unique selling points
- Advertising
- Sponsorship
- Social media presence and activity
- Emotional branding
- Brands are constructed through various methods, including:
Examples of the ways Brands have been Built
Benefits of Branding to a Business
- Business differentiation is achieved through branding, which sets a business apart from its competitors, facilitating effective marketing and advertising efforts.
- Strong branding reduces the price elasticity of demand, as customers become less price-sensitive, especially those loyal to the brand who continue purchasing despite price increases.
- Well-established brands can command premium prices, as customers perceive them to offer higher quality, making them willing to pay extra.
- Robust branding establishes recognition and identity, fostering trust and credibility, and forging emotional connections with customers, thereby encouraging repeat purchases.
The Role of Packaging
- Packaging serves as the physical container or wrapping for a product. It plays a crucial role in not only protecting the product but also in enhancing its visual appeal.
- Additionally, packaging is a powerful tool for marketing and sales purposes, as it is designed to:
- Present products in a way that is both practical and visually attractive to consumers.
- Convey the quality of the product to potential buyers.
- Capture the attention of customers while they are shopping.
- Provide essential information to customers regarding the product.
- Establish and reinforce the brand image of the business.
- In the competitive market landscape, businesses are increasingly investing in innovative and eco-friendly packaging designs to differentiate themselves, foster consumer loyalty, and align with sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
- Creative and environmentally conscious packaging solutions are now more critical than ever for companies seeking to distinguish themselves and build enduring relationships with their customers.
Question for Product: Products & Brand ImageTry yourself: What is the purpose of packaging in marketing and sales?View Solution
The document Product: Products & Brand Image | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
70 videos|93 docs|26 tests
|
FAQs on Product: Products & Brand Image - Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the significance of brand image in product development? |  |
Ans. Brand image plays a crucial role in product development as it helps to create a perception of quality, trust, and credibility among consumers. A strong brand image can differentiate a product from its competitors and influence consumer purchasing decisions.
| 2. How does packaging impact brand image? |  |
Ans. Packaging is an essential component of brand image as it serves as the first point of contact between the product and the consumer. Well-designed packaging can enhance the perceived value of the product and create a positive impression on consumers.
| 3. How does the marketing mix influence product and brand image? |  |
Ans. The marketing mix, which includes the 4Ps (product, price, place, promotion), directly impacts the development of a product and its brand image. By carefully aligning these elements, companies can create a cohesive brand identity that resonates with their target audience.
| 4. How can companies maintain a strong brand image over time? |  |
Ans. Companies can maintain a strong brand image by consistently delivering high-quality products, providing excellent customer service, and staying true to their brand values. Regularly monitoring consumer feedback and adapting to market trends can also help companies stay relevant and maintain a positive brand image.
| 5. What role does consumer perception play in shaping brand image? |  |
Ans. Consumer perception plays a crucial role in shaping brand image, as it is the collective beliefs and attitudes that consumers have towards a brand. By understanding and addressing consumer perceptions, companies can effectively manage their brand image and build strong relationships with their target audience.
Related Searches














