Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Investigating IR Radiation
Investigating IR Radiation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Investigating Thermal Radiation
Aims of the Experiment
The experiment aims to explore how the quantity of infrared radiation absorbed or emitted by a surface is influenced by the characteristics of that surface.
Variables
- Independent variable = Colour
- Dependent variable = Temperature
- Control variables:
- Identical flasks (except for their colour)
- Same amounts of hot water
- Same starting temperature of the water
- Same time interval
Equipment List
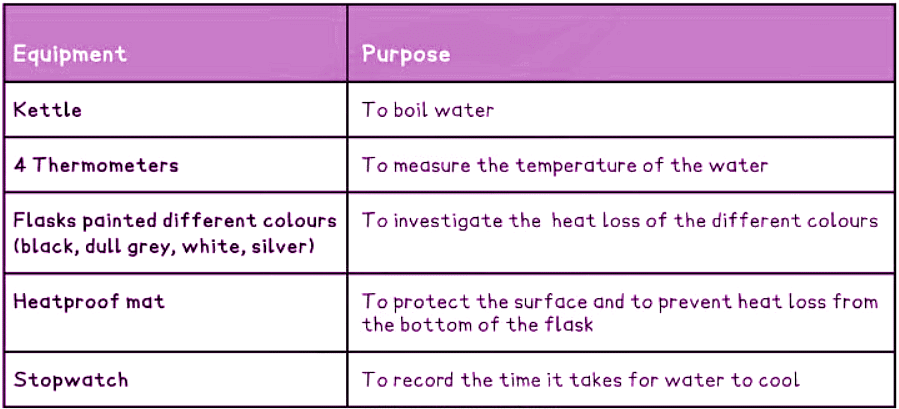
Resolution of measuring equipment:
- Thermometer: 1 degree Celsius
- Stopwatch: 0.01 seconds
Method
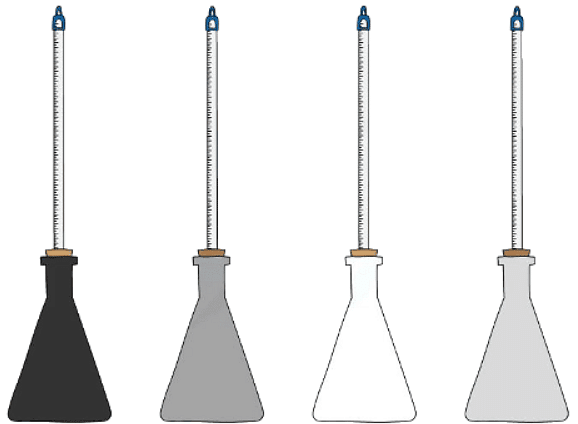
- Prepare four identical flasks painted in black, grey, white, and silver colors.
- Fill the flasks with hot water, ensuring they all start at the same initial temperature.
- Record the starting temperature and measure temperatures at regular intervals (e.g., every 30 seconds for 10 minutes).
Analysis of Results
- All warm objects emit thermal radiation in the form of infrared waves.
- Infrared Radiation: The intensity and wavelength of emitted radiation depend on factors such as the temperature of the body (hotter objects emit more thermal radiation), the surface area of the body (larger surface area allows more radiation emission), and the color of the surface.
- Most heat loss from the beakers occurs through conduction and convection. Color does not significantly affect heat loss in this context. Any differences in heat loss between the beakers are attributed to infrared (thermal) radiation.
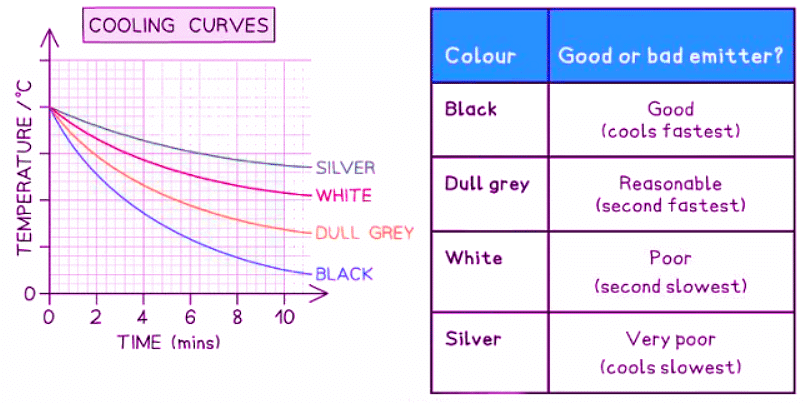
- To compare the rate of heat loss from each flask, a temperature-time graph can be plotted with temperature on the y-axis and time on the x-axis, drawing curves of best fit.
- Refer to the provided graph for expected results.
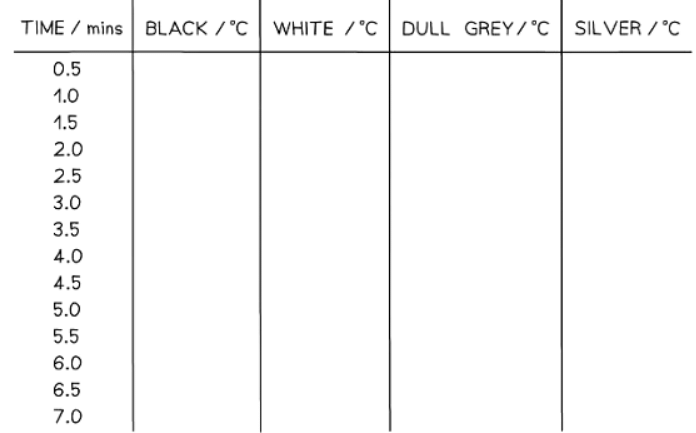
- An example table of results might look like this:
Evaluating the Experiment
Systematic Errors:
- Ensure consistent initial water temperature across all materials, as rapid cooling may occur otherwise.
- Conduct the experiment with a partner to synchronize stopwatch timing and thermometer immersion.
- Employ a data logger paired with a digital thermometer for improved precision in measurements.
Random Errors:
- Ensure the thermometer hole is appropriately sized to prevent heat loss.
- Take multiple readings for each colored flask to reduce variability.
- Read thermometer values at eye level to minimize parallax errors.
Safety Considerations
- Keep water away from all electrical equipment.
- Ensure not to touch hot water directly; in case of burns, run the affected area under cold water for at least 5 minutes.
- Do not overfill the kettle.
- Position all equipment in the middle of the desk to prevent beakers from being knocked over.
- Conduct experiments while standing to promptly address any spills.
Question for Investigating IR RadiationTry yourself: How does the color of a surface affect the rate of heat loss through thermal radiation?View Solution
The document Investigating IR Radiation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Investigating IR Radiation - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is thermal radiation? |  |
Ans. Thermal radiation is the process by which an object emits electromagnetic waves due to its temperature. These waves are in the infrared (IR) region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
| 2. How does thermal radiation differ from other forms of heat transfer? |  |
Ans. Thermal radiation does not require a medium for heat transfer, unlike conduction and convection. It can travel through a vacuum and does not rely on direct contact between objects for energy transfer.
| 3. How is thermal radiation related to temperature? |  |
Ans. The amount of thermal radiation emitted by an object is directly proportional to its temperature. The hotter an object is, the more infrared radiation it will emit.
| 4. How can thermal radiation be utilized in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Thermal radiation is used in various applications, such as infrared heaters, thermal imaging cameras, and cooking appliances like toasters and grills.
| 5. What are some safety considerations when working with thermal radiation? |  |
Ans. It is important to be cautious when working with high temperatures and thermal radiation to avoid burns or other injuries. Protective gear such as gloves and goggles should be worn, and proper ventilation should be ensured when using devices that emit thermal radiation.
Related Searches















