Best Study Material for Year 11 Exam
Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE > The Trial Balance
The Trial Balance | Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Uses & Limitations of a Trial Balance
What is a trial balance?
- A trial balance presents a list of all accounts and their balances on a specific date. Each balance is categorized into the debit or credit column.
- The totals of the debit and credit columns are computed, aiming for equality.
- It serves as a statement outside the double entry system, ensuring accuracy in financial records.
- Notably, the inventory account balance typically reflects the opening balance, as current inventory details are captured in the purchases account.
- Further adjustments are made when balances are shifted to the income statement.
Example of a Trial Balance
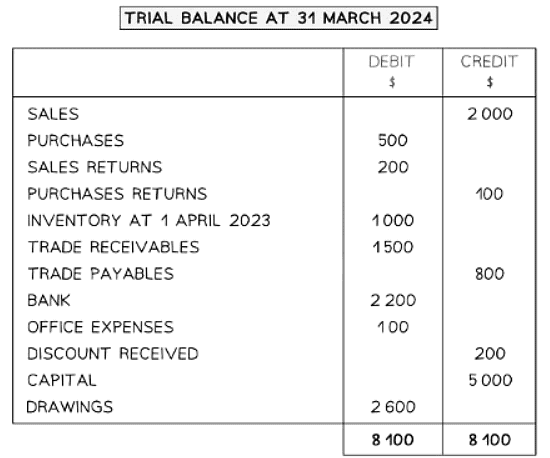
Uses of a Trial Balance
- A trial balance is a crucial tool used to detect arithmetic errors within ledger accounts.
- If a ledger account's balance is incorrectly calculated, it will result in unequal totals in the trial balance.
- Preparing a trial balance plays a key role in facilitating the creation of financial statements, consolidating all balances into a single location.
Limits of a Trial Balance
- While a trial balance is helpful, it does not catch all errors that may exist within the accounts.
- Even with errors present, the totals in the trial balance could still match, leading to potential oversight.
- Additional measures like bank reconciliation statements and control accounts may be necessary to pinpoint errors that escape the trial balance.
 |
Download the notes
The Trial Balance
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Preparing a Trial Balance
How do I prepare a trial balance?
In the process of preparing a trial balance, it is important to follow a series of steps to ensure accuracy and balance in financial records.
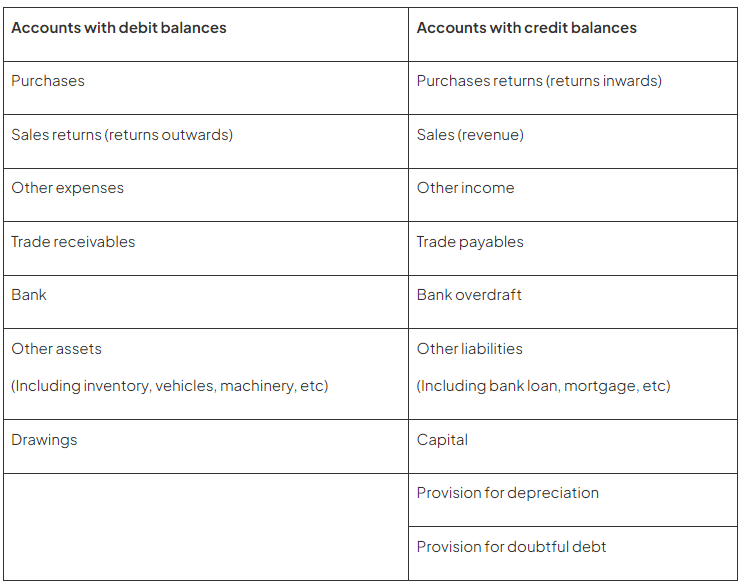
- Step 1: Determine whether each account should maintain a debit or credit balance based on the provided list of accounts and balances.
- Step 2: Verify that the sum of the debits matches the sum of the credits.
- Step 3: Record each account in the trial balance and allocate its balance to the appropriate column.
- Step 4: Calculate the total for each column in the trial balance.
Question for The Trial Balance
Try yourself:
What is the purpose of a trial balance in accounting?View Solution
How do I amend a trial balance?
You might encounter a trial balance containing inaccuracies or balances placed in incorrect columns.
- Step 1: Rectify any inaccuracies in the trial balance to determine the accurate balances for each account.
- Step 2: Verify that each account has been accurately classified as either a debit or a credit.
- Step 3: Compile a corrected trial balance where the sum of the debit balances equals the sum of the credit balances.
The document The Trial Balance | Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
22 videos|29 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on The Trial Balance - Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the purpose of a trial balance? |  |
| 2. What are some limitations of a trial balance? |  |
Ans. Some limitations of a trial balance include the fact that it may not detect all types of errors, such as errors of omission, errors of principle, or errors of commission. It also does not provide information about the accuracy of individual transactions.
| 3. How do you prepare a trial balance? |  |
Ans. To prepare a trial balance, list all the account names and their balances (debit or credit) from the general ledger. Calculate the total debits and credits, ensuring they match. If they do not match, investigate and correct any errors.
| 4. Can a trial balance be amended? |  |
Ans. Yes, a trial balance can be amended if errors are discovered. This can be done by identifying the error, making the necessary adjustments in the accounts, and then recalculating the trial balance to ensure it is balanced.
| 5. Why is it important to review and analyze the trial balance? |  |
Ans. Reviewing and analyzing the trial balance is important to ensure the accuracy of the financial statements. It helps to identify any discrepancies or errors that may have occurred in the recording of transactions, allowing for corrections to be made before finalizing the financial reports.
Related Searches


























