Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Wave Behaviour
Wave Behaviour | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Reflection, Refraction & Diffraction
- All waves, regardless of their type—transverse or longitudinal—can undergo reflection, refraction, and diffraction.
Reflection
- Reflection occurs when:
- A wave hits a boundary between two media and does not pass through, but instead stays in the original medium.
- The law of reflection states:
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- When waves hit an object, such as a barrier, they can be reflected:
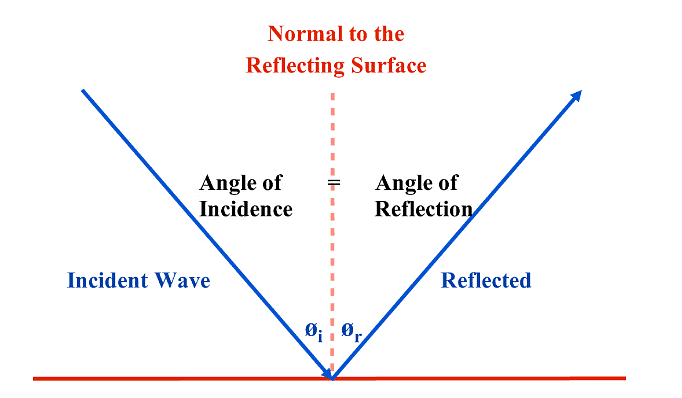 When waves reflect off a barrier, the angle of reflection, r, is equal to the angle of incidence, i
When waves reflect off a barrier, the angle of reflection, r, is equal to the angle of incidence, i
Refraction
- When waves transition into another medium, their velocity may vary. This phenomenon, known as refraction, happens when:
- A wave crosses the boundary between two distinct transparent media, leading to a modification in speed.
- During refraction, besides altering speed, the wave also experiences:
- A modification in wavelength (while frequency remains constant).
- A deviation in direction.
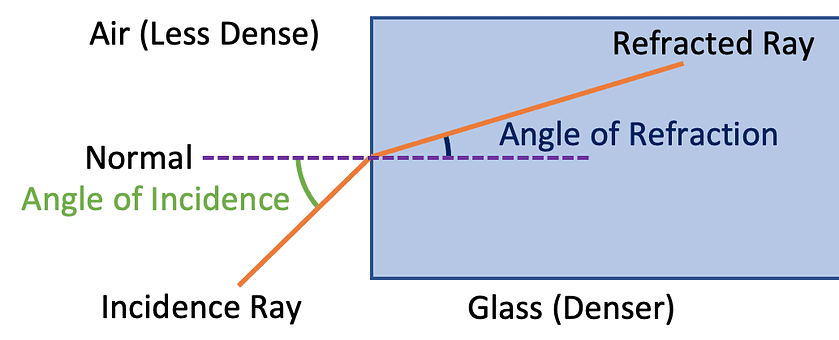
- When waves decelerate, they will bunch up, resulting in a reduction in wavelength. Additionally, they will exhibit a slight inclination towards the normal direction.
- Conversely, when waves accelerate, they will disperse, leading to an increase in wavelength. Furthermore, they will show a slight deviation away from the normal direction.
Diffraction
- When waves traverse a narrow aperture, they disperse. This phenomenon is referred to as diffraction.
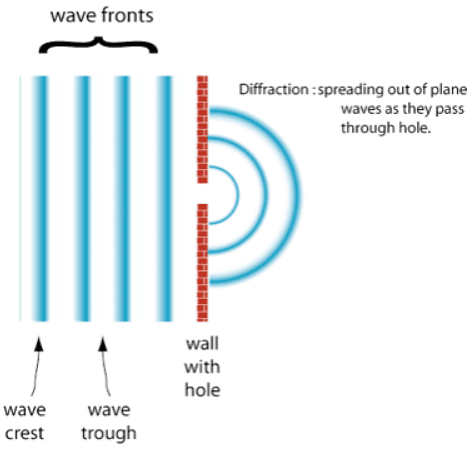
Factors Influencing Diffraction
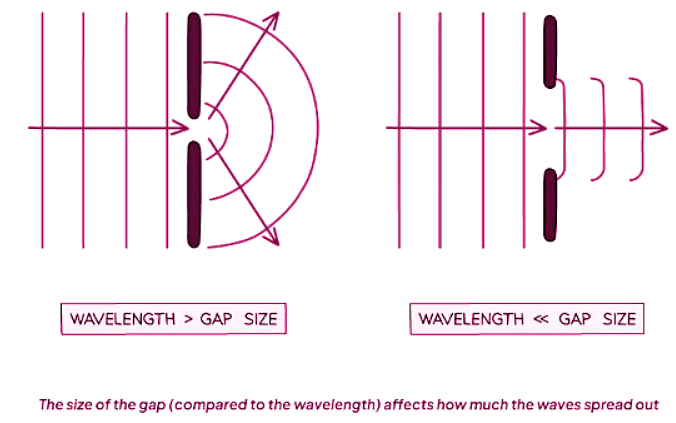
- Diffraction generally occurs when the gap is smaller than the wavelength of the wave.
- As the gap widens, the effect becomes less noticeable.
- If the gap is much larger than the wavelength, the waves no longer spread out at all.
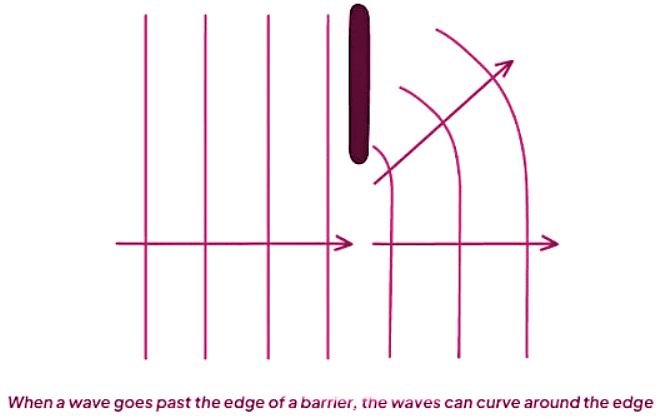
- Diffraction can also happen when waves encounter an edge.
The document Wave Behaviour | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Wave Behaviour - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between reflection and refraction of waves? |  |
Ans. Reflection of waves occurs when a wave bounces off a surface, changing direction without changing medium, while refraction of waves occurs when a wave changes direction as it passes from one medium to another at an angle.
| 2. How does wave behavior change when it undergoes diffraction? |  |
Ans. Diffraction of waves causes them to bend around obstacles or spread out when passing through a narrow opening, demonstrating wave-like behavior such as interference patterns.
| 3. What are the characteristics of refraction and how do they influence wave behavior? |  |
Ans. Refraction can cause waves to change speed and direction depending on the medium's properties, leading to phenomena like bending towards the normal or away from it.
| 4. What factors influence the diffraction of waves? |  |
Ans. The wavelength of the wave, the size of the obstacle or opening, and the nature of the medium through which the wave is passing all play a role in influencing the extent of diffraction.
| 5. How do reflection and refraction of waves play a role in everyday applications such as mirages or lenses? |  |
Ans. Reflection and refraction are essential in phenomena like mirages, where light waves are refracted due to temperature gradients, and in lenses where refraction is used to focus light for vision correction or photography.
Related Searches















