Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Digital & Analogue Signals
Digital & Analogue Signals | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Digital & Analogue Signals
- Types of Signals:
- Analogue Signals
- Digital Signals
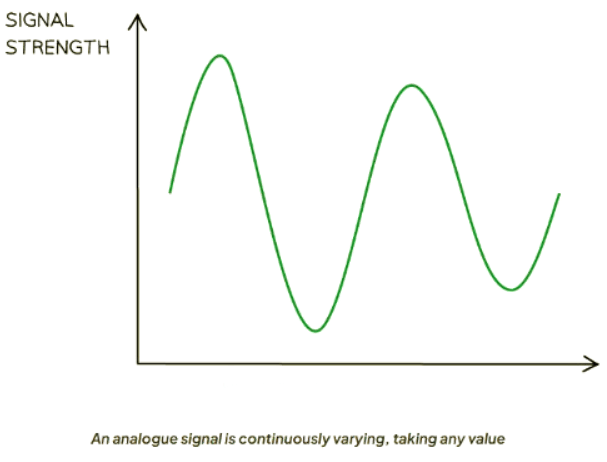
- Analogue Signals: Analogue signals vary continuously, representing a range of values.
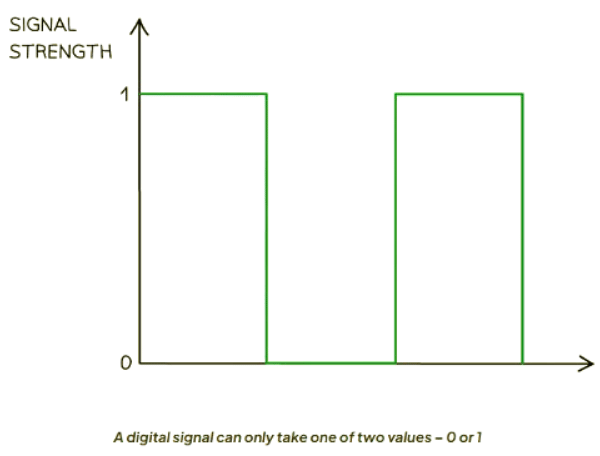
- Digital Signals: Digital signals can only be in one of two discrete states, typically represented as 1s and 0s, or high and low, on and off.
Transmission of Sound
- Sound waves that can be transmitted as a digital or analogue signal
- Sound waves can be sent as either digital or analogue signals
- Signals for speech or music consist of various frequencies. To ensure clear information transmission, the signal must be sent with minimal interference.
- Speech or music signals comprise different frequencies. To ensure clarity, the signal should be transmitted with minimal disruption.
- The signal undergoes conversion both before transmission and after reception:
- Before Transmission: Conversion from analogue to digital
- After Reception: Conversion from digital to analogue
Question for Digital & Analogue SignalsTry yourself: Which type of signal can only be in one of two discrete states?View Solution
Benefits of Digital Signalling
- An analogue signal involves varying frequency or amplitude. For instance, technologies like telephone transmission and certain broadcasting methods rely on analogue signals.
- Digital signals are represented and processed using two states: 1 or 0, corresponding to high or low states, respectively.
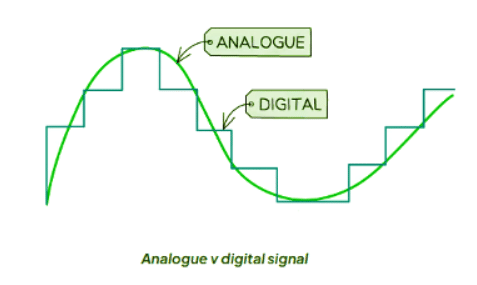
- The advantages of transmitting data in digital form over analogue include:
- Digital signals can be regenerated, resulting in minimal noise interference.
- The range of digital signals is typically larger than that of analogue, enabling them to cover greater distances.
- Digital transmission allows for a higher rate of data transfer compared to analogue methods.
- Additional data can be incorporated into digital signals to facilitate error checking.
The document Digital & Analogue Signals | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Digital & Analogue Signals - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between digital and analogue signals? |  |
Ans. Digital signals are discrete, representing data as a sequence of numbers, while analogue signals are continuous, representing data as a continuous waveform.
| 2. How is sound transmitted using digital signals? |  |
Ans. Sound is converted into digital data through a process called sampling, where the sound wave is measured at regular intervals to create a digital representation.
| 3. What is the signal conversion process in digital signalling? |  |
Ans. In digital signalling, the analogue signal is converted into digital form through sampling, quantization, and encoding processes.
| 4. What are the benefits of using digital signalling over analogue signalling? |  |
Ans. Digital signalling offers higher quality, less susceptibility to noise, easier storage and processing, and the ability to transmit over long distances without loss of quality.
| 5. Why are digital signals preferred in modern communication systems? |  |
Ans. Digital signals are preferred in modern communication systems due to their versatility, reliability, ease of processing, and compatibility with various devices and technologies.
Related Searches
















