Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Resistance of a Wire
Resistance of a Wire | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Resistance of a Wire
- When electrons move through a wire, they interact with metal ions, causing collisions.
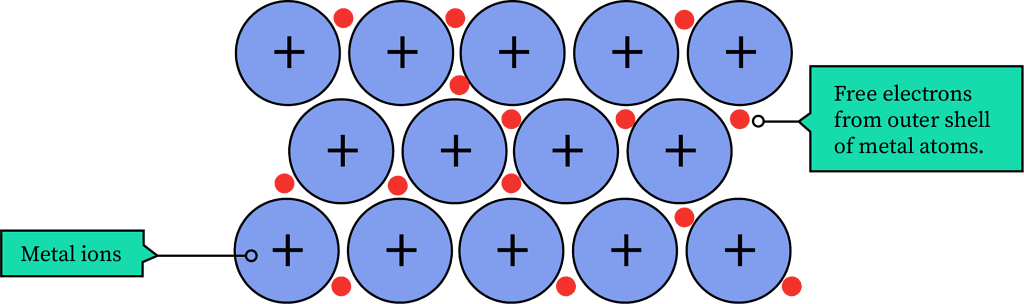
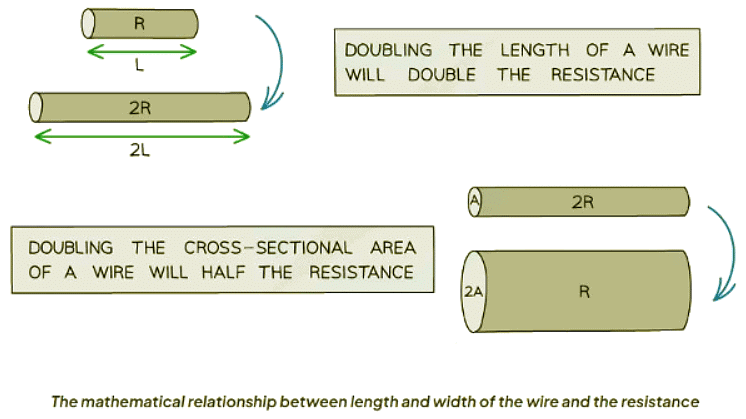
- The longer the wire, the higher its resistance.
- A thicker wire (with a larger diameter) offers more room for electrons to flow:
- A thicker wire has lower resistance due to increased space for electron movement.
- Resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area (width or thickness) of the wire.
- Thicker wires accommodate greater electron movement space, thereby decreasing resistance.
Proportionality Relationships for Electrical Conductors
Understanding these relationships is crucial in various applications, such as designing circuits and selecting appropriate wires for electrical installations.
- Resistance is directly proportional to length
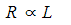
- Resistance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area (width, or thickness)
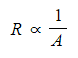
Question for Resistance of a WireTry yourself: Which of the following is true about the resistance of a wire?View Solution
The document Resistance of a Wire | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Resistance of a Wire - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What factors affect the resistance of a wire? |  |
Ans. The resistance of a wire is affected by its length, cross-sectional area, material, and temperature. As the length of the wire increases, the resistance also increases. A thinner wire will have a higher resistance compared to a thicker wire of the same material. Different materials have different resistivities, with some materials being better conductors than others. Additionally, the resistance of a wire typically increases with temperature.
| 2. How does the resistance of a wire change with temperature? |  |
Ans. In general, the resistance of a wire increases with temperature. This is due to the fact that as temperature increases, the atoms in the wire vibrate more vigorously, leading to more frequent collisions with the moving electrons, which increases resistance. However, this relationship can vary depending on the material of the wire.
| 3. What is the formula to calculate the resistance of a wire? |  |
Ans. The formula to calculate the resistance of a wire is R = ρ * (L/A), where R is the resistance, ρ (rho) is the resistivity of the material, L is the length of the wire, and A is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
| 4. How does the cross-sectional area of a wire affect its resistance? |  |
Ans. The cross-sectional area of a wire is inversely proportional to its resistance - meaning that as the cross-sectional area increases, the resistance decreases. This is because a larger cross-sectional area allows for more pathways for electrons to flow through, resulting in lower resistance.
| 5. How can the resistance of a wire be decreased? |  |
Ans. The resistance of a wire can be decreased by using a shorter wire, using a wire with a larger cross-sectional area, using a material with lower resistivity, or keeping the wire at a lower temperature. Additionally, connecting multiple wires in parallel can also decrease the overall resistance.
Related Searches




















