Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Electrical Power
Electrical Power | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Electrical Power Equation
- In mechanics, power (P) represents how quickly work is performed.
- Potential difference denotes the amount of work conducted per unit charge.
- Current signifies how quickly charge moves through a circuit.
- Therefore, electrical power is described as the rate at which work done alters.
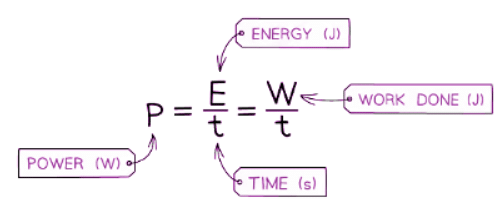
- The work done corresponds to the energy transferred, hence power denotes the energy transferred per second within an electrical component.
- The power either dissipated or produced by an electrical device can also be expressed as:
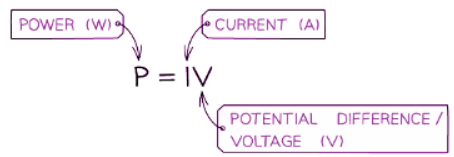
- Utilizing Ohm's Law V = IR and rearranging for either V or I, then substituting into the power equation, allows power to be expressed in terms of resistance R.
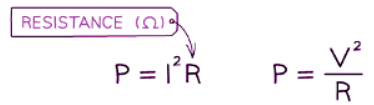
- For a given resistor, if the current or voltage doubles, the power will increase fourfold.
- The choice of equation to use depends on whether the question provides the value of current or voltage.
- Rearranging the energy and power equation, the energy can be expressed as:
E = VIt - Where:
- E = energy transferred (J)
- V = potential difference (V)
- I = current (A)
- t = time (s)
Measuring Energy Usage
- Energy consumption in households and businesses is typically measured and compared using a unit known as the kilowatt hour (kWh).
- The kilowatt hour is essentially defined as the amount of energy equivalent to one kilowatt of power being consumed for one hour.
- Appliances are assigned power ratings, which provide information to consumers regarding the rate of energy transfer to the device per second.
- Energy usage is commonly quantified in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is then utilized to determine the overall cost of energy consumed.
Question for Electrical PowerTry yourself: What is electrical power?View Solution
Calculating with kWh
- The kilowatt-hour (kWh) can also be mathematically expressed through an equation.
E = Pt - The energy equation involves key variables:
- E = energy (kWh)
- P = power (kW)
- t = time (h)
- This equation stands out because it doesn't use the standard International System of Units (S.I.). Both energy and power are multiplied by 103, and time is measured in hours instead of seconds.
- Considering the typical unit for energy is joules (J), where 1 Watt (W) equals 1 joule per second, i.e., 1 W in 1 s.
- Therefore,
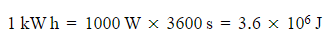
- Given 1 kW = 1000 W and 1 h = 3600 s
- Conversion from Joule to kW h:
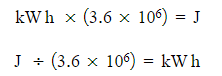
- The kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a significant unit of energy, commonly employed to measure energy consumption in various settings such as homes, businesses, factories, and other industrial applications.
The document Electrical Power | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Electrical Power - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the electrical power equation? |  |
Ans. The electrical power equation is P = IV, where P represents power in watts, I represents current in amperes, and V represents voltage in volts.
| 2. How is energy usage measured in electrical systems? |  |
Ans. Energy usage in electrical systems is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is calculated by multiplying the power consumption in kilowatts by the time in hours that the power is consumed.
| 3. How can electrical power be calculated if only the current and resistance are known? |  |
Ans. Electrical power can be calculated using the equation P = I^2R, where P represents power in watts, I represents current in amperes, and R represents resistance in ohms.
| 4. What are some common units of measurement for electrical power? |  |
Ans. Some common units of measurement for electrical power include watts (W), kilowatts (kW), and megawatts (MW).
| 5. How does the electrical power equation relate to the efficiency of electrical devices? |  |
Ans. The electrical power equation can be used to calculate the efficiency of electrical devices by comparing the input power (P_in) to the output power (P_out), with efficiency (%) = (P_out / P_in) x 100%.
Related Searches




















