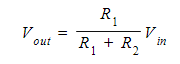Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Potential Dividers
Potential Dividers | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Variable Potential Dividers
- When two resistors are linked in series, they divide the potential difference across the power source between them.
 A potential divider splits the potential difference of a power source between two components
A potential divider splits the potential difference of a power source between two components
- The potential difference across individual resistors varies according to their resistance.
- The resistor with the greatest resistance will encounter a greater potential difference than the other resistor.
- Increasing the resistance of one resistor results in it receiving a larger fraction of the potential difference, while the remaining resistor receives a reduced fraction.
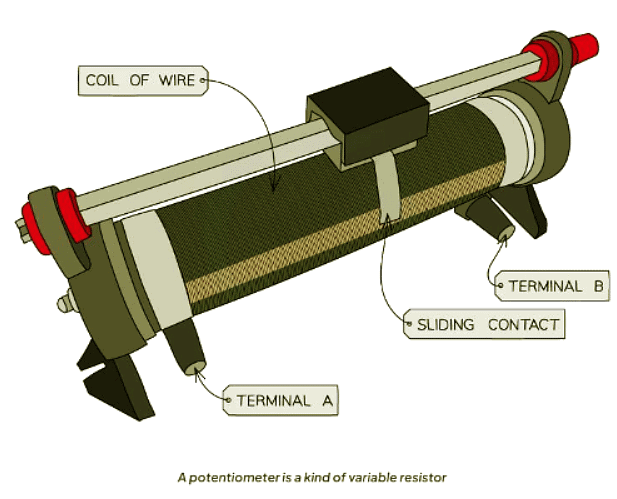
- A potentiometer is a component consisting of a coil of wire with a sliding contact at its midpoint.

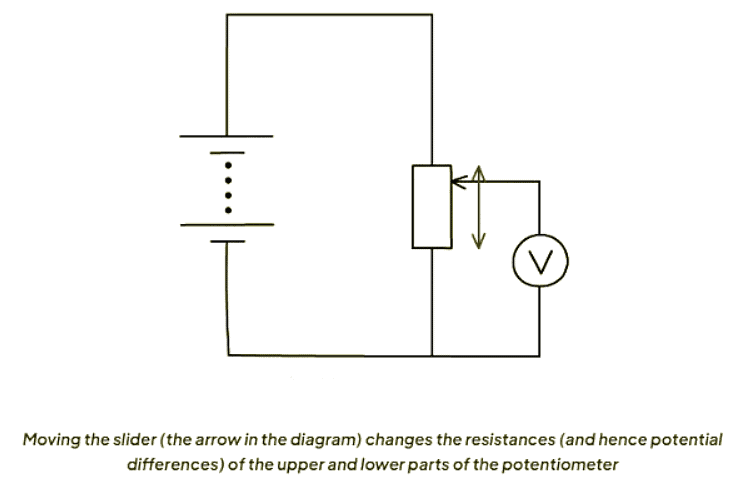
- When the slider is moved upwards, the resistance in the lower portion increases, causing a rise in the potential difference across it.

- Moving the slider upward in the diagram raises the resistance of the lower section, causing an increase in the potential difference across it.
Question for Potential DividersTry yourself: How does increasing the resistance of one resistor in a potential divider affect the potential difference across the resistors?View Solution
Resistors as Potential Dividers
- When two resistors are connected in series, according to Kirchhoff's Second Law, the potential across the power source gets distributed between them.
- Potential dividers, essentially circuits, create an output voltage that is a fraction of the input voltage.
- These dividers serve two primary functions:
- one, to offer a variable potential difference, and
- two, to allow for a specific potential difference selection,
- thus dividing the power source's potential among multiple components.
- The concept of potential dividers is extensively utilized in various applications including volume controls and sensory circuits that incorporate Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs) and thermistors.
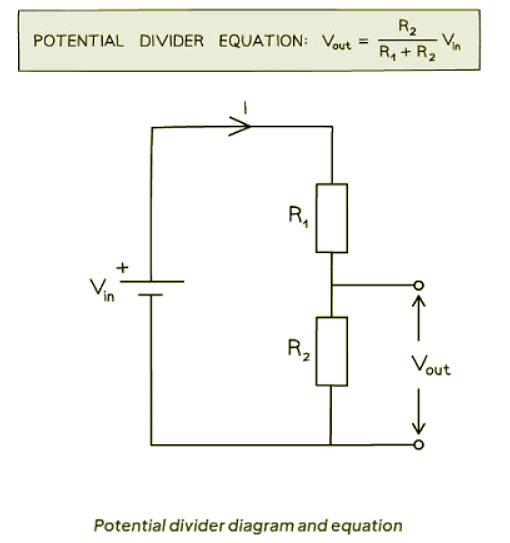
- In a potential divider circuit, the output voltage ratio is determined by the resistor values. This ratio equals the ratio of resistances of the resistors within the circuit. The relationship can be mathematically expressed as follows:

- Where:
- R2 is the numerator and the resistance of the resistor over Vout
- R1 is the other resistance in series
- Vout is the output potential difference
- Vin is the input potential difference
- The potential divider equation can also be expressed as:

- When considering electrical resistance,
- R1 represents the numerator and signifies the resistance of the resistor over Vout.
- Meanwhile, R2 denotes the other resistance present in series.
- Irrespective of the notation utilized, the outcome will always be the same.
- It is essential for the numerator to signify the resistance of the resistor over Vout.
Understanding Potential Divider Circuits
- The input voltage (Vin) is connected across two series resistors.
- The output voltage (Vout) is measured across one of the resistors (R2).
- The voltage across each resistor is determined by its resistance (R):
- The resistor with higher resistance will have a greater voltage drop.
- According to Ohm's Law (V = IR), if the resistance of one resistor increases, it takes a larger proportion of the total voltage, leaving less for the other resistor.
- In a potential divider circuit, the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to its resistance (V = IR).
The document Potential Dividers | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Potential Dividers - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is a variable potential divider? |  |
Ans. A variable potential divider is a circuit that consists of resistors arranged in a way that allows the output voltage to be adjusted by changing the resistance of one of the resistors.
| 2. How do resistors function as potential dividers? |  |
Ans. Resistors function as potential dividers by dividing the input voltage in proportion to the ratio of their resistances. The output voltage can be calculated using the formula Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2)).
| 3. How are potential dividers used in Year 11 electronics? |  |
Ans. Potential dividers are used in Year 11 electronics to provide a specific output voltage level from a varying input voltage source, such as a sensor or a power supply.
| 4. What are some common applications of potential dividers in electronics? |  |
Ans. Some common applications of potential dividers in electronics include volume controls in audio equipment, brightness controls in display screens, and voltage regulation in power supplies.
| 5. How can the output voltage of a potential divider be adjusted? |  |
Ans. The output voltage of a potential divider can be adjusted by changing the resistance of one of the resistors in the circuit. This can be done manually using a variable resistor or automatically using feedback control mechanisms.
Related Searches