Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Transformer Calculations
Transformer Calculations | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Transformer Calculations |

|
| Transformer Efficiency |

|
| High-Voltage Transmission |

|
| Calculating Power Losses |

|
Transformer Calculations
- The potential difference (voltage) output of a transformer is determined by:
- The number of turns on both the primary and secondary coils.
- The input potential difference (voltage).
- It can be calculated using the following equation:

- This equation can be represented symbolically as:
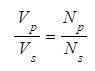
- Where
- Vp = Potential difference (voltage) across the primary coil in volts (V)
- Vs = Potential difference (voltage) across the secondary coil in volts (V)
- np = Number of turns on the primary coil
- ns = Number of turns on the secondary coil
- The equation can be inverted to:
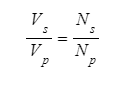
- The equations presented indicate that the ratio of potential differences across the primary and secondary coils of a transformer equals the ratio of the number of turns on each coil.
Transformer Efficiency
- An ideal transformer would be 100% efficient. While transformers can increase the voltage of a power source, according to the law of conservation of energy, they cannot increase the power output.
- Transformers, in an ideal scenario, are 100% efficient. Despite their ability to boost voltage, they are unable to amplify power output due to energy conservation principles.
- If a transformer operates at 100% efficiency, the input power must equal the output power.
- The formula for calculating electrical power is: P = V × I
- Where:
- P = power in Watts (W),
- V = potential difference in volts (V),
- I = current in amps (A)
- If a transformer is 100% efficient:
Vp × Ip = Vs × Is - Where:
- Vp = Potential difference across primary coil in volts (V)
- Ip = Current through primary coil in amps (A)
- Vs = Potential difference across secondary coil in volts (V)
- Is = Current through secondary coil in amps (A)
- The equation above can also be expressed as:
Ps = Vp × Ip
Question for Transformer CalculationsTry yourself: What determines the potential difference output of a transformer?View Solution
High-Voltage Transmission
Transformers play several crucial roles in the electricity system:
- They boost the voltage of electricity for efficient transmission across the national grid.
- They decrease the high voltage used in power lines to levels suitable for household use.
- Transformers are also vital in adapters, reducing mains voltage to levels appropriate for various electronic devices.
Advantages of High Voltage Transmission
- When electricity travels long distances, the wires experience heating due to current flow, leading to energy dissipation.
- To convey the same power as input, the transmission voltage should be raised.
- This action causes a decrease in the current carried by the power lines.
- Since power equals voltage multiplied by current (P = IV), if voltage increases, current must decrease to maintain the same power transmission.
- Reduced current flow through the power lines leads to lower heat generation in the wires.
- Consequently, this minimizes energy loss within the power lines.
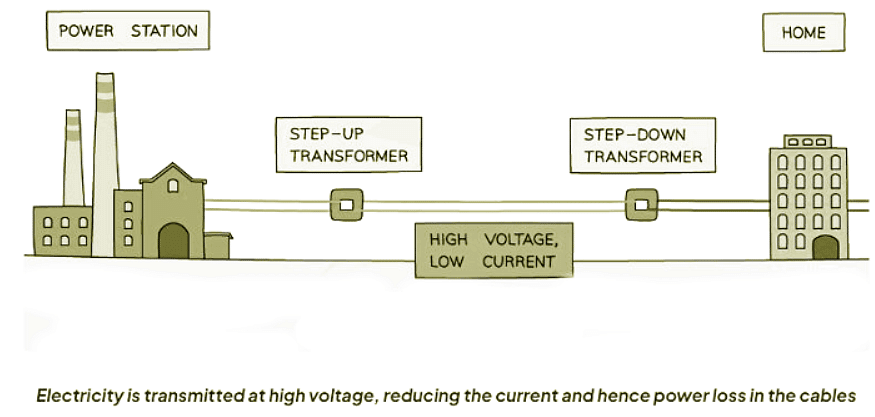
Calculating Power Losses
- When an electric current flows through a wire, it generates heat, causing the wire to warm up.
- This heat results in the loss of electrical energy in the form of heat, thereby reducing the efficiency of the transformer. This loss is primarily due to electrical resistance present in all wires.
- The power lost in the wire per unit time can be calculated using the formula: P = I2 * R
- Where:
- P represents power measured in watts (W).
- I represents the current measured in amperes (A).
- R represents the resistance measured in ohms (Ω).
- The total energy lost within a duration t can be calculated using the formula: E = P × t.
- Where,
- E represents energy in joules (J).
- t denotes time in seconds (s).
- A step-up transformer is employed to amplify the voltage of a power supply during transmission.
- The relationship between the number of turns and voltage in the transformer is governed by a specific equation.
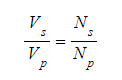
- Where,
- Vp signifies the potential difference across the primary coil in volts (V).
- Vs symbolizes the potential difference across the secondary coil in volts (V).
- np stands for the number of turns on the primary coil.
- ns represents the number of turns on the secondary coil.
- A step-up transformer has more turns on the secondary coil (Ns) than on the primary coil (Np).
- Since a transformer cannot output more power than is put into it, increasing the voltage must result in the current being lowered.
Ip Vp = Is Vs - Where,
- Ip: Current in the primary coil in amperes (A)
- Is: Current in the secondary coil in amperes (A)
- Lowering the current in cables reduces power and energy loss, enhancing efficiency in electrical energy transfer.
The document Transformer Calculations | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Transformer Calculations - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How is transformer efficiency calculated? |  |
Ans. Transformer efficiency is calculated by dividing the output power (power delivered to the load) by the input power (power supplied to the transformer) and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. The formula for efficiency is Efficiency = (Output Power / Input Power) x 100.
| 2. Why is transformer efficiency important? |  |
Ans. Transformer efficiency is important because it determines how much of the input power is successfully transferred to the output without being lost as heat. A higher efficiency means less energy is wasted, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
| 3. What factors can affect transformer efficiency? |  |
Ans. Factors that can affect transformer efficiency include the quality of the transformer's materials, the design of the transformer, the load being supplied, operating temperature, and the frequency of the input power.
| 4. How does high-voltage transmission improve efficiency in transformers? |  |
Ans. High-voltage transmission reduces the current flowing through the transformer, which in turn reduces the I²R losses (heat losses due to current flowing through the resistance of the transformer windings). By decreasing these losses, high-voltage transmission can improve the overall efficiency of the transformer system.
| 5. How can transformer efficiency be improved? |  |
Ans. Transformer efficiency can be improved by using high-quality materials, designing the transformer for optimal performance, maintaining proper cooling systems, operating the transformer at its rated capacity, and using high-voltage transmission methods. Regular maintenance and monitoring can also help identify and address any efficiency issues.
Related Searches















