Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Uses of Radiation
Uses of Radiation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Uses of Radiation
- Radiation finds diverse applications in different fields:
- Medical Procedures: Used for diagnosing and treating cancer.
- Sterilizing Food: By irradiating it to eliminate bacteria.
- Sterilizing Medical Equipment: Utilizing gamma rays for disinfection purposes.
- Age Determination: Assisting in determining the age of ancient artifacts.
- Material Thickness Check: Employed to measure the thickness of materials.
- Smoke Detectors: Utilized in smoke alarms for safety purposes.
- The choice of radiation type depends on the specific application requirements.
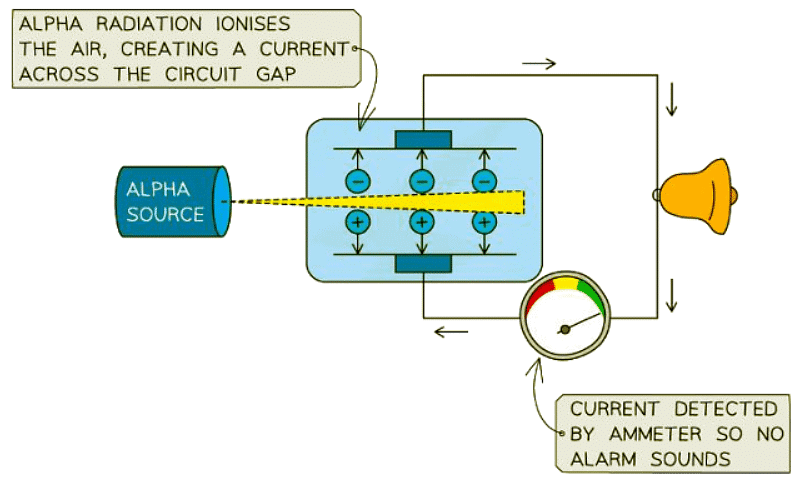
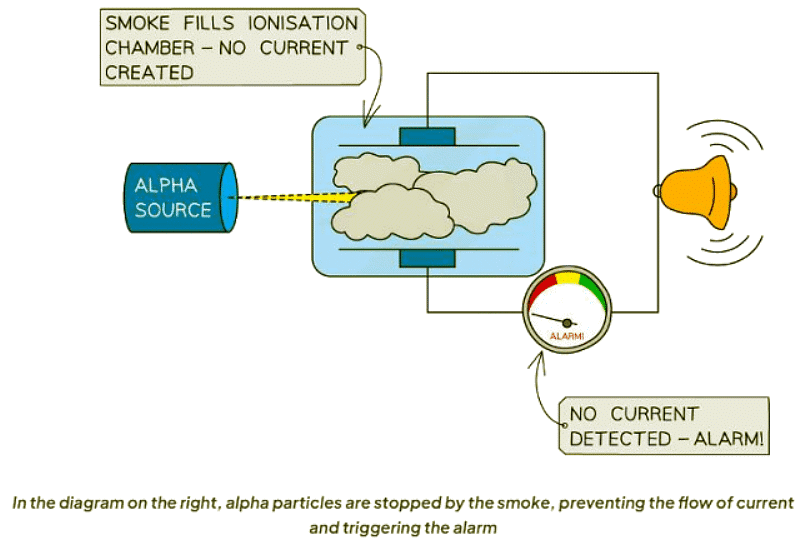
Smoke Detectors
- Smoke detectors utilize alpha particles for their operation.
- Alpha radiation ionizes the air inside the detector, which establishes a current.
- When smoke interferes with the alpha emitter, the current flow is disrupted.
- This disruption triggers the alarm through a connected microchip.
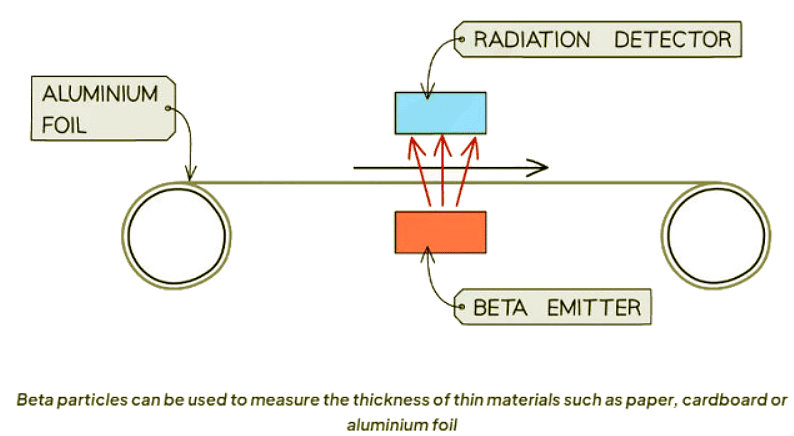
Measuring the Thickness of Materials
- Radiation, particularly beta particles, is commonly utilized for tracing and gauging thickness.
- As a material passes over a beta radiation source, a detector monitors the particles that can penetrate it.
- When the material thickens, more particles are absorbed, resulting in fewer particles passing through; conversely, when the material thins, the opposite effect occurs.
- This process enables the machine to make necessary adjustments to maintain a consistent material thickness.
- Beta radiation is chosen for its partial absorption by materials, allowing some particles to pass through.
- Alpha particles, if utilized, would be entirely absorbed, hindering their detection on the other side.
- Gamma radiation, on the other hand, would almost entirely penetrate the material, making it challenging to detect changes in thickness.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer
- Radiotherapy is a cancer treatment involving radiation, distinct from chemotherapy which uses chemicals.
- While radiation can potentially cause cancer, it is a highly effective method for treating it.
- Radiation has the ability to destroy living cells, with certain cells like bacteria and cancer cells being more vulnerable to its effects.
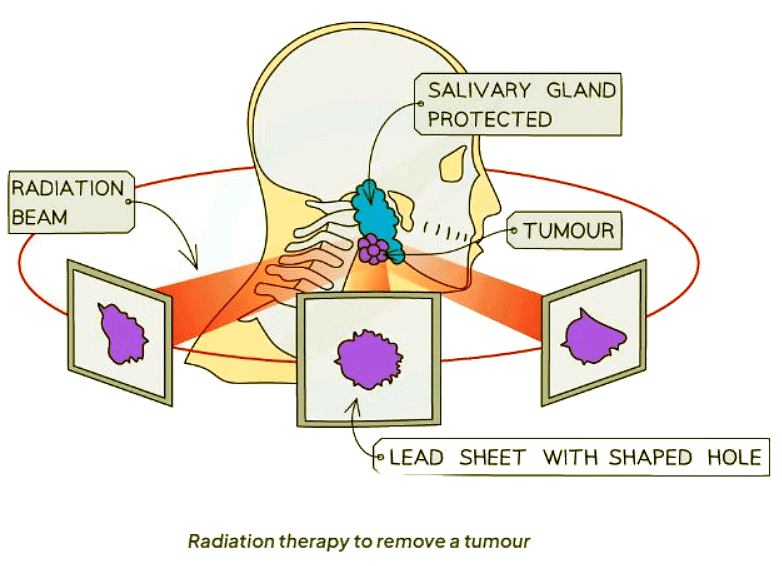
Usage of Gamma Rays
- Gamma rays are directed at cancerous tumors due to their capacity to penetrate the body, reaching the tumor site.
- To minimize damage to healthy tissue, the beams of gamma rays are carefully manipulated while targeting the tumor.
Role of Tracers and PET Scans
- A tracer, a radioactive isotope, is employed to monitor the movement of substances like blood within the body.
- PET scans utilize emissions from tracers to diagnose cancer and pinpoint the location of tumors.
- A PET Scan in Cancer Diagnosis: A PET scan is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses a tracer to detect emissions in the body, aiding in the diagnosis of cancer and pinpointing the location of tumors.
Question for Uses of RadiationTry yourself: What type of radiation is commonly utilized in smoke detectors?View Solution
Sterilising Food and Medical Equipment
Gamma radiation finds extensive application in sterilizing medical equipment due to several reasons:
- Gamma radiation boasts the highest level of penetration among all radiation types, ensuring thorough irradiation.
- Its penetrating capability enables it to irradiate all facets of instruments effectively.
- Medical instruments can be sterilized without necessitating the removal of packaging.
- Additionally, gamma radiation is employed in irradiating food items to eliminate microorganisms, enhancing their longevity and diminishing the likelihood of food-borne infections.

The document Uses of Radiation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Uses of Radiation - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are some common uses of radiation in various industries? |  |
Ans. Some common uses of radiation in various industries include sterilization of medical equipment, food irradiation to extend shelf life, and non-destructive testing in manufacturing.
| 2. How is radiation used in medicine for diagnostic purposes? |  |
Ans. Radiation is used in medicine for diagnostic purposes through techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and nuclear medicine imaging like PET scans.
| 3. What are some benefits of radiation therapy in cancer treatment? |  |
Ans. Radiation therapy in cancer treatment helps to destroy cancer cells, shrink tumors, and relieve cancer symptoms, ultimately improving a patient's quality of life.
| 4. How is radiation used in agriculture to improve crop production? |  |
Ans. Radiation is used in agriculture to induce genetic mutations in crops, leading to the development of new plant varieties with desirable traits such as disease resistance and increased yield.
| 5. Can radiation be used in environmental remediation processes? |  |
Ans. Yes, radiation can be used in environmental remediation processes such as groundwater treatment, soil decontamination, and air pollution control to effectively remove pollutants and contaminants from the environment.
Related Searches