Best Study Material for Year 11 Exam
Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Calculating Orbital Speeds
Calculating Orbital Speeds | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Orbital Speed
- When celestial bodies like planets orbit, they move in circular paths around a central object like the Sun or a planet.
- In one complete orbit, a planet covers a distance that is equal to the circumference of the circular path it follows.
- This distance is precisely 2π times the radius of the circle it traces.
- The relationship between speed, distance and time is:
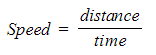
- The average orbital speed of an object can be defined by the equation:
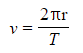
- Where:
- v = orbital speed in meters per second (m/s)
- r = average radius of the orbit in meters (m)
- T = orbital period in seconds (s)
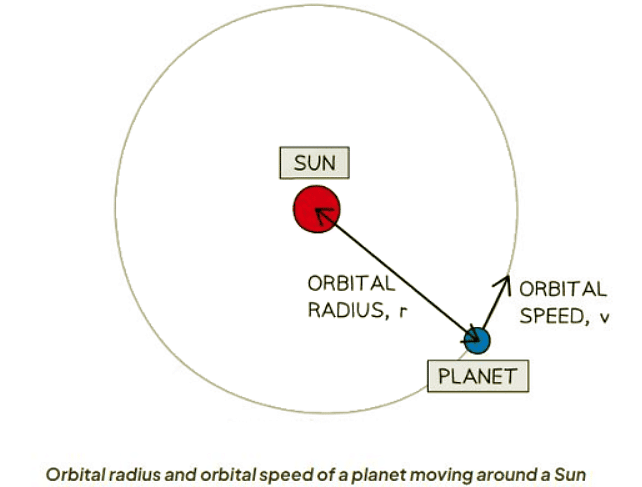
- The orbital period is the time taken for an object to complete one full orbit.
- The orbital radius 'r' is measured from the center of the object being orbited to the object in orbit.
The document Calculating Orbital Speeds | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Calculating Orbital Speeds - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is orbital speed? |  |
| 2. How is orbital speed calculated? |  |
Ans. Orbital speed can be calculated using the formula: orbital speed = √(GM/r), where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the larger body, and r is the distance from the center of the larger body to the object.
| 3. Why is it important to calculate orbital speed? |  |
Ans. Calculating orbital speed is important for understanding how objects move in space and for predicting their trajectories. It is crucial for spacecraft navigation and satellite positioning.
| 4. Does orbital speed vary for different objects in orbit? |  |
Ans. Yes, orbital speed can vary depending on the mass of the larger body and the distance of the object from the center of the body. Objects closer to the body will have higher orbital speeds.
| 5. Can orbital speed be changed? |  |
Ans. Orbital speed can be changed by altering the velocity of the object, either by applying thrust or by using gravitational assists from other bodies in space.
Related Searches



















