Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > The Expanding Universe
The Expanding Universe | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Galaxies & Redshift
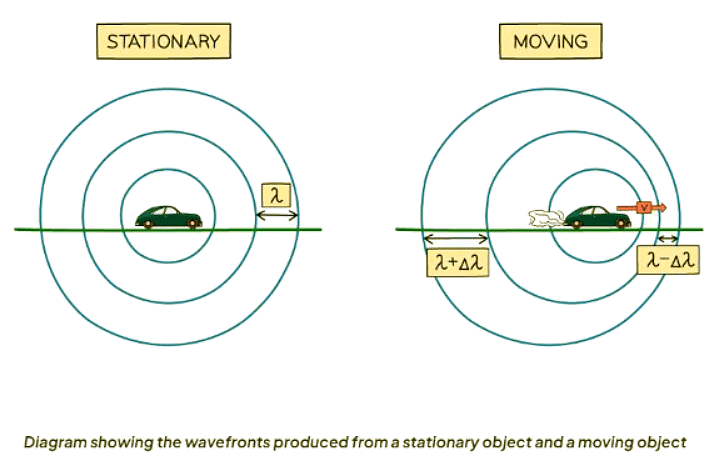
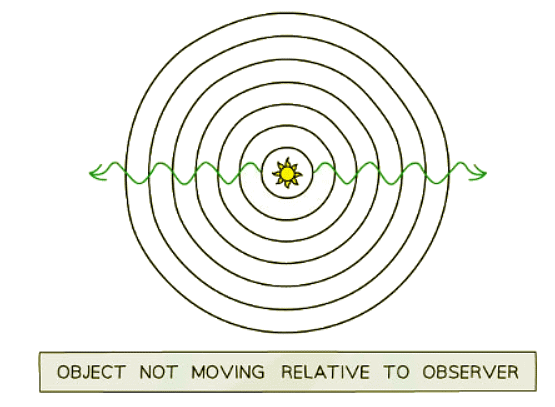
- Objects emitting waves typically have wavefronts spreading out symmetrically.
- Movement of the wave source can lead to wave compression or stretching.
Understanding the Doppler Effect
- When an object is in motion, it alters the wavelength (λ) and frequency of waves:
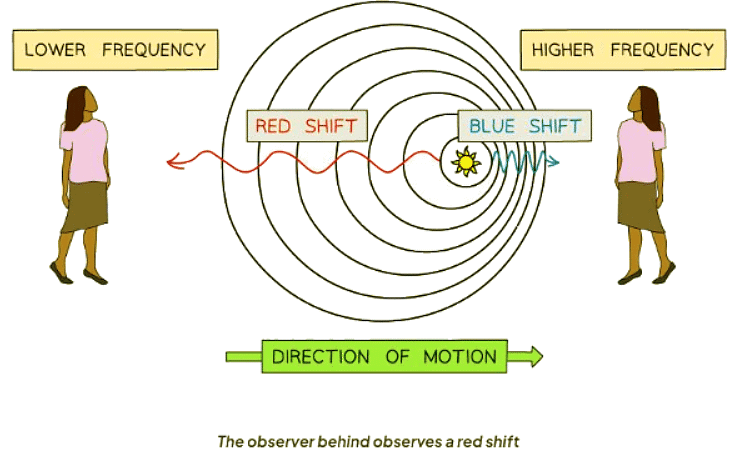
- In front of the moving source, the wavelength decreases, and the frequency increases.
- Behind the moving source, the wavelength increases, and the frequency decreases.
- This phenomenon is referred to as the Doppler effect.
Impact on Wavelength
- The wavelength in front of the source decreases, leading to an increase in frequency.
- The wavelength behind the source increases, causing a decrease in frequency.
Impact on Light
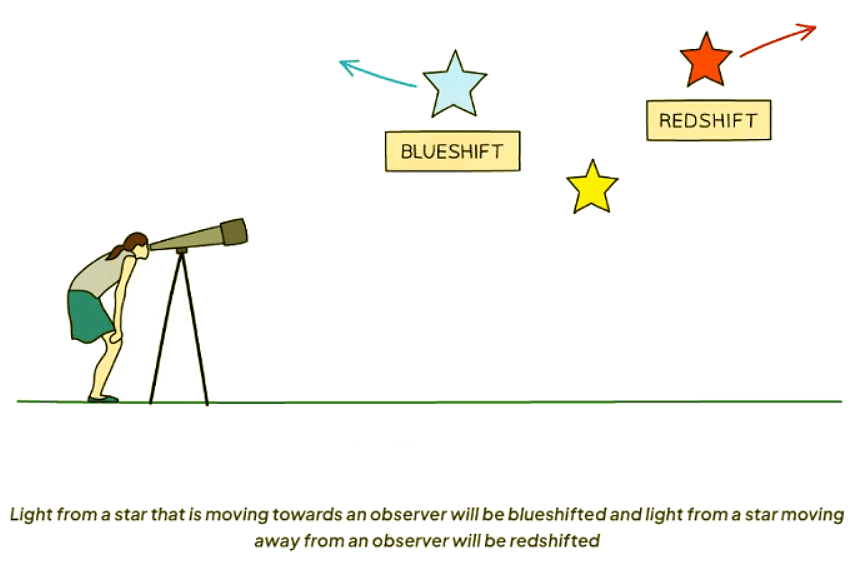
- The Doppler effect is also applicable to light:
- When an object moves away from an observer, the wavelength of light increases.
- This phenomenon is known as redshift, as the light shifts towards the red end of the spectrum.
Redshift and Blueshift in Astronomy
- If an object moves away from an observer, the wavelength of light increases. This phenomenon is known as redshift, indicating that the light shifts towards the red end of the spectrum.
Understanding Redshift
- Redshift refers to the increase in the observed wavelength of electromagnetic radiation emitted from receding stars and galaxies.
Observing Redshift
- The Milky Way is just one of billions of galaxies in the Universe. Light emitted from distant galaxies appears redshifted when compared to light emitted on Earth.
Comparing Light from Close Objects and Distant Galaxies
- The illustration below depicts how light appears from a nearby object like the Sun and a far-off galaxy.
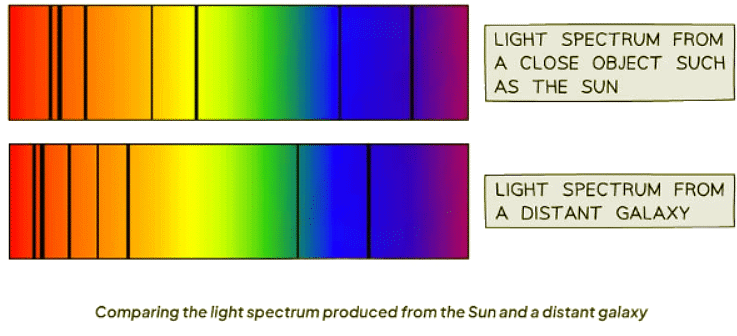
- The diagram also reveals that light reaching us from remote galaxies experiences redshift.
- Redshift indicates a shift of spectral lines towards the red end, suggesting galaxies' recession.
- This redshift implies the universe's expansion, aligning with the Big Bang theory.
The Expanding Universe
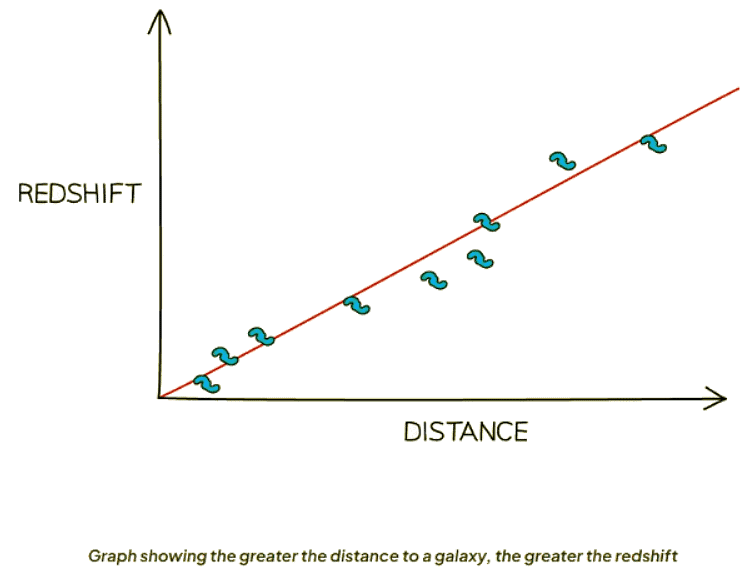
- Observation from Light Spectrums of Distant Galaxies:
- As galaxies get farther, redshift increases, indicating faster movement away from us.
- This relationship implies that distance correlates with the speed of galactic motion.
- Hubble's Law and Redshift:
- Greater distances to galaxies result in greater redshifts, illustrating accelerated galactic recession.
- The phenomenon suggests an expanding universe where galaxies move away from each other over time.
Question for The Expanding UniverseTry yourself: What is the Doppler effect?View Solution
The document The Expanding Universe | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on The Expanding Universe - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is redshift in the context of galaxies and the expanding universe? |  |
Ans. Redshift refers to the phenomenon where light from galaxies moving away from us is stretched to longer wavelengths, causing a shift towards the red end of the spectrum. This is a key piece of evidence for the expanding universe.
| 2. How does redshift provide evidence for the expanding universe? |  |
Ans. The observation of redshift in the light from distant galaxies indicates that they are moving away from us, and the amount of redshift is directly proportional to the distance of the galaxy. This supports the idea of an expanding universe.
| 3. What is the significance of studying galaxies and redshift in understanding the universe's evolution? |  |
Ans. Studying galaxies and their redshift allows astronomers to trace the history and expansion of the universe. By analyzing the redshift of galaxies at different distances, scientists can piece together the timeline of the universe's evolution.
| 4. How do astronomers measure redshift in galaxies? |  |
Ans. Astronomers measure redshift by examining the spectrum of light emitted by a galaxy. By comparing the observed spectrum to the known spectrum of elements on Earth, they can calculate the redshift and determine how fast the galaxy is moving away from us.
| 5. What implications does the concept of redshift have for the future of the universe? |  |
Ans. The observation of redshift in galaxies suggests that the universe is expanding at an accelerating rate. This has implications for the eventual fate of the universe, with theories suggesting a continued expansion or a potential "Big Crunch" scenario.
Related Searches















