Android App Development Fundamentals for Beginners - Software Development PDF Download
Android App Development Fundamentals for Beginners
Last Updated : 08 Jul, 2022Android is an operating system designed primarily for mobile devices, based on the Linux Kernel and open-source software, developed by Google. Originally intended for smartphones and tablets, Android now powers a range of devices like cars, TVs, watches, and cameras. It stands as one of the most popular OS for smartphones, initially developed by Android Inc. and acquired by Google in 2005. The ecosystem includes a vast array of applications available on the Google Play store, with more than 3.3 million apps. Development of Android apps typically occurs in Android Studio, and they are distributed as APKs (Android Package Kits).
Androidoperating systemGoogleAndroid IncGoogle Play storeAndroid Studio.APK(Android Package Kit)Android Fundamentals
1. Android Programming Languages
Android app development involves programming primarily in JAVA or Kotlin along with XML for designing interfaces. XML focuses on the front-end, managing layouts and presentation, while JAVA or Kotlin handles the app's functionality, including buttons, variables, and data storage.
JAVA or KotlinXML (Extension Markup Language)2. Android Components
Android apps are constructed using various components, each with specific roles and lifecycles that impact the app's behavior from launch to closure. These components may interact with each other, serving distinct purposes within the app. The key app components are:
- Activities
- Services
- Broadcast Receivers
- Content Provider
Android Components Overview
- Activities
- Services
- Broadcast Receivers:
- Content Provider:
Activities
Activities in Android are responsible for managing the user interface and user interactions within an application. They represent different screens that the user can interact with. The MainActivity is a key starting point for any Android app.
Think of an Activity as a single, focused thing a user can do. For instance, an email app might have one activity that shows a list of emails, another activity to compose an email, and another to read an email.
Services
Services in Android are background tasks that can execute long-running operations without needing user interaction. For example, playing music in the background while using other apps. Services ensure the app runs smoothly and doesn't interrupt the user experience.
Imagine a music app. Even if you switch to another app, the music continues playing in the background thanks to a Service.
Broadcast Receivers
Broadcast Receivers in Android respond to system-wide broadcast announcements. They don't have a user interface but can perform tasks or respond to system events. For instance, when the battery is low, a Broadcast Receiver can trigger an action like activating a battery saver mode.
Consider a messaging app that sends a notification when you receive a new message. This is made possible through Broadcast Receivers listening for new message events.
Content Provider
Content Providers in Android manage access to structured data. They allow data sharing between different applications. One app can query or modify data from another app using a Content Provider. This mechanism ensures secure and consistent data access across apps.
For instance, a contacts app can provide access to its contact list to other apps through a Content Provider.
Content Provider
- Syntax: To know more about Content Providers, please refer to this article: Content Providers in Android with Example.
Structural Layout Of Android Studio
The basic structural layout of Android Studio is as follows:
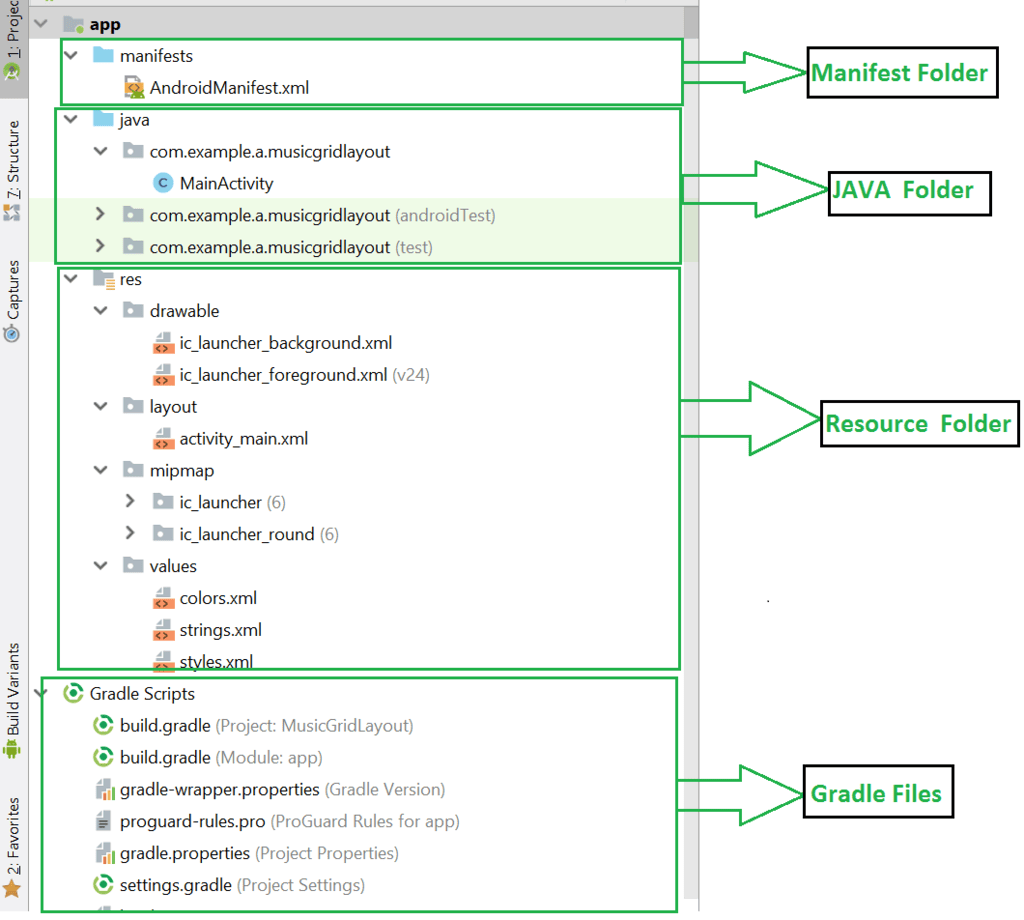
Manifest Folder: Android Manifest
The Android Manifest is an XML file that serves as the root of the project source set. It provides crucial information about the app, Android build tools, the Android Operating System, and Google Play. This file includes permissions required by the app to execute specific tasks. Additionally, it outlines the hardware and software features of the app, which determine its compatibility on the Play Store. Moreover, it encompasses special activities such as services, broadcast receivers, content providers, package names, and more.
Java Folder
The JAVA folder comprises Java files essential for executing background tasks within the app. These files handle various functions like button functionalities, calculations, variable storage, toast messages, and programming functions. The number of Java files depends on the activities created within the app.
Resource Folder
The Resource folder (res) contains diverse resources utilized by the app. It is segmented into sub-folders such as drawable, layout, mipmap, raw, and values. The drawable folder stores images, while the layout folder houses XML files defining the user interface layout. These files are stored in res.layout and accessed through the R.layout class. The raw folder contains resources like audio or music files, accessed via R.raw.filename. The values folder is used for storing hardcoded strings, integers, and colors. It encompasses various other directories.
Resource Folder
- R.array: Contains resource arrays in arrays.xml
- R.integer: Contains resource integers in integers.xml
- R.bool: Contains resource boolean values in bools.xml
- R.color: Contains color values in colors.xml
- R.string: Contains string values in strings.xml
- R.dimen: Contains dimension values in dimens.xml
- R.style: Contains styles in styles.xml
Gradle Files
Gradle is a sophisticated toolkit used for managing the build process. It allows the definition of flexible custom build configurations. Each build configuration can specify its unique set of code and resources while utilizing common parts across all app versions.
The Android plugin for Gradle collaborates with the build toolkit to offer processes and configurable settings tailored for building and testing Android applications. It operates independently of Android Studio, enabling app building directly within the environment. This flexibility allows for custom build configurations without altering the core source files of the app.
Basic Layout
The basic layout can be structured in a tree format.
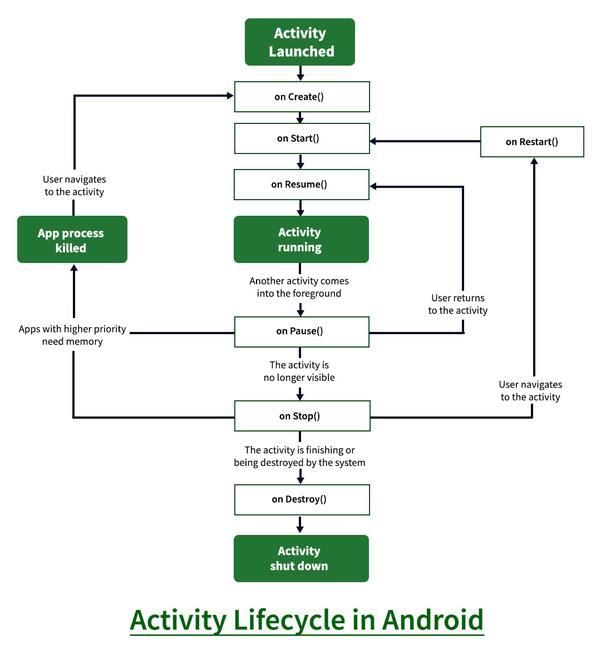
Lifecycle of Activity in Android App
The activity lifecycle in an Android app is crucial and can be depicted through a diagram. The various states of the Android lifecycle include:
- OnCreate: Triggered when the activity is first created.
- OnStart: Activated when the activity becomes visible to the user.
- OnResume: Executed when the activity begins user interaction.
- OnPause: Invoked when the activity is not visible to the user.
- OnStop: Called when the activity is no longer visible.
- OnRestart: Initiated when the activity is stopped and then restarted.
- OnDestroy: Used when the activity is to be closed or destroyed.
For further insights into the Activity Lifecycle in Android, please refer to the article titled "Activity Lifecycle in Android with Demo App."
To know more about Activity Lifecycle in Android Please refer to this article:
To begin your journey in Android, you may refer to these tutorials:
- Android Tutorial
- Kotlin Android Tutorial
- Android Studio Tutorial
- Android Projects – From Basic to Advanced Level
Please Login to comment...
LoginLikeUnderstanding Activity Lifecycle in Android
The activity lifecycle in Android refers to the stages an activity goes through during its lifetime in an application.
- Creation: This is the initial stage where the activity is created.
- Starting: The activity is started but not yet visible to the user.
- Resumed: The activity is visible and interacts with the user.
- Paused: Another activity partially covers the current activity.
Importance of Android Tutorials
Android tutorials are essential for beginners to grasp the fundamental concepts of Android app development.
- Android Tutorial: Provides a comprehensive overview of Android development.
- Kotlin Android Tutorial: Focuses on developing Android apps using Kotlin programming language.
- Android Studio Tutorial: Guides users on using Android Studio for app development.
- Android Projects – From Basic to Advanced Level: Offers hands-on projects for varying skill levels.




















