How to Request Permissions in Android Application? - Software Development PDF Download
How to Request Permissions in Android Application?
Last Updated : 30 Apr, 2021- Starting from Android 6.0 (API 23), users are not asked for permissions at the time of installation rather developers need to request the permissions at the run time. Only the permissions that are defined in the manifest file can be requested at run time.
Types of Permissions
- Install-Time Permissions: If the Android 5.1.1 (API 22) or lower, the permission is requested at the installation time at the Google Play Store.

- If the user Accepts the permissions, the app is installed. Else the app installation is canceled.
- Run-Time Permissions: If the Android 6 (API 23) or higher, the permission is requested at the run time during the running of the app.
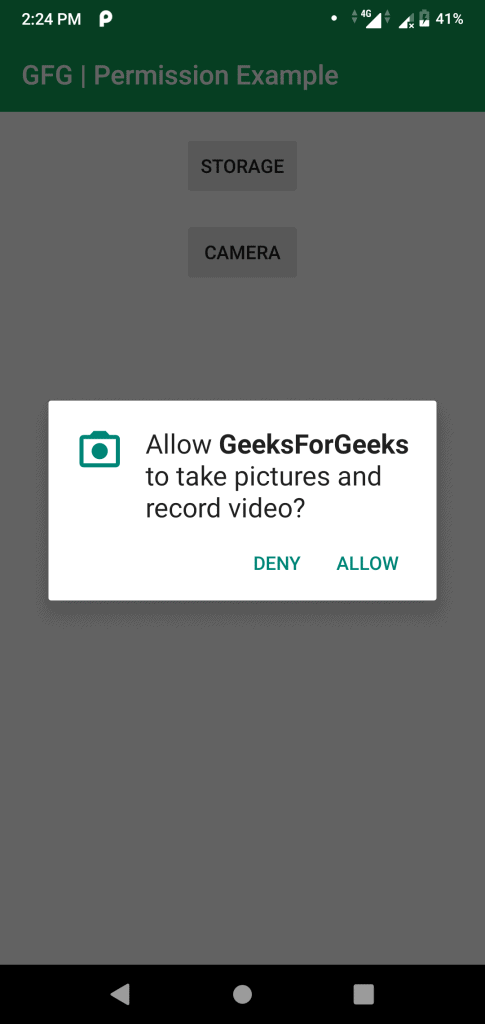
- If the user Accepts the permissions, then that feature of the app can be used. Else to use the feature, the app requests permission again.
So, now the permissions are requested at runtime. In this article, we will discuss how to request permissions in an Android Application at run time.
Steps for Requesting Permissions at Run Time
- Declare the Permission in the Android Manifest File: Permissions in Android are specified in the AndroidManifest.xml file using the uses-permission tag. This is where permissions like storage and camera are declared.
- Modify the activity_main.xml File to Add Buttons for Permission Requests: In this step, you need to add buttons to the activity_main.xml file to request permissions when clicked. For instance, you can have buttons for requesting storage and camera permissions.
- Check and Request Permissions: Before using certain services or features, it's crucial to ensure that the necessary permissions are granted. If permissions are lacking, users should be prompted to grant them.
Declare the Permission in the Android Manifest File
When working with Android applications, it is essential to declare permissions in the AndroidManifest.xml file. This file holds vital information about the application's components and requirements. For instance, permissions like reading from external storage, writing to external storage, and accessing the camera need to be declared here.
Modify the activity_main.xml File to Add Buttons for Permission Requests
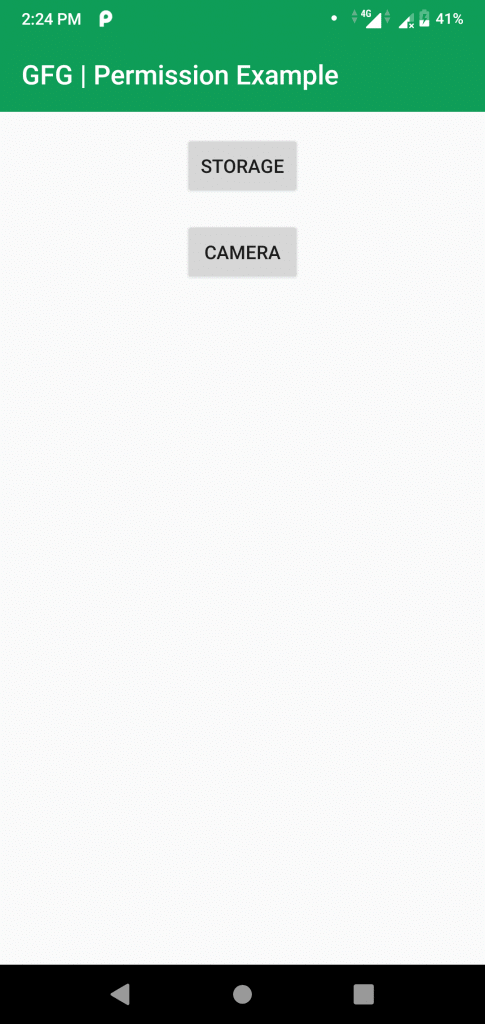
Within the activity_main.xml file, you can customize the user interface of your application. By adding buttons that facilitate permission requests, you enhance user experience and ensure smooth functionality. For example, you can include buttons labeled "Storage" and "Camera" to handle permission requests seamlessly.
Check and Request Permissions
Prior to utilizing specific functionalities within an application, it is imperative to verify if the necessary permissions have been granted. If permissions are missing, users should be prompted to provide them to enable the intended features. This ensures a secure and streamlined user experience.
Step 3: Checking and Requesting Permissions in Android
- Check whether permission is already granted or not:
Before using a service in Android, it is crucial to verify if the required permission has already been granted. If not, the user should be prompted to grant permission.
- Checking for permissions:
Since Android 6.0 (API level 23), users can revoke permissions from apps at any time. Therefore, apps need to check for permissions each time they require access to a certain feature or service.
- Syntax for checking permissions:
Apps can use the
checkSelfPermissionmethod to verify if a specific permission has been granted or not. - Requesting Permissions:
When the
checkSelfPermission()method returns PERMISSION_DENIED, the app should request the necessary permission from the user. Android offers methods likerequestPermissions()for this purpose. - Example:
- Java
- Kotlin
- Function to check and request permission:
public void checkPermission(String permission, int requestCode) {if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(MainActivity.this, permission) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED) {ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(MainActivity.this, new String[] { permission }, requestCode);} else {Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Permission already granted", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}}
Function to Check and Request Permission
- This function checks if a permission is granted and requests it if not.
- If permission is already granted, a toast message is displayed.
Step 4: Override onRequestPermissionsResult() method
This method is called when the user accepts or declines permission.
- The method checks the requestCode to determine the type of permission requested.
- If the camera permission is granted, a toast message for camera access is displayed.
- If the storage permission is granted, a toast message for storage access is displayed.
Explaining Android App Permissions Handling in Code
Handling Permissions in Android App
- When developing an Android app, it's crucial to handle permissions properly to ensure the app works as intended.
onRequestPermissionsResult Function
- The
onRequestPermissionsResultfunction is essential for managing permission requests in Android. - It is triggered when the user either grants or denies a specific permission.
- This function takes in parameters such as
requestCode,permissions, andgrantResults. - Here is an example of how this function is used in handling camera and storage permissions:
Camera Permission Handling
- When the app requests camera permission (
CAMERA_PERMISSION_CODE), the app checks if the permission is granted. - If the camera permission is granted, a message "Camera Permission Granted" is shown.
- If the permission is denied, a message "Camera Permission Denied" is displayed.
Storage Permission Handling
- Similarly, when the app requests storage permission (
STORAGE_PERMISSION_CODE), the app verifies the permission status. - Upon granting the storage permission, the app shows "Storage Permission Granted".
- If the permission is not granted, the message "Storage Permission Denied" is shown.
Code Snippets
Below are the code snippets for the application:
activity_main.xml
| RelativeLayout | xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" | xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" | xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" | android:layout_width="match_parent" | android:layout_height="match_parent" | tools:context=".MainActivity" | ||
| Button | android:id="@id/storage" | android:layout_width="wrap_content" | android:layout_height="wrap_content" | android:text="Storage" | android:layout_marginTop="16dp" | android:padding="8dp" | android:layout_below="@id/toolbar" | android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" |
| Button | android:id="@id/camera" | android:layout_width="wrap_content" | android:layout_height="wrap_content" | android:text="Camera" | android:layout_marginTop="16dp" | android:padding="8dp" | android:layout_below="@id/storage" | android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" |
AndroidManifest.xml
Below is the code for the AndroidManifest.xml file.
AndroidManifest.xml
- AndroidManifest.xml is a crucial file in Android development.
- It contains essential information about the Android app.
- Permissions are declared within the AndroidManifest.xml file.
- Permissions like READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE, WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE, and CAMERA are commonly declared.
- The
manifesttag encloses all the components of the AndroidManifest.xml file. - The
packageattribute specifies the package name of the Android app.
Main Activity in AndroidManifest.xml
- The main activity is declared within the
applicationtag. - It is the entry point of the Android application.
- The main activity is launched when the app is opened.
- Within the main activity, an intent-filter is defined to specify how the activity can be started.
Code for MainActivity File
Below is the code snippet for the MainActivity file:
Below is the code for the MainActivity file.- Kotlin and Java are commonly used languages for Android app development.
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
android:allowBackup | Specifies whether the app data can be backed up. |
android:icon | Sets the icon for the Android app. |
android:label | Defines the label for the app displayed on the device. |
android:roundIcon | Sets a round icon for the Android app. |
android:supportsRtl | Indicates whether the app supports right-to-left layout. |
android:theme | Sets the theme for the Android app. |
activity | Specifies an activity in the Android app. |
intent-filter | Filters the intents that an activity can respond to. |
action | Specifies the action to be performed. |
category | Defines the category for an intent filter. |
Explanation of Android Permissions Handling in Kotlin
- Android Permissions in Kotlin
- In Android app development using Kotlin, permissions play a crucial role in ensuring that apps have the necessary access to device resources.
- Defining Permission Codes
- Permission codes like CAMERA_PERMISSION_CODE and STORAGE_PERMISSION_CODE are defined to uniquely identify different types of permissions in the app.
- Handling Permission Requests
- The
checkPermissionfunction is used to check and request permissions in the app. - When a user triggers a permission request by interacting with a specific feature like accessing the camera or storage, the app checks if the permission is already granted.
- The
- Requesting Permissions
- If the required permission is not granted, the app requests the user's permission using
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions. - For instance, when the user clicks on a button to access the camera or storage, the app requests the corresponding permission.
- If the required permission is not granted, the app requests the user's permission using
- Handling Permission Responses
- The
onRequestPermissionsResultfunction handles the user's response to the permission request. - Depending on whether the user grants or denies the permission, the app displays an appropriate message using
Toast.makeText.
- The
Understanding Android Permissions in an App
- Android permissions are crucial for allowing apps to access certain features and data on a device.
- Each permission is associated with a unique code to identify it within the app.
- When users interact with an app, they may be prompted to grant specific permissions.
- Let's delve into the process of handling permissions in an Android app:
Defining Buttons and Permission Codes
- Buttons like 'storage' and 'camera' are defined to trigger specific actions in the app.
- Unique codes, such as CAMERA_PERMISSION_CODE and STORAGE_PERMISSION_CODE, are allocated for each permission.
Requesting Permissions
- When a user triggers a permission-dependent action, the app checks if the required permission is granted.
- If the permission is not granted, a request is sent to the user for permission.
Handling Permission Responses
- Upon user response to a permission request, the app distinguishes between camera and storage permissions.
- If permission is granted, a corresponding message is displayed to the user.
- If permission is denied, the app informs the user accordingly.
Example Scenario
- Imagine an app that captures photos and saves them to the device.
- When the user tries to access the camera, the app requests camera permission.
- If the user grants permission, the app can utilize the camera functionality seamlessly.
- Conversely, denying permission restricts the app from accessing the camera feature.
Step-by-Step Guide to Android Development with Kotlin
- On starting the application:
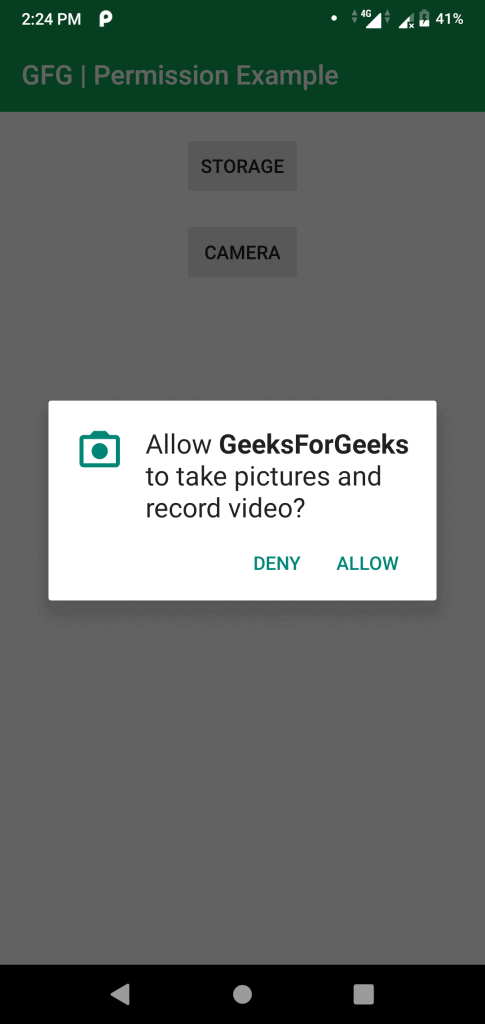
- On clicking the camera button for the first time:
- On Granting the permission:

- On clicking the camera button again:

Embarking on Your Android Development Journey
- Ready to start your adventure in Android Development with Kotlin? It's an exciting opportunity to delve into the world of mobile app creation.
- Are you prepared to learn and grow as you progress from a beginner to a pro in Android Development with Kotlin? This self-paced learning experience promises a transformative journey.
Login to Engage
- Login: Sign in to access exclusive content and features.
- Like: Show your appreciation for content that resonates with you.














