How Does Android App Work? - Software Development PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| How Does Android App Work? |

|
| Step 1: Building the APK File |

|
| Step 2: Deploy the Application |

|
| Step 3: Running the Application |

|
| Summary of Android App Execution Process |

|
How Does Android App Work?
Last Updated : 29 Dec, 2020Developing an android application involves several processes that happen in a sequential manner. After writing the source code files, when developers click the Run button on the Android studio, plenty of operations and process starts at the backend. Every operation happening in the background is a crucial step and are interdependent. The IDE builds all the application files, make them device compatible in order to deploy, and assure that the application runs successfully on the device. This article broadly explains each and every critical step involved in the journey of an android app, from the IDE files to a working device application.
Run button- Source Code Files: Developers begin by writing the source code files that form the foundation of the Android application.
- Run Button Click: When developers click the Run button in Android Studio, a series of backend operations kick off.
- IDE Operations: The Integrated Development Environment (IDE) carries out essential operations in the background.
- Build Process: The IDE assembles all application files and ensures they are compatible with the target device.
- Deployment: After building, the application is deployed on the device for testing and execution.
- Device Compatibility: It is crucial to make sure that the application runs smoothly on the intended device.
- Ensuring Success: The final goal is to guarantee that the application functions correctly on the device.
Step 1: Building the APK File
- Code Compilation
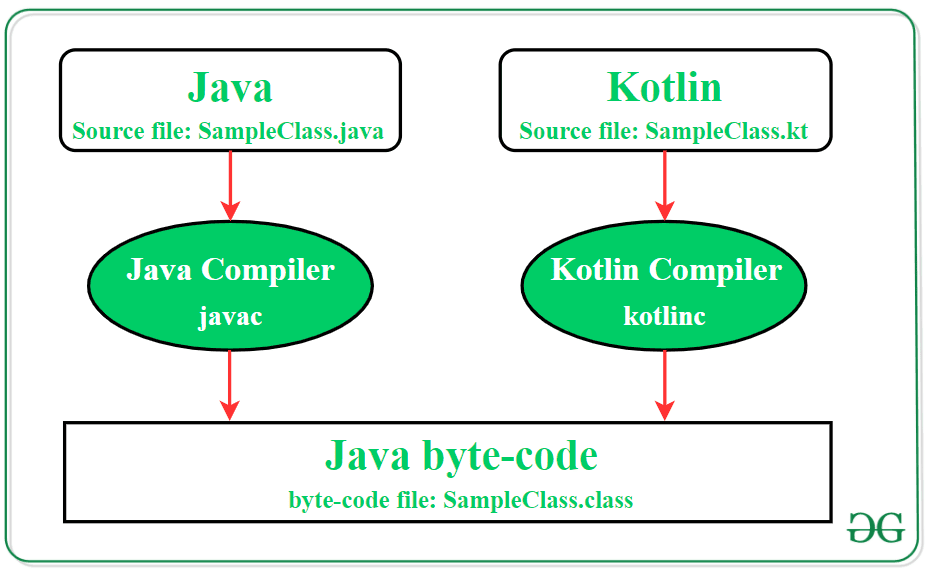
The android application source files are written in either Java (*.java files) or Kotlin (*.kt files) programming languages. Although the syntax of writing code in these two languages differs, their compilation processes are quite similar. Both languages produce code that can be compiled into Java byte-code, which is executable on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
- Java (*.java files)
- Kotlin (*.kt files)
- Java byte-code
- Java class file (*.class)
- javac
- kotlinc
- Conversion into Dalvik bytecodes
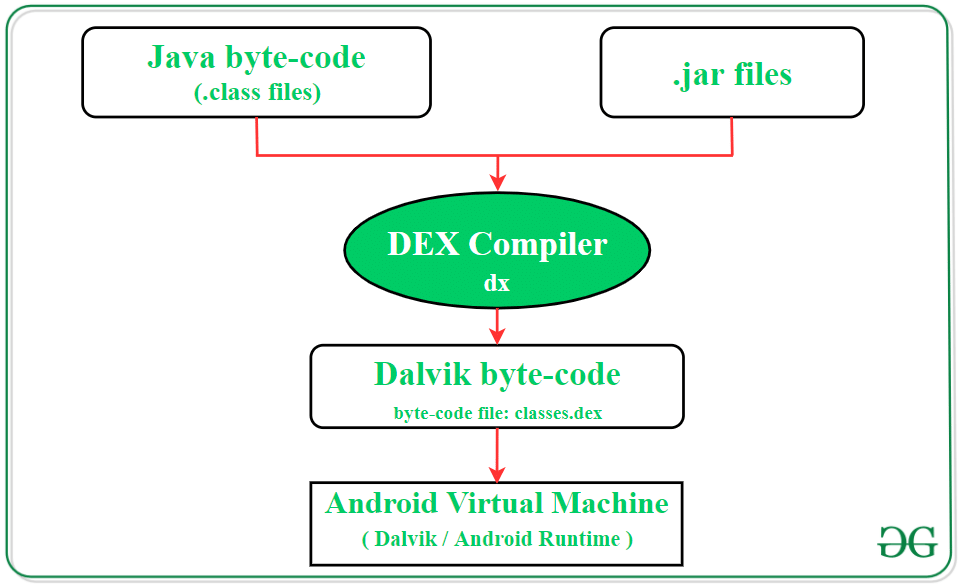
The Java class (*.class) file generated in the previous step is designed to run on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) since it contains standard Oracle JVM Java byte-codes. However, this format is not compatible with Android devices. Android utilizes its unique byte-code format called Dalvik byte-code.
- Oracle JVM Java byte-codes
- Dalvik byte-code
- Dex compiler
- dx command
- .class files
- .jar files
- classes.dex file
- Android Runtime
- Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM)
Java regular code:
- Method for Adding Two Numbers:
- Java Byte-code:
- Equivalent Java byte-code for adding two numbers has been provided.
- Dalvik Byte-code:
- Equivalent Dalvik byte-code for adding two numbers is explained.
- Java Byte-code:
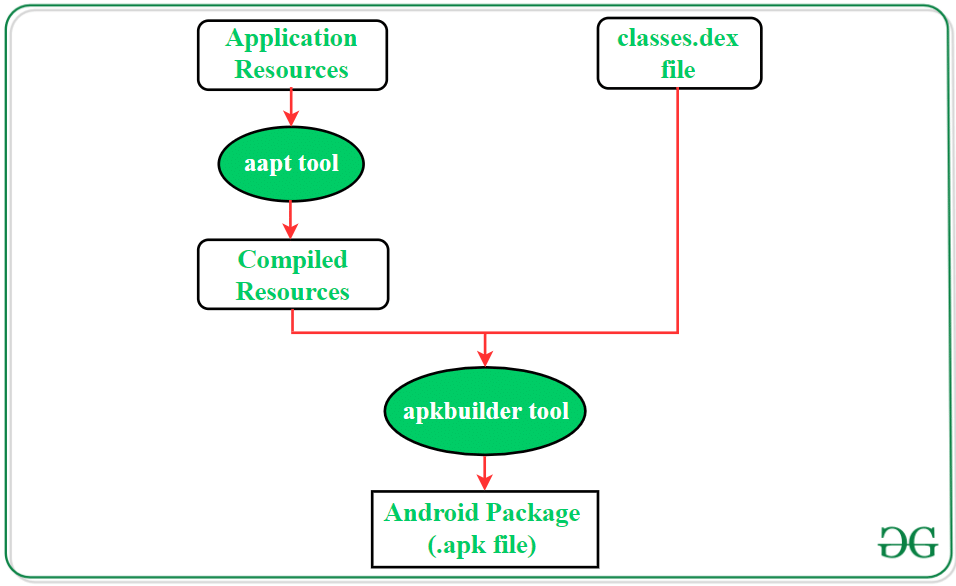
- Generating .apk File:
- The Android Asset Packaging Tool (aapt) compiles resource files into a single unit for the Android application.
- The apkbuilder tool compresses the compiled resource unit along with classes.dex into an Android Package (.apk file).
- The .apk file contains all necessary data to execute the Android application.
- App Distribution:
- The .apk file is prepared for app distribution after the previous steps.
- To distribute an app through Google Play Store, developers must sign the .apk file.
- Applications need to be digitally signed with a certificate for installation.
- The certificate, self-signed, helps Android identify the app's author and is stored in the .apk file.
- Oracle Java Development Kit (JDK) provides the jarsigner tool for signing .jar and .apk files.
- The zipalign tool ensures byte alignment in the signed .apk file for efficient reading by Android OS.
- jarsigner tool
- zipalign tool
Step 2: Deploy the Application
1. Establish the ADB Server
- Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a command-line tool that helps deploy applications to Android devices. It acts as an interface for developers to communicate with Android devices.
- ADB Server Process: The ADB server process starts by checking if the ADB server process is running on the device. If not, it initiates the server process using the ADB command. The server binds to local TCP port 5037.
- ADB Client: ADB server communicates with ADB clients using port 5037, establishing connections with running devices and ADB daemons.
- ADB Daemon: ADB daemon (adbd) is a background process on the emulator or device instance, enabling communication with applications and debugging functionalities.
2. Transfer .apk file to the Device
- The ADB command facilitates transferring the .apk file to the local file system of the target Android device.
- The location of the app in the device file system is determined by its package name. For instance, if the package is com.example.sampleapp, the .apk file will be stored at /data/app/com.example.sampleapp.
Step 3: Running the Application
1. Initiating App Launch
At the core of Android app launches lies the Zygote process, acting as the progenitor to all Android applications. When a user triggers an app launch, this process springs into action. Essentially, the Zygote process, a specialized Android OS entity, facilitates code sharing among diverse instances operating on Android virtual devices (Dalvik/Android Runtime). It preloads essential resources, classes, and code libraries into its memory space, ensuring swift and efficient app launches. Upon receiving a request to initiate a new application, the Zygote process clones itself using the fork system call (a characteristic of the Linux-based Android system) and kickstarts the new app. The preloaded resources play a pivotal role in expediting app launches within the Android ecosystem.
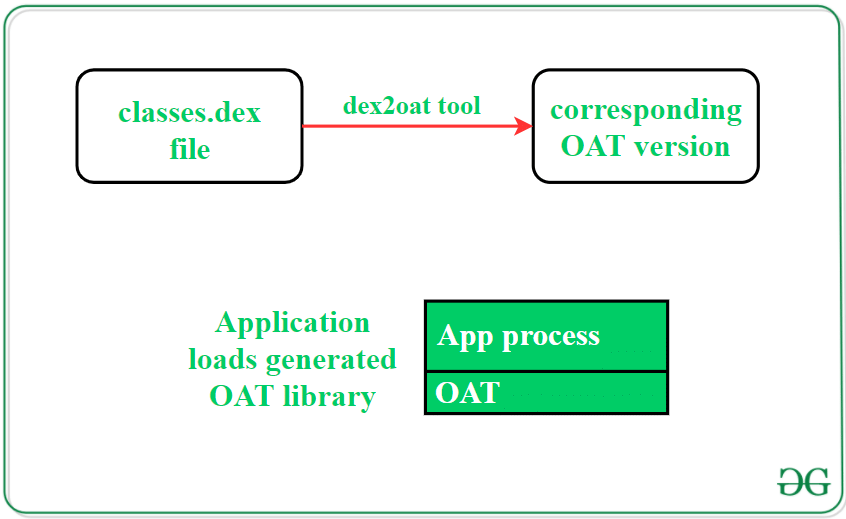
Zygote Process2. .dex to OAT Conversion
Upon installing a new application, Android undertakes the optimization of app data, culminating in the creation of an OAT (Optimized Application Technique) file. This file, generated by the Android OS, accelerates application loading times significantly. The process commences with the extraction of the classes.dex file housed within the .apk application package. Subsequently, the classes.dex file is segregated into a distinct directory, where Android undertakes the compilation of Dalvik byte-code through an ahead-of-time (AOT) conversion into native machine code. By leveraging this native OAT file, the Android system enhances user experience through rapid and seamless application loading.
.apk, ahead-of-time (AOT, also as OAT)Prior to the advent of AOT, the dexopt tool was utilized to transform .dex files into .odex files (optimized DEX) containing refined byte-code. However, with AOT's integration into Android, the dex2oat tool now converts and optimizes .dex files into OAT file formats housing machine code inscribed in ELF (Executable and Linkable Format). This native library is subsequently linked to the application process's memory. OAT files are conventionally stored in the directory: /data/dalvik-cache/.
Summary of Android App Execution Process
- dexopt tool: This tool is crucial in optimizing the execution of Android applications.
- dex2oat tool: Another essential tool used in converting dex code into native OAT format for better performance.
- ELF format (Executable and Linkable Format): This format is significant in organizing and linking executable files during app execution.
Upon completion of the above processes, the Android application will initiate, and the primary activity will become visible on the device screen.


















