Implicit and Explicit Intents with Examples - Software Development PDF Download
Implicit and Explicit Intents in Android with Examples
Last Updated : 12 Sep, 2022Pre-requisites:
- Android App Development Fundamentals for Beginners
- Guide to Install and Set up Android Studio
- Android | Starting with the first app/android project
- Android | Running your first Android app
This article aims to explain Implicit and Explicit intents and how to use them in an Android app.
Implicit Intents
- Implicit intents are used when you want to request functionality from other apps on the device.
- They do not specify the component. Instead, they declare an action to perform.
- An example of an implicit intent is opening a web page using the browser app.
Explicit Intents
- Explicit intents are used when you want to specifically communicate with another component within your app.
- They explicitly define the target component.
- An example of an explicit intent is switching from one activity to another within the same app.
What is intent in Android?
The concept of intent in Android revolves around a messaging object that facilitates communication between various components such as services, content providers, and activities. Typically, the startActivity() method is employed to trigger the launch of any activity. Here are some fundamental functions of an intent:
- Start service
- Launch Activity
- Display web page
- Display contact list
- Message broadcasting
Methods and their Description
| Method | Description |
| Context.startActivity() | This method is utilized to either initiate a new activity or bring an existing activity into action. |
| Context.startService() | It is used to commence a new service or convey instructions to an already existing service. |
| Context.sendBroadcast() | With this method, messages can be broadcasted to broadcast receivers. |
Intent Classification:
- Implicit Intent
- Explicit Intent
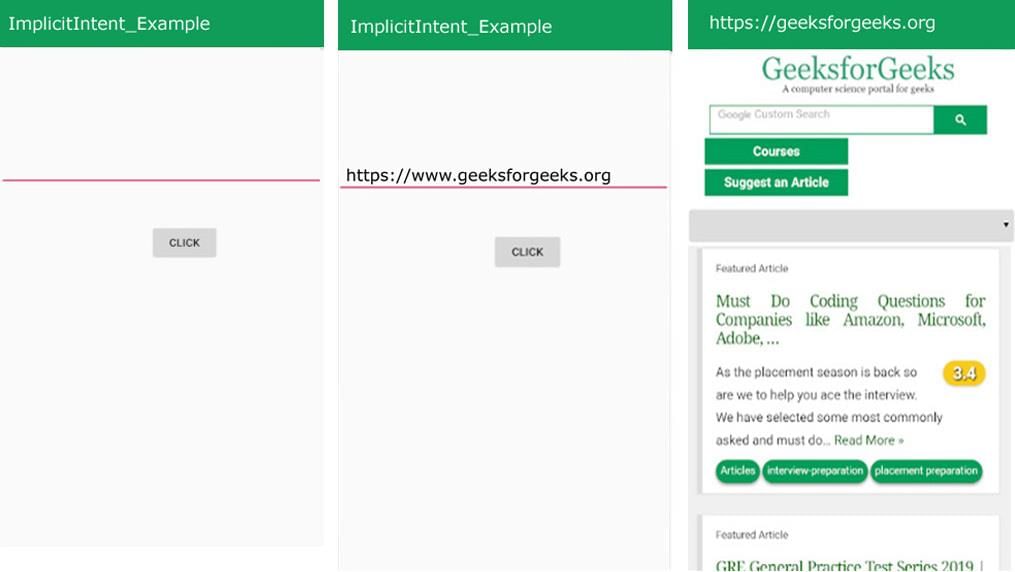
Implicit Intents do not specify components directly. Instead, they declare an action to be performed. The Android operating system then filters out components capable of responding to the action. For instance, consider the scenario where a webpage needs to be opened. By typing the desired webpage name and clicking on the 'CLICK' button, the webpage is successfully accessed.
Step by Step Implementation
- Step 1: Create a New Project in Android Studio
To initiate a fresh project in Android Studio, follow the guidelines in setting up a new project. The instructions are provided in Java and Kotlin programming languages for Android. Generate an XML file and a Java File. It is recommended to review the prerequisites for a better understanding of this phase.
- How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio
- Java and Kotlin Programming Language for Android.
- Step 2: Working with the XML Files
Proceed to the activity_main.xml file, which visually represents the user interface (UI) of the project. Below is an excerpt of the code within the activity_main.xml file. Embedded comments within the code aim to facilitate a deeper comprehension of the code structure.
- activity_main.xml file
- activity_main.xml
- Syntax:
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android=\"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android\" xmlns:app=\"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto\" xmlns:tools=\"http://schemas.android.com/tools\" android:layout_width=\"match_parent\" android:layout_height=\"match_parent\" tools:context=\".MainActivity\"> <EditText android:id=\"@id/editText\" android:layout_width=\"match_parent\" android:layout_height=\"wrap_content\" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf=\"parent\" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf=\"parent\" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf=\"parent\" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf=\"parent\" /> <Button android:id=\"@id/btn\" android:text=\"Search\" android:onClick=\"search\" android:layout_width=\"wrap_content\" android:layout_height=\"wrap_content\" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf=\"parent\" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf=\"parent\" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf=\"parent\" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf=\"@id/editText\" />
Step 3: Working with the MainActivity File
Now, let's delve into how to work with the MainActivity file to create the backend of the app.
- Instantiate the component (Button) created in the XML file by utilizing the findViewById() method. This crucial step binds the object created to the UI components through the assigned ID.
- Here is a snippet of code in Java and Kotlin for your reference:
- Java
- Kotlin
Below is a code snippet demonstrating the MainActivity file:
Understanding Explicit Intent in Android
- Definition: Explicit intent in Android is used to specify a particular target component, ensuring that only the specified component will be invoked when the intent is triggered.
- Key Points:
- Targeted Component: With explicit intent, a specific component is targeted for invocation.
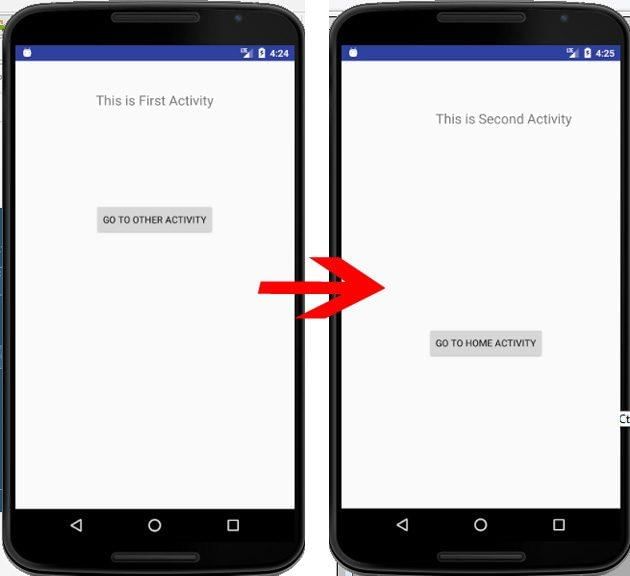
- Example: Consider two activities, FirstActivity and SecondActivity. When a user clicks on the 'GO TO OTHER ACTIVITY' button in FirstActivity, they are directed to SecondActivity. Similarly, clicking 'GO TO HOME ACTIVITY' in SecondActivity navigates back to FirstActivity. This navigation is facilitated through explicit intent.
Code Snippet for Explicit Intent
| import android.content.Intent | import android.net.Uri | import android.os.Bundle |
| import android.widget.Button | import android.widget.EditText | import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity |
Java Code Example
MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {lateinit var editText: EditTextoverride fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {.onCreate(savedInstanceState)setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)editText = findViewById(R.id.editText)fun search() {val url = editText.text.toString()val urlIntent = Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse(url))startActivity(urlIntent)
Visual Example
- Creating a New Project in Android Studio:
- Refer to the guide on How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio, which includes code samples in Java and Kotlin for Android development.
- Ensure you have the necessary prerequisites before proceeding with the project setup.
- Working with the activity_main.xml File:
- Access the activity_main.xml file, responsible for defining the project's user interface.
- Below is a snippet of the code from the activity_main.xml file:
After setting up the UI, proceed to creating the backend of the application by navigating to the MainActivity file. Use the findViewById() method to link the components (Button, TextView) from the XML file to the corresponding UI elements based on their assigned IDs.
Step 4: Working with the activity_main2.xml File
- Create a second activity as a destination activity.
- Follow these steps to create the second activity:
- Click on File
- Select new
- Choose Activity
- Opt for Empty Activity
File > new > Activity > Empty Activity.

Next, navigate to the activity_main2.xml file, which represents the UI of the project. Below is the code for the activity_main2.xml file. Comments are added inside the code for better understanding.
activity_main2.xml file
activity_main2.xml
Android App Layout
- Key Components of Android Layouts:
- ConstraintLayout: A powerful layout with a flat view hierarchy.
- TextView: Displays text to the user and optionally allows editing.
- Button: Represents a clickable button.
- Attributes of TextView:
- android:text: Sets the text to be displayed.
- android:textAlignment: Specifies the text alignment within the TextView.
- android:textSize: Defines the text size.
- Attributes of Button:
- android:text: Text displayed on the button.
- android:onClick: Specifies the method to be executed when the button is clicked.
- Layout Constraints:
- app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf: Aligns the bottom of the view to the bottom of another view.
- app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf: Aligns the end of the view to the end of another view.
- app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias: Sets the horizontal bias.
- app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf: Aligns the top of the view to the top of another view.
Example Layout Code:
Step 5: Working with the MainActivity2 File
- Understanding the MainActivity2 File in Java:
- In Java, the MainActivity2 file is crucial for defining the behavior of the application.
- It extends the AppCompatActivity class and overrides the onCreate method to set up the initial state of the activity.
- An example code snippet from the MainActivity2 Java file:
- Corresponding Kotlin Implementation:
- In Kotlin, the MainActivity2 file serves a similar purpose with concise syntax.
- The class MainActivity2 inherits from AppCompatActivity and initializes the activity in the onCreate method.
- An illustrative snippet from the MainActivity2 Kotlin file:
MainActivity2 extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2); } public void homeScreen(View view) { Intent i = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MainActivity.class); startActivity(i); } } class MainActivity2 : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2) } fun homeScreen() { val i = Intent(applicationContext, MainActivity::class.java) startActivity(i) } } Complete Roadmap to Become a Developer
- Sequential Steps to Follow:
- Start by mastering Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) to build a solid foundation.
- Progress to mastering either Frontend, Backend, or Full Stack development based on your interests.
- Engage in building diverse projects to apply and reinforce your skills.
- Continuously apply to job opportunities to gain real-world experience.
- Special Program Offer:
- EduRev's DSA to Development Program offers a comprehensive guide to navigate this journey efficiently.
- Enroll now to benefit from personalized guidance and support from our experienced counselors.
Please Login to Comment...
- Interactive Engagement:
- Login to share your thoughts, experiences, and feedback.
- Show appreciation by liking the content that resonates with you.














