Animals Chapter Notes | EVS for Class 2 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Who are Animals? |

|
| Types of Animals Based on Size |

|
| Different Kinds of Animals |

|
| Food of Animals |

|
| Summary of Animals |

|
Who are Animals?

Animals are living things like your pets, birds, and bugs. They can move around, eat food, and some even make sounds. Animals are living beings that can move, eat, and grow. They come in many shapes and sizes, from tiny insects to massive whales.
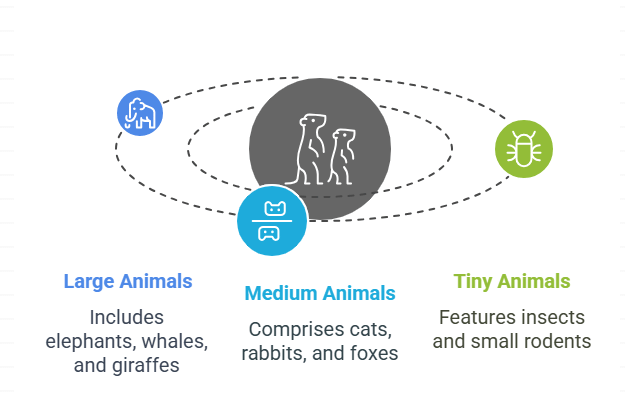
Types of Animals Based on Size
- Large Animals: Large animals are those that are big, like elephants, whales, and giraffes. They can be as tall as buildings or weigh as much as several cars. Examples include rhinos, giraffes, and elephants.
- Medium Animals: Medium animals are larger than very small creatures but smaller than large animals. Examples include cats, rabbits, and foxes.
- Tiny Animals: Tiny animals are very small creatures, often so small that you might need a magnifying glass to see them clearly! These include insects like ants, bees, and butterflies, as well as tiny rodents like mice and shrews.
Different Kinds of Animals
Animals can be classified into different types based on where they live and how they interact with humans. Here are the main types of animals:
1. Domestic Animals
- Domestic animals are those that live with humans.
- They are often kept as pets or for various tasks.
- Examples of domestic animals include dogs, cats, and parrots.

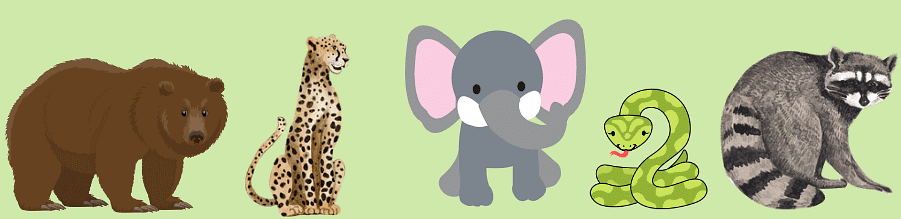
2. Wild Animals
- Wild animals are those that live freely in nature, such as in jungles or forests.
- They are not usually kept as pets because they are adapted to live in the wild.
- Examples of wild animals include lions, tigers, and elephants.
3. Farm Animals
- Farm animals are those that live on farms and in fields.
- They are often raised by people for various purposes, such as for food, labor, or other products.
- Examples of farm animals include goats, cows, and hens.

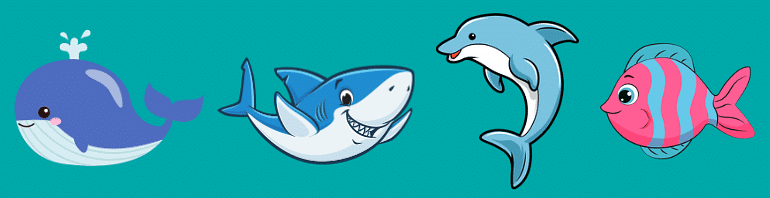
4. Aquatic Animals
- Aquatic animals are those that live in water for their entire life.
- These animals have specialized organs called gills that allow them to breathe underwater.
- Some common examples of aquatic animals include: Whale, Shark, Dolphin, Seahorse, Fish, Octopus etc.
5. Birds
- Birds are animals characterized by feathers, wings, and two legs.
- All birds have a beak, which is an essential part of their anatomy.
- While most birds are capable of flight, some species are also proficient swimmers.
- Examples of common birds include: sparrow, crow, pigeon etc

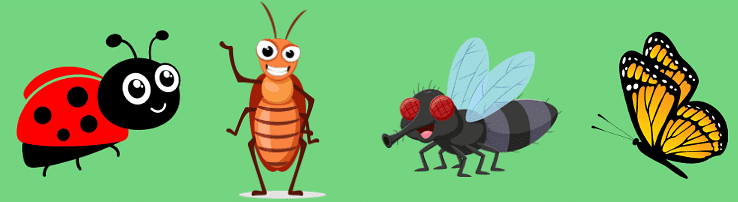
6. Insects
- Insects are animals that have six legs.
- On the other hand, arachnids, such as spiders, have eight legs.
- Insects may have one or two pairs of wings, depending on the species.
- Examples of insects include: ladybird, cockroach, housefly, butterfly, grasshopper etc.
Food of Animals
Different animals have different food habits. For example: Cows, buffalos and goats eat grass. Lions and tigers eat the flesh of other animals. Let us study the different eating habits of animals.
1. Herbivorous Animals
Those animals which eat grass and other plants are called herbivorous animals.
For example: Cow, buffalo, goat, deer, giraffe, donkey, elephant etc.
2. Carnivorous Animals
Those animals that eat only the flesh of other animals are known as carnivorous animals.
For example: Lion, Tiger, Leopard, Hawk, Whale etc.
3. Omnivorous Animals
Some animals like crows, bear, jackal, gorilla etc eat both plants as well as the flesh of other animals. These type of animals are known as Omnivorous animals.

Summary of Animals
• Animals are living creatures that can move, eat, and make sounds.
• They come in different sizes like big, medium, and small.
• Some animals live with humans, while others live in the wild, on farms, or in water.
• Birds have feathers, wings, and a beak, while insects are small creatures with six legs.
• Animals eat different kinds of food – some eat plants, some eat meat, and some eat both.
• Herbivores eat plants, carnivores eat meat, and omnivores eat both plants and meat.
• Animals are important for nature and help keep the environment balanced.
|
30 videos|304 docs|48 tests
|
FAQs on Animals Chapter Notes - EVS for Class 2
| 1. What are the main classifications of animals based on size? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of different kinds of animals? |  |
| 3. What do animals eat, and how does their diet vary? |  |
| 4. How do animals adapt to their environments? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to study and understand animals? |  |















